哈希表
一、简介
如果所有的键都是小整数,那么我们可以用一个数组来实现无序的符号表,将键作为数组的索引i而数组中i(键)处储存的就是对应的值。
这样就可以快速地访问任意键的值,哈希表是这种简易方法的拓展并能够处理更加复杂类型的键。
哈希表需要用算术操作将键转换为数组的索引来访问数组中的键值对。
哈希表的查找算法主要分为两步:
第一步是用哈希函数将键转换为数组的一个索引,理想情况下不同的键都能转换为不同的索引值,但是实际上会有多个键哈希到到相同索引值上。
因此,第二步就是处理碰撞冲突的过程。这里有两种处理碰撞冲突的方法:separate chaining(拉链法)和linear probing(线性探测法)。
哈希表是算法在时间和空间上做出权衡的经典例子。
如果没有内存限制,算法可以直接将键作为数组(可能是超级大)的索引,那么所有的查找操作只需要访问一次内存即可完成。但这种理想情况一般不会出现,因为当键很多时,需要的内存太大。
如果没有时间限制,算法可以使用无序数组并进行顺序查找,这样只需要很少的内存。
哈希表使用了适度的空间和时间并在这两种极端之间找到了一种平衡。
算法只需要调整某些参数就可以在时间和空间之间做出取舍,这里需要使用概率论的经典结论来选择适当的参数。
概率论是数学分析中的重大成果,哈希表利用了这些知识。使用哈希表可以使应用拥有常数级别的查找和插入操作的符号表。这使得其在很多情况下成为实现简单符号表的最佳选择。
二、哈希函数
如果算法用一个大小为M的数组来储存键值对,那么需要一个能够将任意键转为该数组范围内的索引(0-M-1)的哈希函数。
这个哈希函数应该易于计算并且能够均匀分布所有的键。即对于任意键,0到M-1之间的每个整数都有相等可能性与之对应。
1、正整数
将整数哈希最常用的方法是除留余数法。这个方法选择大小为素数M的数组,对于任意正整数k,计算k除以M的余数。
如果M不是素数的话,将不能有效利用键中所包含的所有信息,导致算法不能均匀地分布所有键。
比如,键值是十进制而M为10k,则哈希函数只能利用最后k位(10001%100=01,只利用了后2位)。
2、浮点数
四舍五入的方法比较容易理解,但有缺陷,因为这种情况高位起的作用更大,地位对哈希的结果没什么影响。
更好的方法是先将浮点数转为为二进制数,再用除留余数法。
3、字符串
用除留余数法也能处理较长的键,如字符串。只是将字符串当做一个大整数。
int hash = 0;for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)hash = (R * hash + s.charAt(i)) % M;
这种计算把字符串当做一个N位的R进制值,并将其除以M并取余。
这里要注意字符串表示的数字,高位在前,即s.charAt(0)为最高位。
R取值要足够小,使之不造成溢出,这里选31。
Java的String默认实现采用了类似的方法:
public int hashCode() {int h = hash;if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {char val[] = value;for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {h = 31 * h + val[i];}hash = h;}return h;}
只是这里的M值默认为int的最大值加1。
4、组合键
如果键的类型含有多个整型变量,算法可以向String一样,将其混合起来。
5、Java的约定
每种数据类型都需要相应的哈希函数,Java中每个数据类型都继承了hashCode方法。
每个数据类型的hashCode方法都必须和equas方法一致。
也就是说,如果a.equals(b)方法返回true,那么a.hashCode和b.hashCode的返回值相同。
相反两个对象的哈希值不一样,那这两个对象是不同的。如果两个对象的哈希值一样,那这两个对象不一定是相同的。
总:hashCode是equals的必要不充分条件。
6、将hashCode的返回值转换为数组索引
因为实际应用需要的是数组的索引而不是一个32位的整数,所以在实际实现中会将默认的hashCode方法和除留余数法结合起来产生一个0大M-1的整数。
private int hash(Key x) {return (x.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % M;}
7、自定义hashCode方法
自定义hashCode方法必须将键平均分布到32位整数中去。
8、缓存
如果哈希值计算很麻烦,那么可以将每个键的哈希值缓存起来(储存到变量hash),第一次调用时计算,之后都是直接返回哈希值。
一个优秀的哈希方法需要满足三个条件:
一致性——等价的键必须产生相等的哈希值
高效性——计算简便
均匀性——均匀地哈希所有键
保证均匀性的最好办法是保证键的每一位都在哈希值的计算中起到了相同的作用。
9、假设
假设:算法使用的哈希函数能够将所有键均匀并独立地分布到0和M-1之间。
这个假设是实际上无法达到的理想模型,但是是算法实现哈希函数的指导思想。
三、基于拉链法的哈希表
1、简介
哈希函数将键转化为数组索引,第二步就是需要进行碰撞处理。
一种最直接的方法是将大小为M的数组的每个元素指向一条链表,链表的每个节点都储存了哈希值为该位置数组下标的键值对。
这种方法称为拉链法(separate chaining)。因为冲突的元素都放在同一个链表上。
这种方法的思想就是:选择足够大的M使得链表都尽可能短以保证高效查找。
查找顺序:先根据哈希值找到相应的链表,然后遍历链表查找相应的键。
2、实现
这里可以用两种方式实现,第一种是用原始的链表数据类型,第二种是用之前已经实现了的SequentialSearchST。
算法使用了M条链表来保存N个键,所以链表的平均长度是N/M。
官方实现:
public class SeparateChainingHashST<Key, Value> {private static final int INIT_CAPACITY = 4;private int n; // number of key-value pairsprivate int m; // hash table sizeprivate SequentialSearchST<Key, Value>[] st; // array of linked-list symbol tables/*** Initializes an empty symbol table.*/public SeparateChainingHashST() {this(INIT_CAPACITY);}/*** Initializes an empty symbol table with {@code m} chains.* @param m the initial number of chains*/public SeparateChainingHashST(int m) {this.m = m;st = (SequentialSearchST<Key, Value>[]) new SequentialSearchST[m];for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)st[i] = new SequentialSearchST<Key, Value>();}// resize the hash table to have the given number of chains,// rehashing all of the keysprivate void resize(int chains) {SeparateChainingHashST<Key, Value> temp = new SeparateChainingHashST<Key, Value>(chains);for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for (Key key : st[i].keys()) {temp.put(key, st[i].get(key));}}this.m = temp.m;this.n = temp.n;this.st = temp.st;}// hash value between 0 and m-1private int hash(Key key) {return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % m;}/*** Returns the number of key-value pairs in this symbol table.** @return the number of key-value pairs in this symbol table*/public int size() {return n;}/*** Returns true if this symbol table is empty.** @return {@code true} if this symbol table is empty;* {@code false} otherwise*/public boolean isEmpty() {return size() == 0;}/*** Returns true if this symbol table contains the specified key.