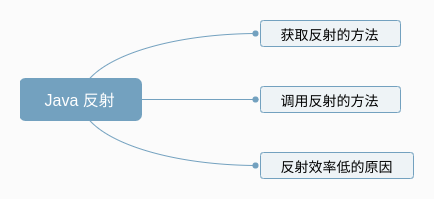
大家都说 Java 反射效率低,你知道原因在哪里么
预备知识
- 了解 Java 反射基本用法
看完本文可以达到什么程度
- 了解 Java 反射原理及 Java 反射效率低的原因
文章概览
我们在 Java 开发中,难免会接触到反射,而在一些框架中,反射的运用更是常见。我相信,每次提到反射,大家的第一反应一定是反射效率低,尽量少使用。
但是反射的效率到底低多少?反射效率低的原因在哪里?
这篇文章就来探索一下这些问题。
由于本机上安装的是 openjdk 12,所以这里就使用 openjdk 12 源码进行分析。
我们先看结论,然后分析一下 Java 反射的原理,过程中大家可以根据结论,对源码做一些思考,然后再根据原理中的一些实现,看看 Java 反射效率低的原因。
零、先放结论
Java 反射效率低主要原因是:
- Method#invoke 方法会对参数做封装和解封操作
- 需要检查方法可见性
- 需要校验参数
- 反射方法难以内联
- JIT 无法优化
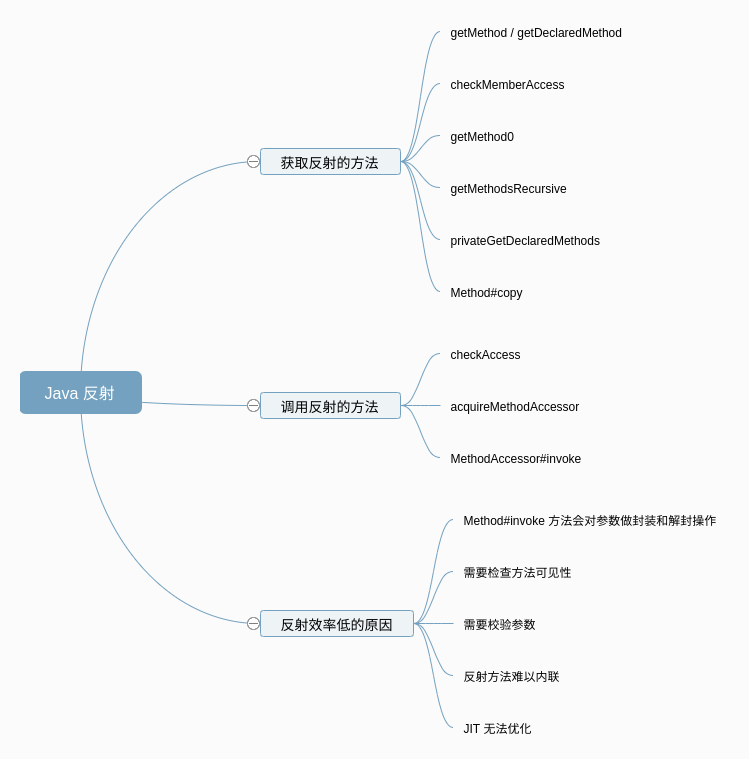
一、Java 反射原理—获取要反射的方法
1.1 反射的使用
我们先来看看 Java 反射使用的一段代码:
public class RefTest {public static void main(String[] args) {try {Class clazz = Class.forName("com.zy.java.RefTest");Object refTest = clazz.newInstance();Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("refMethod");method.invoke(refTest);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public void refMethod() {}}复制代码
我们在调用反射时,首先会创建 Class 对象,然后获取其 Method 对象,调用 invoke 方法。
获取反射方法时,有两个方法,getMethod 和 getDeclaredMethod,我们就从这两个方法开始,一步步看下反射的原理。
接下来就进入代码分析,大家做好准备。
1.2 getMethod / getDeclaredMethod
这里我们先整体看一下 getMethod 和 getDeclaredMethod 的实现。
class Class {@CallerSensitivepublic Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {Objects.requireNonNull(name);SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();if (sm != null) {// 1. 检查方法权限checkMemberAccess(sm, Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);}// 2. 获取方法Method method = getMethod0(name, parameterTypes);if (method == null) {throw new NoSuchMethodException(methodToString(name, parameterTypes));}// 3. 返回方法的拷贝return getReflectionFactory().copyMethod(method);}@CallerSensitivepublic Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {Objects.requireNonNull(name);SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();if (sm != null) {// 1. 检查方法是权限checkMemberAccess(sm, Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);}// 2. 获取方法Method method = searchMethods(privateGetDeclaredMethods(false), name, parameterTypes);if (method == null) {throw new NoSuchMethodException(methodToString(name, parameterTypes));}// 3. 返回方法的拷贝return getReflectionFactory().copyMethod(method);}}复制代码
从上面的代码,我们可以看到,获取方法的流程分三步走:
- 检查方法权限
- 获取方法 Method 对象
- 返回方法的拷贝
这里主要有两个区别:
getMethod 中 checkMemberAccess 传入的是
Member.PUBLIC,而 getDeclaredMethod 传入的是Member.DECLARED这两个值有什么区别呢?我们看下代码中的注释:interface Member {
/*** Identifies the set of all public members of a class or interface,* including inherited members.*/public static final int PUBLIC = 0;/*** Identifies the set of declared members of a class or interface.* Inherited members are not included.*/public static final int DECLARED = 1;
}
复制代码
注释里清楚的解释了 PUBLIC 和 DECLARED 的不同,PUBLIC 会包括所有的 public 方法,包括父类的方法,而 DECLARED 会包括所有自己定义的方法,public,protected,private 都在此,但是不包括父类的方法。
这也正是 getMethod 和 getDeclaredMethod 的区别。
getMethod中获取方法调用的是getMethod0,而getDeclaredMethod获取方法调用的是privateGetDeclaredMethods关于这个区别,这里简单提及一下,后面具体分析代码。
privateGetDeclaredMethods 是获取类自身定义的方法,参数是 boolean publicOnly,表示是否只获取公共方法。private Method[] privateGetDeclaredMethods(boolean publicOnly) {
//...
}
复制代码
而 getMethod0 会递归查找父类的方法,其中会调用到 privateGetDeclaredMethods 方法。
