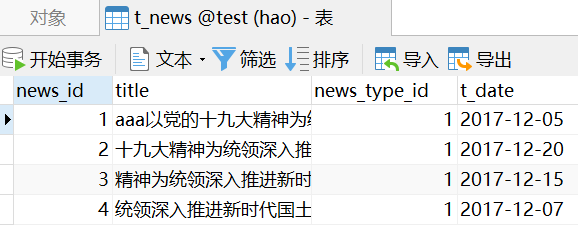
ubuntu dpkg安装卸载软件命令
dpkg --help命令查看用法:
用法:dpkg [<选项> ...] <命令>命令:-i|--install <.deb 文件名> ... | -R|--recursive <目录> ...--unpack <.deb 文件名> ... | -R|--recursive <目录> ...-A|--record-avail <.deb 文件名> ... | -R|--recursive <目录> ...--configure <软件包名> ... | -a|--pending--triggers-only <软件包名> ... | -a|--pending-r|--remove <软件包名> ... | -a|--pending-P|--purge <软件包名> ... | -a|--pending-V|--verify <软件包名> ... 检查包的完整性。--get-selections [<表达式> ...] 把已选中的软件包列表打印到标准输出。--set-selections 从标准输入里读出要选择的软件。--clear-selections 取消选中所有不必要的软件包。--update-avail <软件包文件> 替换现有可安装的软件包信息。--merge-avail <软件包文件> 把文件中的信息合并到系统中。--clear-avail 清除现有的软件包信息。--forget-old-unavail 忘却已被卸载的不可安装的软件包。-s|--status <软件包名> ... 显示指定软件包的详细状态。-p|--print-avail <软件包名> ... 显示可供安装的软件版本。-L|--listfiles <软件包名> ... 列出属于指定软件包的文件。-l|--list [<表达式> ...] 简明地列出软件包的状态。-S|--search <表达式> ... 搜索含有指定文件的软件包。-C|--audit [<表达式> ...] 检查是否有软件包残损。--yet-to-unpack 列出标记为待解压的软件包。--predep-package 列出待解压的预依赖。--add-architecture <体系结构> 添加 <体系结构> 到体系结构列表。--remove-architecture <体系结构> 从架构列表中移除 <体系结构>。--print-architecture 显示 dpkg 体系结构。--print-foreign-architectures 显示已启用的异质体系结构。--assert-<特性> 对指定特性启用断言支持。--validate-<属性> <字符串> 验证一个 <属性>的 <字符串>。--compare-vesions <a> <关系> <b> 比较版本号 - 见下。--force-help 显示本强制选项的帮助信息。-Dh|--debug=help 显示有关出错调试的帮助信息。-?, --help 显示本帮助信息。--version 显示版本信息。Assert 特性: support-predepends, working-epoch, long-filenames,multi-conrep, multi-arch, versioned-provides.可验证的属性:pkgname, archname, trigname, version.调用 dpkg 并带参数 -b, --build, -c, --contents, -e, --control, -I, --info,-f, --field, -x, --extract, -X, --vextract, --ctrl-tarfile, --fsys-tarfile是针对归档文件的。 (输入 dpkg-deb --help 获取帮助)选项:--admindir=<目录> 使用 <目录> 而非 /var/lib/dpkg。--root=<目录> 安装到另一个根目录下。--instdir=<目录> 改变安装目录的同时保持管理目录不变。--path-exclude=<表达式> 不要安装符合Shell表达式的路径。--path-include=<表达式> 在排除模式后再包含一个模式。-O|--selected-only 忽略没有被选中安装或升级的软件包。-E|--skip-same-version 忽略版本与已安装软件版本相同的软件包。-G|--refuse-downgrade 忽略版本早于已安装软件版本的的软件包。-B|--auto-deconfigure 就算会影响其他软件包,也要安装。--[no-]triggers 跳过或强制随之发生的触发器处理。--verify-format=<格式> 检查输出格式('rpm'被支持)。--no-debsig 不去尝试验证软件包的签名。--no-act|--dry-run|--simulate仅报告要执行的操作 - 但是不执行。-D|--debug=<八进制数> 开启调试(参见 -Dhelp 或者 --debug=help)。--status-fd <n> 发送状态更新到文件描述符<n>。