MySQL 用 limit 为什么会影响性能?
点击上方 Java后端,选择 设为星标
优质文章,及时送达

作者 | zhangyachen
编辑 | Java之间
来源 | zhangyachen.github.io
#
一,前言
首先说明一下MySQL的版本:
mysql> select version();+-----------+| version() |+-----------+| 5.7.17 |+-----------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)
表结构:
mysql> desc test; +--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | bigint(20) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | val | int(10) unsigned | NO | MUL | 0 | | | source | int(10) unsigned | NO | | 0 | | +--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
id为自增主键,val为非唯一索引。
灌入大量数据,共500万:
mysql> select count(*) from test;+----------+| count(*) |+----------+| 5242882 |+----------+1 row in set (4.25 sec)
我们知道,当limit offset rows中的offset很大时,会出现效率问题:
mysql> select * from test where val=4 limit 300000,5; +---------+-----+--------+ | id | val | source | +---------+-----+--------+ | 3327622 | 4 | 4 | | 3327632 | 4 | 4 | | 3327642 | 4 | 4 | | 3327652 | 4 | 4 | | 3327662 | 4 | 4 | +---------+-----+--------+ 5 rows in set (15.98 sec)
为了达到相同的目的,我们一般会改写成如下语句:
mysql> select * from test a inner join (select id from test where val=4 limit 300000,5) b on a.id=b.id;+---------+-----+--------+---------+| id | val | source | id |+---------+-----+--------+---------+| 3327622 | 4 | 4 | 3327622 || 3327632 | 4 | 4 | 3327632 || 3327642 | 4 | 4 | 3327642 || 3327652 | 4 | 4 | 3327652 || 3327662 | 4 | 4 | 3327662 |+---------+-----+--------+---------+5 rows in set (0.38 sec)
时间相差很明显。
为什么会出现上面的结果?我们看一下select * from test where val=4 limit 300000,5;的查询过程:
查询到索引叶子节点数据。
根据叶子节点上的主键值去聚簇索引上查询需要的全部字段值。
类似于下面这张图:
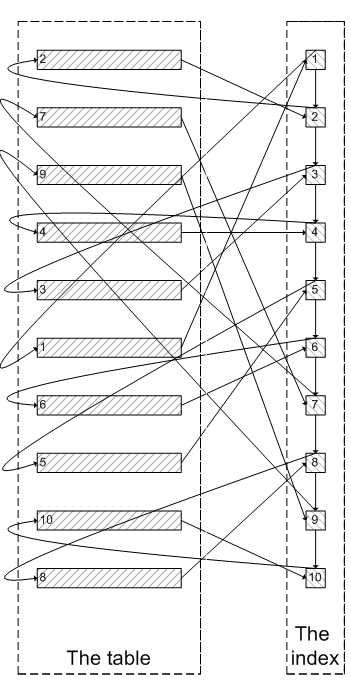
像上面这样,需要查询300005次索引节点,查询300005次聚簇索引的数据,最后再将结果过滤掉前300000条,取出最后5条。MySQL耗费了大量随机I/O在查询聚簇索引的数据上,而有300000次随机I/O查询到的数据是不会出现在结果集当中的。
肯定会有人问:既然一开始是利用索引的,为什么不先沿着索引叶子节点查询到最后需要的5个节点,然后再去聚簇索引中查询实际数据。这样只需要5次随机I/O,类似于下面图片的过程:
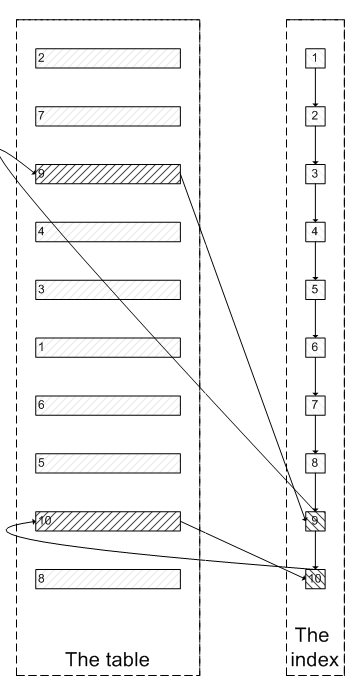
其实我也想问这个问题。
证实
下面我们实际操作一下来证实上述的推论:
为了证实select * from test where val=4 limit 300000,5是扫描300005个索引节点和300005个聚簇索引上的数据节点,我们需要知道MySQL有没有办法统计在一个sql中通过索引节点查询数据节点的次数。我先试了Handler_read_*系列,很遗憾没有一个变量能满足条件。
我只能通过间接的方式来证实:
InnoDB中有buffer pool。里面存有最近访问过的数据页,包括数据页和索引页。所以我们需要运行两个sql,来比较buffer pool中的数据页的数量。预测结果是运行select * from test a inner join (select id from test where val=4 limit 300000,5) b>之后,buffer pool中的数据页的数量远远少于select * from test where val=4 limit 300000,5;对应的数量,因为前一个sql只访问5次数据页,而后一个sql访问300005次数据页。
select * from test where val=4 limit 300000,5
mysql> select index_name,count(*) from information_schema.INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE where INDEX_NAME in('val','primary') and TABLE_NAME like '%test%' group by index_name; Empty set (0.04 sec)
可以看出,目前buffer pool中没有关于test表的数据页。