既然我们上面看了 getMethod 和 getDeclaredMethod 的区别,我们自然选择 getMethod 方法进行分析,这样可以走到整个流程。
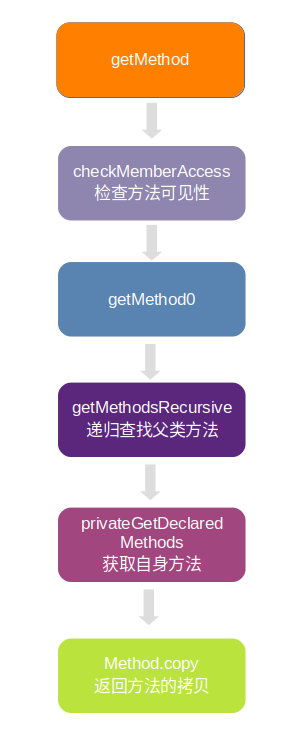
1.3 getMethod 方法
getMethod 方法流程如下图:
class Class {public Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {Objects.requireNonNull(name);SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();if (sm != null) {// 1. 检查方法权限checkMemberAccess(sm, Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);}// 2. 获取方法 Method 对象Method method = getMethod0(name, parameterTypes);if (method == null) {throw new NoSuchMethodException(methodToString(name, parameterTypes));}// 3. 返回方法拷贝return getReflectionFactory().copyMethod(method);}}复制代码
我们上面说到获取方法分三步走:
- 检查方法权限
- 获取方法 Method 对象
- 返回方法的拷贝
我们先看看检查方法权限做了些什么事情。
1.3.1 checkMemberAccess
class Class {private void checkMemberAccess(SecurityManager sm, int which,Class<?> caller, boolean checkProxyInterfaces) {/* Default policy allows access to all {@link Member#PUBLIC} members,* as well as access to classes that have the same class loader as the caller.* In all other cases, it requires RuntimePermission("accessDeclaredMembers")* permission.*/final ClassLoader ccl = ClassLoader.getClassLoader(caller);if (which != Member.PUBLIC) {final ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0();if (ccl != cl) {sm.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.CHECK_MEMBER_ACCESS_PERMISSION);}}this.checkPackageAccess(sm, ccl, checkProxyInterfaces);}}复制代码
在这里可以看到,对于非 Member.PUBLIC 的访问,会增加一项检测,SecurityManager.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.CHECK_MEMBER_ACCESS_PERMISSION); 这项检测需要运行时申请 RuntimePermission("accessDeclaredMembers")。
这里就不继续往下看了,方法整体是在检查是否可以访问对象成员。
接着看下是如何获取方法的 Method 对象。
1.3.2 getMethod0
class Class {private Method getMethod0(String name, Class<?>[] parameterTypes) {PublicMethods.MethodList res = getMethodsRecursive(name,parameterTypes == null ? EMPTY_CLASS_ARRAY : parameterTypes,/* includeStatic */ true);return res == null ? null : res.getMostSpecific();}}复制代码
这里是通过 getMethodsRecursive 获取到 MethodList 对象,然后通过 MethodList#getMostSpecific 方法筛选出对应的方法。 MethodList#getMOstSpecific 会筛选返回值类型最为具体的方法,至于为什么会有返回值的区别,后面会讲到。
(这里的具体,指的是有两个方法,返回值分别是 Child 和 Parent,Child 继承自 Parent,这里会筛选出返回值为 Child 的方法)。
接着看 getMethodsRecursive 方法,是如何获取方法的。
1.3.3 getMethodsRecursive
class Class {private PublicMethods.MethodList getMethodsRecursive(String name,Class<?>[] parameterTypes,boolean includeStatic) {// 1. 获取自己的 public 方法Method[] methods = privateGetDeclaredMethods(/* publicOnly */ true);// 2. 筛选符合条件的方法,构造 MethodList 对象PublicMethods.MethodList res = PublicMethods.MethodList.filter(methods, name, parameterTypes, includeStatic);// 找到方法,直接返回if (res != null) {return res;}// 3. 没有找到方法,就获取其父类,递归调用 getMethodsRecursive 方法Class<?> sc = getSuperclass();if (sc != null) {res = sc.getMethodsRecursive(name, parameterTypes, includeStatic);}// 4. 获取接口中对应的方法for (Class<?> intf : getInterfaces(/* cloneArray */ false)) {res = PublicMethods.MethodList.merge(res, intf.getMethodsRecursive(name, parameterTypes,/* includeStatic */ false));}return res;}}复制代码
这里获取方法有四个步骤:
- 通过