--status-logger=<命令> 发送状态更新到 <命令> 的标准输入。--log=<文件名> 将状态更新和操作信息到 <文件名>。--ignore-depends=<软件包>,...忽略关于 <软件包> 的所有依赖关系。--force-... 忽视遇到的问题(参见 --force-help)。--no-force-...|--refuse-...当遇到问题时中止运行。--abort-after <n> 累计遇到 <n> 个错误后中止。可供--compare-version 使用的比较运算符有:lt le eq ne ge gt (如果版本号为空,那么就认为它先于任意版本号);lt-nl le-nl ge-nl gt-nl (如果版本号为空,那么就认为它后于任意版本号);< << <= = >= >> > (仅仅是为了与主控文件的语法兼容)。'apt' 和 'aptitude' 提供了更为便利的软件包管理。用法:dpkg-deb [<选项> ...] <命令>命令:-b|--build <目录> [<deb>] 构建一个软件包。-c|--contents <deb> 列出所含内容。-I|--info <deb> [<cfile> ...] 打印相关信息到标准输出。-W|--show <deb> 打印对应软件包的简明信息。-f|--field <deb> [<cfield> ...] 把字段内容打印到标准输出。-e|--control <deb> [<目录>] 将主控信息解压。-x|--extract <deb> <目录> 将所有文件解压。-X|--vextract <deb> <目录> 解压所有文件并打印其列表。-R|--raw-extract <deb> <目录>解压控制信息和控制文件。--ctrl-tarfile <deb> 输出控制文件的tar文件。--fsys-tarfile <deb> 输出文件系统的 tar 文件。-?, --help 显示本帮助信息。--version 显示版本信息。<deb> 是 Debian 格式归档文件的文件名。<cfile> 是管理文件组件的文件名。<cfield> 是主控文件中的属性字段的名字。Options:-v, --verbose Enable verbose output.-D, --debug Enable debugging output.--showformat=<format> Use alternative format for --show.--deb-format=<format> Select archive format.Allowed values: 0.939000, 2.0 (default).--nocheck Suppress control file check (build badpackages).--root-owner-group Forces the owner and groups to root.--[no-]uniform-compression Use the compression params on all members.-z# Set the compression level when building.-Z<type> Set the compression type used when building.Allowed types: gzip, xz, zstd, none.-S<strategy> Set the compression strategy when building.Allowed values: none; extreme (xz);filtered, huffman, rle, fixed (gzip).格式串的语法:格式串是用于显示每一个软件包的字符串。格式串可以包含标准的脱字符(escape sequences),如 \n (换行)、\r (回车)、或是 \\ (反斜杠)。还可以通过加入软件包属性的变量引用来反映软件包的相关信息,要在某些字段引用属性变量的话,可以用这样的语法:${var[;width]}。字段一般是靠右对齐的,除非它的宽度是负数。若其宽度是负数,那么字段将会靠左对齐。使用 dpkg 命令可以在系统中安装和卸载软件包,apt 或 aptitude 命令则用于简便的软件包管理。另外,通过 dpkg-deb --extract 命令解压的软件包将不会被正确安装!
具体示例:
linux软件卸载方法及dpkg命令的使用


























![vue 报错 [Vue warn]: Duplicate keys detected: 'a'. This may cause an update error. vue 报错 [Vue warn]: Duplicate keys detected: 'a'. This may cause an update error.](https://image.dandelioncloud.cn/images/20230531/2d80bd18d31e4608a6dee1e2add77ba8.png)




还没有评论,来说两句吧...