mysql> select * from test where val=4 limit 300000,5; +---------+-----+--------+ | id | val | source | +---------+-----+--------+ | 3327622 | 4 | 4 | | 3327632 | 4 | 4 | | 3327642 | 4 | 4 | | 3327652 | 4 | 4 | | 3327662 | 4 | 4 | +---------+-----+--------+ 5 rows in set (26.19 sec) mysql> select index_name,count(*) from information_schema.INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE where INDEX_NAME in('val','primary') and TABLE_NAME like '%test%' group by index_name; +------------+----------+ | index_name | count(*) | +------------+----------+ | PRIMARY | 4098 | | val | 208 | +------------+----------+ 2 rows in set (0.04 sec)
可以看出,此时buffer pool中关于test表有4098个数据页,208个索引页。
select * from test a inner join (select id from test where val=4 limit 300000,5) b>为了防止上次试验的影响,我们需要清空buffer pool,重启mysql。 mysqladmin shutdown /usr/local/bin/mysqld_safe & mysql> select index_name,count(*) from information_schema.INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE where INDEX_NAME in('val','primary') and TABLE_NAME like '%test%' group by index_name; Empty set (0.03 sec) 运行sql: mysql> select * from test a inner join (select id from test where val=4 limit 300000,5) b on a.id=b.id; +---------+-----+--------+---------+ | id | val | source | id | +---------+-----+--------+---------+ | 3327622 | 4 | 4 | 3327622 | | 3327632 | 4 | 4 | 3327632 | | 3327642 | 4 | 4 | 3327642 | | 3327652 | 4 | 4 | 3327652 | | 3327662 | 4 | 4 | 3327662 | +---------+-----+--------+---------+ 5 rows in set (0.09 sec) mysql> select index_name,count(*) from information_schema.INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE where INDEX_NAME in('val','primary') and TABLE_NAME like '%test%' group by index_name; +------------+----------+ | index_name | count(*) | +------------+----------+ | PRIMARY | 5 | | val | 390 | +------------+----------+ 2 rows in set (0.03 sec) 我们可以看明显的看出两者的差别:第一个sql加载了4098个数据页到buffer pool,而第二个sql只加载了5个数据页到buffer pool。符合我们的预测。也证实了为什么第一个sql会慢:读取大量的无用数据行(300000),最后却抛弃掉。 而且这会造成一个问题:加载了很多热点不是很高的数据页到buffer pool,会造成buffer pool的污染,占用buffer pool的空间。 遇到的问题
#
为了在每次重启时确保清空buffer pool,我们需要关闭innodb_buffer_pool_dump_at_shutdown和innodb_buffer_pool_load_at_startup,这两个选项能够控制数据库关闭时dump出buffer pool中的数据和在数据库开启时载入在磁盘上备份buffer pool的数据。
参考资料:
1.https://explainextended.com/2009/10/23/mysql-order-by-limit-performance-late-row-lookups/
2.https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/innodb-information-schema-buffer-pool-tables.html
【END】
如果看到这里,说明你喜欢这篇文章,请转发**、点赞**。微信搜索「web_resource」,关注后回复「进群」或者扫描下方二维码即可进入无广告交流群。
↓扫描二维码进群↓
推**荐阅读 **
1. 如果我是面试官,我会问你 Spring 那些问题?
2. Spring Boot 整合 Spring-cache
3. 我们再来聊一聊 Java 的单例吧
4. * *我采访了一位 Pornhub 工程师
5. 团队开发中 Git 最佳实践

喜**欢文章,点个在看 **
































还没有评论,来说两句吧...