privateGetDeclaredMethods获取自己所有的 public 方法 - 通过
MethodList#filter查找 方法名,参数相同的方法,如果找到,直接返回 - 如果自己没有实现对应的方法,就去父类中查找对应的方法
- 查找接口中对应的方法
通过上面四个步骤,最终获取到的是一个 MethodList 对象,是一个链表结点,其 next 指向下一个结点。也就是说,这里获取到的 Method 会有多个。
这里稍微解释一下,在我们平时编写 Java 代码时,同一个类是不能有方法名和方法参数都相同的方法的,而实际上,在 JVM 中,一个方法签名是和 返回值,方法名,方法参数 三者相关的。 也就是说,在 JVM 中,可以存在 方法名和方法参数都相同,但是返回值不同的方法。
所以这里返回的是一个方法链表。
所以上面最终返回方法时会通过 MethodList#getMostSpecific 进行返回值的筛选,筛选出返回值类型最具体的方法。
这里我们先暂停回顾一下整体的调用链路:
getMethod -> getMethod0 -> getMethodsRecursive -> privateGetDeclaredMethods复制代码
通过函数调用,最终会调用到 privateGetDeclaredMethods 方法,也就是真正获取方法的地方。
1.3.4 privateGetDeclaredMethods
class Class {private Method[] privateGetDeclaredMethods(boolean publicOnly) {Method[] res;// 1. 通过缓存获取 Method[]ReflectionData<T> rd = reflectionData();if (rd != null) {res = publicOnly ? rd.declaredPublicMethods : rd.declaredMethods;if (res != null) return res;}// 2. 没有缓存,通过 JVM 获取res = Reflection.filterMethods(this, getDeclaredMethods0(publicOnly));if (rd != null) {if (publicOnly) {rd.declaredPublicMethods = res;} else {rd.declaredMethods = res;}}return res;}}复制代码
在 privateGetDeclaredMethods 获取方法时,有两个步骤:
- relectionData 通过缓存获取
- 如果缓存没有命中的话,通过 getDeclaredMethods0 获取方法
先看看 relectionData 方法:
class Class {private ReflectionData<T> reflectionData() {SoftReference<ReflectionData<T>> reflectionData = this.reflectionData;int classRedefinedCount = this.classRedefinedCount;ReflectionData<T> rd;if (reflectionData != null &&(rd = reflectionData.get()) != null &&rd.redefinedCount == classRedefinedCount) {return rd;}// else no SoftReference or cleared SoftReference or stale ReflectionData// -> create and replace new instancereturn newReflectionData(reflectionData, classRedefinedCount);}}复制代码
在 Class 中会维护一个 ReflectionData 的软引用,作为反射数据的缓存。
ReflectionData 结构如下:
private static class ReflectionData<T> {volatile Field[] declaredFields;volatile Field[] publicFields;volatile Method[] declaredMethods;volatile Method[] publicMethods;volatile Constructor<T>[] declaredConstructors;volatile Constructor<T>[] publicConstructors;// Intermediate results for getFields and getMethodsvolatile Field[] declaredPublicFields;volatile Method[] declaredPublicMethods;volatile Class<?>[] interfaces;// Cached namesString simpleName;String canonicalName;static final String NULL_SENTINEL = new String();// Value of classRedefinedCount when we created this ReflectionData instancefinal int redefinedCount;}复制代码
可以看到,保存了 Class 中的属性和方法。 如果缓存为空,就会通过 getDeclaredMethods0 从 JVM 中查找方法。
getDeclaredMethods0 是一个 native 方法,这里暂时先不看。
通过上面几个步骤,就获取到 Method 数组。
这就是 getMethod 方法的整个实现了。
我们再回过头看一下 getDeclaredMethod 方法的实现,通过 privateGetDeclaredMethods 获取方法以后,会通过 searchMethods 对方法进行筛选。
public Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {// ...Method method = searchMethods(privateGetDeclaredMethods(false), name, parameterTypes);// ...}复制代码
searchMethods 方法实现比较简单,就是对比方法名,参数,方法返回值。
