Python学习系列《二》【变量和基本数据类型】
二、变量和简单数据类型
2.1 变量的命名规则
Python中变量的命名需要遵守以下规则:
(1)变量名只能包含字母、数字和下划线,且不能以数字开头。例如dxc1994、_num等都是合法的,2x、&age这种是不合法的;
(2)不能使用Python的关键字和函数名用作变量名。关键字自不用说,函数名尤其是Python自带的一些内置函数,将内置函数名用作变量名称时,由于函数名称被占用,导致这些函数的行为被覆盖了,这些函数就无法使用了。这里举个栗子:Python内置求最大值函数 max();
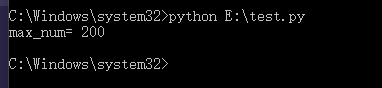
max()使用,E:\\test.py代码如下:max_num = max(100,200,123)print("max_num=",max_num)
输出结果为:
现在,我们首先定义一个变量叫做max,给它赋值之后,再使用max()函数时就会报错了,如下:
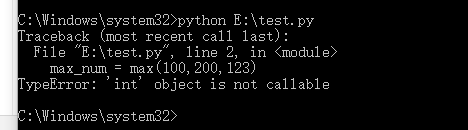
max =12max_num = max(100,200,123)print("max_num=",max_num)
Python解释器会报如下错误:
所以不应该使用函数名作为变量名称。
(3)变量名中不能包含有空格。
2.2 简单数据类型
2.2.1 整数
在Python中,可以对整数执行简单的加(+)减(-)乘(\*)除(/)等运算:
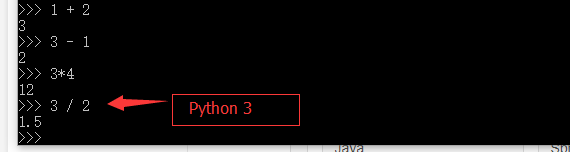
需要注意的是除(/)运算,Python 3中整数除以整数计算的结果是浮点数,Python 2中结果是整数。还有一种,就是其他语言中常见的整数除法,称之为地板除(//),二者区别见如下代码执行效果:
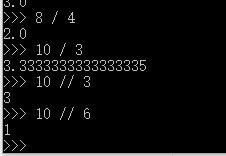
可见地板除(//),直接将结果的小数点抹去了。
2.2.2 浮点数
浮点数就是我们常用的小数,但是使用时需要注意一下几点:
(1)浮点数运算结果的位数可能是不确定的:

(2)可以使用科学计数法表示浮点数,如0.0000016可以记为1.6e-6,120000000.0可以表示为1.2E8,如下:

2.2.3 字符串
Python的字符串,可以用单引号,也可以使用双引号:>>> print('hello world')hello world>>> print("hello world")hello world>>>字符串拼接使用加号(+):>>> greet = "hello," + "my name is LingYingQiaoRen.">>> print(greet)hello,my name is LingYingQiaoRen.>>>字符串有一些常用函数,如upper()起全部大写作用,lower()起全部小写作用,title()起首字母大写作用等,但这些函数并不改变原有的参数实际值:>>> greet = "hello," + "my name is LingYingQiaoRen.">>> print(greet)hello,my name is LingYingQiaoRen.>>> print(greet.upper())HELLO,MY NAME IS LINGYINGQIAOREN.>>> print(greet.lower())hello,my name is lingyingqiaoren.>>> print(greet.title())Hello,My Name Is Lingyingqiaoren.>>> print(greet)hello,my name is LingYingQiaoRen.>>>
还有左侧删除空白函数lstrip(),右侧删除空白函数rstrip(),两端删除空白函数strip(),这些函数也不改变原有的参数值:
>>> string = ' python '>>> print(string.lstrip())python>>> print(string.rstrip())python>>> print(string.strip())python>>> print(string)python>>>
2.2.4 布尔类型
Python中的布尔类型只有True和False(注意这两个单词的大小写,全部小写和全部大写都是错误的),与运算符(and)、或运算符(or)和非运算符(not),这三个运算符只能是小写。>>> 3 > 2True>>> 3 == 2False>>> 3 > 2 or 1 == 2True>>> not trueTraceback (most recent call last):File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>NameError: name 'true' is not defined>>> not TRUETraceback (most recent call last):File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>NameError: name 'TRUE' is not defined>>> not TrueFalse>>> NOT TrueFile "<stdin>", line 1NOT True^SyntaxError: invalid syntax>>> 3 > 2 OR 1 == 2File "<stdin>", line 13 > 2 OR 1 == 2^SyntaxError: invalid syntax>>> 3 > 2 Or 1 == 2File "<stdin>", line 13 > 2 Or 1 == 2^SyntaxError: invalid syntax>>> not FalseTrue>>> True and FalseFalse>>> True or FalseTrue>>>
2.2.5 空值
Python中的空值用None表示:>>> var = None>>> print(var)None>>>
2.3 注释
Python中的单行注释使用井号(#)标识,,多行注释使用三个单引号 ‘’’ 或者三个双引号 “”” 将注释括起来:
#这是注释import sys"""这也是注释"""i = sys.maxsize'''这还是注释'''print(i)print("end !")
输出结果为:
C:\Windows\system32>python E:\test.py9223372036854775807end !






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...