Java 生成订单号或唯一id(高并发)方案
1、直接使用uuid
public static String getUUID() {String replaceUUID = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "");return replaceUUID;}
但由于生成的数据没有规律性,并且太长;
测试:循环1000w次
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();Set set=new HashSet<>();for(int i=0;i<10000000;i++){String uuid = getUUID();System.out.println("uuid---"+i+"======="+uuid);set.add(uuid);}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("set.size():"+set.size());System.out.println("endTime-startTime:"+(endTime-startTime));}
控制台提示:

2、用时间(精确到毫秒)+随机数
//时间(精确到毫秒)DateTimeFormatter ofPattern = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS");String localDate = LocalDateTime.now().format(ofPattern);//随机数String randomNumeric = RandomStringUtils.randomNumeric(8);
for循环1000w次,发现重复数据太多。因此光靠随机数并不可靠。
3、使用 时间(精确到毫秒)+随机数+用户id(业务id)
注意:如果是类似用户id,项目当中集成了权限框架,使用工具类获取即可,就不用传参了
/*** 生成订单号(25位):时间(精确到毫秒)+3位随机数+5位用户id*/public static synchronized String getOrderNum(Long userId) {//时间(精确到毫秒)DateTimeFormatter ofPattern = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS");String localDate = LocalDateTime.now().format(ofPattern);//3位随机数String randomNumeric = RandomStringUtils.randomNumeric(3);//5位用户idint subStrLength = 5;String sUserId = userId.toString();int length = sUserId.length();String str;if (length >= subStrLength) {str = sUserId.substring(length - subStrLength, length);} else {str = String.format("%0" + subStrLength + "d", userId);}String orderNum = localDate + randomNumeric + str;log.info("订单号:{}", orderNum);return orderNum;}
在2的基础上改造,加入用户的id等其他的业务id。
4.Java实现Snowflake算法的方案(高并发下,推荐使用这个)
package com.lucifer.order.util.idgenerate;/*** Twitter_Snowflake<br>* SnowFlake的结构如下(每部分用-分开):<br>* 0 - 0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0 - 00000 - 00000 - 000000000000 <br>* 1位标识,由于long基本类型在Java中是带符号的,最高位是符号位,正数是0,负数是1,所以id一般是正数,最高位是0<br>* 41位时间截(毫秒级),注意,41位时间截不是存储当前时间的时间截,而是存储时间截的差值(当前时间截 - 开始时间截)* 得到的值),这里的的开始时间截,一般是我们的id生成器开始使用的时间,由我们程序来指定的(如下下面程序IdWorker类的startTime属性)。41位的时间截,可以使用69年,年T = (1L << 41) / (1000L * 60 * 60 * 24 * 365) = 69<br>* 10位的数据机器位,可以部署在1024个节点,包括5位datacenterId和5位workerId<br>* 12位序列,毫秒内的计数,12位的计数顺序号支持每个节点每毫秒(同一机器,同一时间截)产生4096个ID序号<br>* 加起来刚好64位,为一个Long型。<br>* SnowFlake的优点是,整体上按照时间自增排序,并且整个分布式系统内不会产生ID碰撞(由数据中心ID和机器ID作区分),并且效率较高,经测试,SnowFlake每秒能够产生26万ID左右。** @author Lucifer*/public class SnowFlake {// ==============================Fields===========================================/*** 开始时间截 (2018-07-03)*/private final long twepoch = 1530607760000L;/*** 机器id所占的位数*/private final long workerIdBits = 5L;/*** 数据标识id所占的位数*/private final long datacenterIdBits = 5L;/*** 支持的最大机器id,结果是31 (这个移位算法可以很快的计算出几位二进制数所能表示的最大十进制数)*/private final long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits);/*** 支持的最大数据标识id,结果是31*/private final long maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits);/*** 序列在id中占的位数*/private final long sequenceBits = 12L;/*** 机器ID向左移12位*/private final long workerIdShift = sequenceBits;/*** 数据标识id向左移17位(12+5)*/private final long datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits;/*** 时间截向左移22位(5+5+12)*/private final long timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits;/*** 生成序列的掩码,这里为4095 (0b111111111111=0xfff=4095)*/private final long sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits);/*** 工作机器ID(0~31)*/private long workerId;/*** 数据中心ID(0~31)*/private long datacenterId;/*** 毫秒内序列(0~4095)*/private long sequence = 0L;/*** 上次生成ID的时间截*/private long