class Class {private static Method searchMethods(Method[] methods,String name,Class<?>[] parameterTypes){ReflectionFactory fact = getReflectionFactory();Method res = null;for (Method m : methods) {// 比较方法名if (m.getName().equals(name)// 比较方法参数&& arrayContentsEq(parameterTypes,fact.getExecutableSharedParameterTypes(m))// 比较返回值&& (res == null|| (res.getReturnType() != m.getReturnType()&& res.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(m.getReturnType()))))res = m;}return res;}}复制代码
1.3.5 Method#copy
在获取到对应方法以后,并不会直接返回,而是会通过 getReflectionFactory().copyMethod(method); 返回方法的一个拷贝。
最终调用的是 Method#copy,我们来看看其实现。
class Method {Method copy() {// This routine enables sharing of MethodAccessor objects// among Method objects which refer to the same underlying// method in the VM. (All of this contortion is only necessary// because of the "accessibility" bit in AccessibleObject,// which implicitly requires that new java.lang.reflect// objects be fabricated for each reflective call on Class// objects.)if (this.root != null)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can not copy a non-root Method");Method res = new Method(clazz, name, parameterTypes, returnType,exceptionTypes, modifiers, slot, signature,annotations, parameterAnnotations, annotationDefault);res.root = this;// Might as well eagerly propagate this if already presentres.methodAccessor = methodAccessor;return res;}}复制代码
会 new 一个 Method 实例并返回。
这里有两点要注意:
- 设置 root = this
- 会给 Method 设置 MethodAccessor,用于后面方法调用。也就是所有的 Method 的拷贝都会使用同一份 methodAccessor。
通过上面的步骤,就获取到了需要反射的方法。
我们再回顾一下之前的流程。
二、Java 反射原理—调用反射方法
获取到方法以后,通过 Method#invoke 调用方法。
class Method {public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException,InvocationTargetException{if (!override) {Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();// 1. 检查权限checkAccess(caller, clazz,Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) ? null : obj.getClass(),modifiers);}// 2. 获取 MethodAccessorMethodAccessor ma = methodAccessor; // read volatileif (ma == null) {// 创建 MethodAccessorma = acquireMethodAccessor();}// 3. 调用 MethodAccessor.invokereturn ma.invoke(obj, args);}}复制代码
invoke 方法的实现,分为三步:
2.1 检查是否有权限调用方法
这里对 override 变量进行判断,如果 override == true,就跳过检查 我们通常在 Method#invoke 之前,会调用 Method#setAccessible(true),就是设置 override 值为 true。
2.2 获取 MethodAccessor
在上面获取 Method 的时候我们讲到过,Method#copy 会给 Method 的 methodAccessor 赋值。所以这里的 methodAccessor 就是拷贝时使用的 MethodAccessor。
如果 ma 为空,就去创建 MethodAccessor。
class Method {private MethodAccessor acquireMethodAccessor() {// First check to see if one has been created yet, and take it// if soMethodAccessor tmp = null;if (root != null) tmp = root.getMethodAccessor();if (tmp != null) {methodAccessor = tmp;} else {// Otherwise fabricate one and propagate it up to the roottmp = reflectionFactory.newMethodAccessor(this);setMethodAccessor(tmp);}return tmp;}}复制代码
这里会先查找 root 的 MethodAccessor,这里的 root 在上面 Method#copy 中设置过。
如果还是没有找到,就去创建 MethodAccessor。
class ReflectionFactory {public MethodAccessor newMethodAccessor(Method method) {// 其中会对 noInflation 进行赋值checkInitted();// ...if (noInflation && !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(method.getDeclaringClass())) {// 生成的是 MethodAccessorImplreturn new MethodAccessorGenerator().generateMethod(method.getDeclaringClass(),method.getName(),method.getParameterTypes(),method.getReturnType(),method.getExceptionTypes(),method.getModifiers());} else {NativeMethodAccessorImpl acc =new NativeMethodAccessorImpl(method);DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl res =new DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl(acc);acc.setParent(res);return res;}}}复制代码
