Codeforces Edu Round 49 A-E
A. Palindromic Twist
由于必须改变。所以要使\(a[i] = a[n - i + 1]\)。
要么同向走,但必须满足之前的\(a[i] = a[n - i + 1]\)。
要么相遇,必须满足两字符相差\(2\)的距离。
#include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <cmath> using namespace std; const int N = 110; int n; char str[N]; bool judge(){ for(int i = 1; i <= n / 2; i++) if(abs(str[i] - str[n - i + 1]) != 2 && abs(str[i] - str[n - i + 1]) != 0) return false; return true; } int main(){ int T; scanf("%d", &T); while(T--){ scanf("%d%s", &n, str + 1); if(judge()) puts("YES"); else puts("NO"); } return 0; }
B. Numbers on the Chessboard
找规律题,如果\(n\)是奇数,则每行有可能\((n - 1) / 2\) 或 \((n + 1) / 2\)个数字,可以分治考虑:
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #define int long long using namespace std; int n, q; signed main(){ scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &q); for(int i = 1; i <= q; i++){ int x, y; scanf("%lld%lld", &x, &y); int num = 0; if(n % 2){ if((x + y) % 2 == 0){ if(x % 2) num = (x - 1) * n / 2 + y / 2 + 1; else num = (x - 2 + 1) * n / 2 + 1 + y / 2; }else{ if(x % 2) num = n * n / 2 + 1 + (x - 1) * n / 2 + y / 2; else num = n * n / 2 + (x - 2 + 1) * n / 2 + 1 + y / 2 + 1; } }else{ if((x + y) % 2 == 0){ if(x % 2) num = (x - 1) * (n / 2) + y / 2 + 1; else num = (x - 1) * (n / 2) + y / 2; }else{ if(x % 2) num = n * n / 2 + (x - 1) * (n / 2) + y / 2; else num = n * n / 2 + (x - 1) * (n / 2) + y / 2 + 1; } } printf("%lld\n", num); } return 0; }
C. Minimum Value Rectangle
设矩形的两边长为\(a\)、\(b\),且\(a <= b\),则:
\(\frac{P ^ 2}{S} = \frac{(2(a + b)) ^ 2}{a * b}= \frac{4a ^ 2 + 4b ^ 2 + 8ab }{a * b} = 4(\frac{a}{b} + \frac{b}{a}) + 8\)
使\(\frac{a}{b} + \frac{b}{a}\) 最小,只需使\(\frac{b}{a}\)最小既可,因为\(\frac{b}{a} >= 1\),但\(\frac{a}{b} <= 1\),故后者对总和没有影响。
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <limits.h> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int SIZE = 10010; int n, a, cnt[SIZE], d[SIZE << 1], tot, ansA, ansB; double c, minn; int main(){ int T; scanf("%d", &T); while(T--){ memset(cnt, 0, sizeof cnt); bool success = false; tot = 0; minn = 10001; scanf("%d", &n); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { scanf("%d", &a), cnt[a]++; if(cnt[a] == 2) d[++tot] = a; if(cnt[a] == 4) d[++tot] = a; } sort(d + 1, d + 1 + tot); for(int i = 1; i < tot; i++){ if(d[i] == d[i + 1]){ ansA = d[i], ansB = d[i + 1]; break; } c = (double)d[i + 1] / d[i]; if(c < minn)ansA = d[i], ansB = d[i + 1], minn = c; } printf("%d %d %d %d\n", ansA, ansA, ansB, ansB); } return 0; }
D. Mouse Hunt
对于每个联通块,选择环中(包括子环)的一个位置设置捕鼠夹既可。
在符合条件的位置上取最小值的和即为答案。
若选择多个点,可证明其代价要大于选一个点。
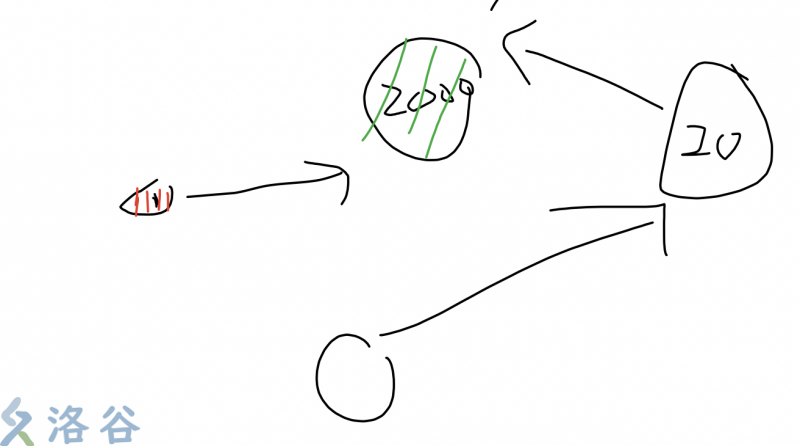
若不选择绿点,选择1 + 20,但为了保证每个房间都能干掉老鼠,所以2000是必选的,所以选择联通快中多个点的花销 > 只选一个点。
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <limits.h> using namespace std; const int N = 200010; int n, c[N], a[N], ans; bool st[N], vis[N]; vector<int> G[N], edge, val; void dfs(int u){ if(vis[u]){ val.push_back(u); while(edge.size() && edge.back() != u) val.push_back(edge.back()), edge.pop_back(); return ; } vis[u] = true, edge.push_back(u), dfs(a[u]); } void mark(int u){ for(int i = 0; i < G[u].size(); i++){ int v = G[u][i]; if(!st[v]) st[v] = true, mark(v); } } int main(){ scanf("%d", &n); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", c + i); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { scanf("%d", a + i); G[i].push_back(a[i]); G[a[i]].push_back(i); } for(int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++){ if(!st[i]){ val.clear(); edge.clear(); dfs(i); int res = INT_MAX; for(int i = 0; i < val.size(); i++) res = min(res, c[val[i]]); ans += res; st[i] = true, mark(i); } } printf("%d", ans); return 0; }
E. Inverse Coloring
自闭,看了题解之后稍微理解了一点点。
设\(f[i][j][k]\) 为长度为\(i\), 最长连续填色数为\(k\), 尾部最长连续涂色数最长为\(j\)的方案数
可以想到,这个状态可以延展到的状态有:
- 当新结尾颜色保持跟之前一样,\(f[i + 1][j + 1][max(j + 1, k)]\)
- 不一样,\(f[i + 1][1][max(1, k)]\)
\(cnt[i]\) 实际上是长度为\(i\)的所有方案数,那么只要符合:
\(i * j < k\),\(cnt[i] * cnt[j]\)就能被加入答案
……
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> using namespace std; const int N = 510, mod = 998244353; typedef long long LL; int n, k, f[2][N][N], cnt[N]; void update(int &a, int b){ a = (a + b) % mod; } int main(){ scanf("%d%d", &n, &k); f[0][0][0] = 1; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ int pre = i & 1, now = pre ^ 1; memset(f[now], 0, sizeof f[now]); for(int j = 0; j <= n; j++){ for(int k = 0; k <= n; k++){ update(f[now][j + 1][max(j + 1, k)], f[pre][j][k]); update(f[now][1][max(1, k)], f[pre][j][k]); } } } for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++){ for(int j = 0; j <= n; j++){ update(cnt[i], f[n & 1][j][i]); } } LL ans = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){ if(i * j < k) ans = (ans + (LL)cnt[i] * cnt[j]) % mod; } } printf("%lld", (ans / 2) % mod); return 0; }
转载于 //www.cnblogs.com/dmoransky/p/11260524.html
//www.cnblogs.com/dmoransky/p/11260524.html





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...