lastTimestamp = -1L;//==============================Constructors=====================================/*** 构造函数** @param workerId 工作ID (0~31)* @param datacenterId 数据中心ID (0~31)*/public SnowFlake(long workerId, long datacenterId) {if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("worker Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxWorkerId));}if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("datacenter Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxDatacenterId));}this.workerId = workerId;this.datacenterId = datacenterId;}// ==============================Methods==========================================/*** 获得下一个ID (该方法是线程安全的)** @return SnowflakeId*/public synchronized long nextId() {long timestamp = timeGen();//如果当前时间小于上一次ID生成的时间戳,说明系统时钟回退过这个时候应当抛出异常if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {throw new RuntimeException(String.format("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds", lastTimestamp - timestamp));}//如果是同一时间生成的,则进行毫秒内序列if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) {sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;//毫秒内序列溢出if (sequence == 0) {//阻塞到下一个毫秒,获得新的时间戳timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp);}}//时间戳改变,毫秒内序列重置else {sequence = 0L;}//上次生成ID的时间截lastTimestamp = timestamp;//移位并通过或运算拼到一起组成64位的IDreturn (((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift)| (datacenterId << datacenterIdShift)| (workerId << workerIdShift)| sequence);}/*** 阻塞到下一个毫秒,直到获得新的时间戳** @param lastTimestamp 上次生成ID的时间截* @return 当前时间戳*/protected long tilNextMillis(long lastTimestamp) {long timestamp = timeGen();while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {timestamp = timeGen();}return timestamp;}/*** 返回以毫秒为单位的当前时间** @return 当前时间(毫秒)*/protected long timeGen() {return System.currentTimeMillis();}//==============================Test=============================================/*** 测试*/public static void main(String[] args) {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();SnowFlake idWorker = new SnowFlake(0, 0);Set set = new HashSet();for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {long id = idWorker.nextId();set.add(id);System.out.println("id----"+i+":"+id);}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("set.size():" + set.size());System.out.println("endTime-startTime:" + (endTime - startTime));}}
也可以在雪花算法生成的id的基础上拼接日期,不过性能有所损耗。
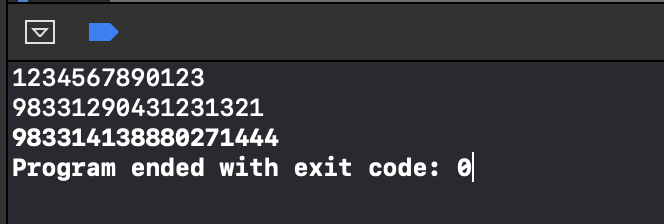
public static String timestampConversionDate(String param) {Instant timestamp = Instant.ofEpochMilli(new Long(param));System.out.println("timestamp:"+param);LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.ofInstant(timestamp, ZoneId.systemDefault());String format = localDateTime.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMdd"));return format;}
测试1:
循环1000w次,发现并无重复

测试2:100个线程,每个线程负责生成10w个id
//多线程测试public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();CountDownLatch countDownLatch=new CountDownLatch(10000000);final SnowFlake idWorker = new SnowFlake(0, 0);Set set = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet());for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 100000; i1++) {long id = idWorker.nextId();System.out.println("id:"+id);set.add(id);countDownLatch.countDown();}});thread.start();}countDownLatch.await();long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("set.size():" + set.size());System.out.println("endTime-startTime:" + (endTime - startTime));}































还没有评论,来说两句吧...