这里可以看到,一共有三种 MethodAccessor。MethodAccessorImpl,NativeMethodAccessorImpl,DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl。
采用哪种 MethodAccessor 根据 noInflation 进行判断,noInflation 默认值为 false,只有指定了 sun.reflect.noInflation 属性为 true,才会 采用 MethodAccessorImpl。
所以默认会调用 NativeMethodAccessorImpl。
MethodAccessorImpl 是通过动态生成字节码来进行方法调用的,是 Java 版本的 MethodAccessor,字节码生成比较复杂,这里不放代码了。大家感兴趣可以看这里的 generate 方法。
DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl 就是单纯的代理,真正的实现还是 NativeMethodAccessorImpl。
class DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl extends MethodAccessorImpl {private MethodAccessorImpl delegate;DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl(MethodAccessorImpl delegate) {setDelegate(delegate);}public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args)throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException{return delegate.invoke(obj, args);}void setDelegate(MethodAccessorImpl delegate) {this.delegate = delegate;}}复制代码
NativeMethodAccessorImpl 是 Native 版本的 MethodAccessor 实现。
class NativeMethodAccessorImpl extends MethodAccessorImpl {public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args)throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException{// We can't inflate methods belonging to vm-anonymous classes because// that kind of class can't be referred to by name, hence can't be// found from the generated bytecode.if (++numInvocations > ReflectionFactory.inflationThreshold()&& !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(method.getDeclaringClass())) {// Java 版本的 MethodAccessorMethodAccessorImpl acc = (MethodAccessorImpl)new MethodAccessorGenerator().generateMethod(method.getDeclaringClass(),method.getName(),method.getParameterTypes(),method.getReturnType(),method.getExceptionTypes(),method.getModifiers());parent.setDelegate(acc);}// Native 版本调用return invoke0(method, obj, args);}private static native Object invoke0(Method m, Object obj, Object[] args);}复制代码
在 NativeMethodAccessorImpl 的实现中,我们可以看到,有一个 numInvocations 阀值控制,numInvocations 表示调用次数。如果 numInvocations 大于 15(默认阀值是 15),那么就使用 Java 版本的 MethodAccessorImpl。
为什么采用这个策略呢,可以 JDK 中的注释:
// "Inflation" mechanism. Loading bytecodes to implement// Method.invoke() and Constructor.newInstance() currently costs// 3-4x more than an invocation via native code for the first// invocation (though subsequent invocations have been benchmarked// to be over 20x faster). Unfortunately this cost increases// startup time for certain applications that use reflection// intensively (but only once per class) to bootstrap themselves.// To avoid this penalty we reuse the existing JVM entry points// for the first few invocations of Methods and Constructors and// then switch to the bytecode-based implementations.//// Package-private to be accessible to NativeMethodAccessorImpl// and NativeConstructorAccessorImplprivate static boolean noInflation = false;复制代码
Java 版本的 MethodAccessorImpl 调用效率比 Native 版本要快 20 倍以上,但是 Java 版本加载时要比 Native 多消耗 3-4 倍资源,所以默认会调用 Native 版本,如果调用次数超过 15 次以后,就会选择运行效率更高的 Java 版本。
那为什么 Native 版本运行效率会没有 Java 版本高呢?从 R 大博客来看,是因为 这是HotSpot的优化方式带来的性能特性,同时也是许多虚拟机的共同点:跨越native边界会对优化有阻碍作用,它就像个黑箱一样让虚拟机难以分析也将其内联,于是运行时间长了之后反而是托管版本的代码更快些。
2.3 调用 MethodAccessor#invoke 实现方法的调用
在生成 MethodAccessor 以后,就调用其 invoke 方法进行最终的反射调用。
这里我们对 Java 版本的 MethodAccessorImpl 做个简单的分析,Native 版本暂时不做分析。
在前面我们提到过 MethodAccessorImpl 是通过 MethodAccessorGenerator#generate 生成动态字节码然后动态加载到 JVM 中的。
其中生成 invoke 方法字节码的是 MethodAccessorGenerator#emitInvoke。
我们看其中校验参数的一小段代码:
// Iterate through incoming actual parameters, ensuring that each// is compatible with the formal parameter type, and pushing the// actual on the operand stack (unboxing and widening if necessary).// num args of other invoke bytecodesfor (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) {// ...if (isPrimitive(paramType)) {// Unboxing code.// Put parameter into temporary local variable// astore_3 | astore_2// ...// repeat for all possible widening conversions:// aload_3 | aload_2// instanceof <primitive boxing type>// ifeq <next unboxing label>// aload_3 | aload_2// checkcast <primitive boxing type> // Note: this is "redundant",// // but necessary for the verifier// invokevirtual <unboxing method>// <widening conversion bytecode, if necessary>// goto <next parameter label>// <next unboxing label:> ...// last unboxing label:// new <IllegalArgumentException>// dup// invokespecial <IllegalArgumentException ctor>// athrow}}复制代码
通过上面的注释以及字节码,我们可以看到,生成的 invoke 方法,会对传入的参数做校验,其中会涉及到 unboxing 操作。
到此,基本上 Java 方法反射的原理就介绍完了。
三、Java 反射效率低的原因
了解了反射的原理以后,我们来分析一下反射效率低的原因。
- Method#invoke 方法会对参数做封装和解封操作
我们可以看到,invoke 方法的参数是 Object[] 类型,也就是说,如果方法参数是简单类型的话,需要在此转化成 Object 类型,例如 long ,在 javac compile 的时候 用了Long.valueOf() 转型,也就大量了生成了Long 的 Object, 同时 传入的参数是Object[]数值,那还需要额外封装object数组。
而在上面 MethodAccessorGenerator#emitInvoke 方法里我们看到,生成的字节码时,会把参数数组拆解开来,把参数恢复到没有被 Object[] 包装前的样子,同时还要对参数做校验,这里就涉及到了解封操作。
因此,在反射调用的时候,因为封装和解封,产生了额外的不必要的内存浪费,当调用次数达到一定量的时候,还会导致 GC。
- 需要检查方法可见性
通过上面的源码分析,我们会发现,反射时每次调用都必须检查方法的可见性(在 Method.invoke 里)
- 需要校验参数
反射时也必须检查每个实际参数与形式参数的类型匹配性(在NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0 里或者生成的 Java 版 MethodAccessor.invoke 里);
- 反射方法难以内联
Method#invoke 就像是个独木桥一样,各处的反射调用都要挤过去,在调用点上收集到的类型信息就会很乱,影响内联程序的判断,使得 Method.invoke() 自身难以被内联到调用方。参见 www.iteye.com/blog/rednax…
- JIT 无法优化
在 JavaDoc 中提到:
Because reflection involves types that are dynamically resolved, certain Java virtual machine optimizations can not be performed. Consequently, reflective operations have slower performance than their non-reflective counterparts, and should be avoided in sections of code which are called frequently in performance-sensitive applications.
因为反射涉及到动态加载的类型,所以无法进行优化。
总结
上面就是对反射原理和反射效率低的一些分析。
参考资料
www.iteye.com/blog/rednax…
作者:ZYLAB
链接:https://juejin.im/post/5da33b2351882509334fc0d3
来源:掘金
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。































还没有评论,来说两句吧...