** @param key the key* @return {@code true} if this symbol table contains {@code key};* {@code false} otherwise* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}*/public boolean contains(Key key) {if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to contains() is null");return get(key) != null;}/*** Returns the value associated with the specified key in this symbol table.** @param key the key* @return the value associated with {@code key} in the symbol table;* {@code null} if no such value* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}*/public Value get(Key key) {if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to get() is null");int i = hash(key);return st[i].get(key);}/*** Inserts the specified key-value pair into the symbol table, overwriting the old* value with the new value if the symbol table already contains the specified key.* Deletes the specified key (and its associated value) from this symbol table* if the specified value is {@code null}.** @param key the key* @param val the value* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}*/public void put(Key key, Value val) {if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("first argument to put() is null");if (val == null) {delete(key);return;}// double table size if average length of list >= 10if (n >= 10*m) resize(2*m);int i = hash(key);if (!st[i].contains(key)) n++;st[i].put(key, val);}/*** Removes the specified key and its associated value from this symbol table* (if the key is in this symbol table).** @param key the key* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}*/public void delete(Key key) {if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to delete() is null");int i = hash(key);if (st[i].contains(key)) n--;st[i].delete(key);// halve table size if average length of list <= 2if (m > INIT_CAPACITY && n <= 2*m) resize(m/2);}// return keys in symbol table as an Iterablepublic Iterable<Key> keys() {Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<Key>();for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for (Key key : st[i].keys())queue.enqueue(key);}return queue;}/*** Unit tests the {@code SeparateChainingHashST} data type.** @param args the command-line arguments*/public static void main(String[] args) {SeparateChainingHashST<String, Integer> st = new SeparateChainingHashST<String, Integer>();for (int i = 0; !StdIn.isEmpty(); i++) {String key = StdIn.readString();st.put(key, i);}// print keysfor (String s : st.keys())StdOut.println(s + " " + st.get(s));}}
注:这个实现动态调整了链表数组的大小,而且动态调整链表数组大小需要重新哈希所有键,因为M的大小发生了变化。
3、性能分析
结论1:在一张含有M条链表和N个键的哈希表中,任意一条链表的长度均在N/M的常数因子范围内的概率无限趋向于1。
这个结论完全依赖于这个假设:算法使用的哈希函数能够将所有键均匀并独立地分布到0和M-1之间。
结论2:在一张含有M条链表和N个键的哈希表中,未命中查找和插入操作所需的比较次数为~N/M。
4、有序性相关操作
哈希表不是合适的选择,这回导致线性级别的运行时间。
四、基于线性探测法的哈希表
1、简介
实现哈希表的另一种方法是用大小为M的数组保存N个键值对,其中M>N。这种方法依靠数组中的空位解决碰撞冲突。
当发生碰撞时,算法检查下一个位置(将索引加1)。
这样线性探测可能会产生三种结果:
命中,该位置的键和要查找的键相同。
未命中,该键为空。
继续查找,该位置的键和要查找的键不相同。
查找的思路:先用哈希函数找到键在数组中的索引,检查其中的键和被查找的键是否相同,如果不同则继续查找,直到找到该键或者遇到一个空元素。
2、实现
官方实现:
使用了两个数组,一个用于保存键,一个用于保存值。
public class LinearProbingHashST<Key, Value> {private static final int INIT_CAPACITY = 4;private int n; // number of key-value pairs in the symbol tableprivate int m; // size of linear probing tableprivate Key[] keys; // the keysprivate Value[] vals; // the values/*** Initializes an empty symbol table.*/public LinearProbingHashST() {this(INIT_CAPACITY);}/*** Initializes an empty symbol table with the specified initial capacity.** @param capacity the initial capacity*/public LinearProbingHashST(int capacity) {m = capacity;n = 0;keys = (Key[]) new Object[m];vals = (Value[]) new Object[m];}/*** Returns the number of key-value pairs in this symbol table.** @return the number of key-value pairs in this symbol table*/public int size() {return n;}/*** Returns true if this symbol table is empty.** @return {@code true} if this symbol table is empty;* {@code false} otherwise*/public boolean isEmpty() {return size() == 0;}/*** Returns true if this symbol table contains the specified key.** @param key the key* @return {@code true} if this symbol table contains {@code key};* {@code false} otherwise* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}*/public boolean contains(Key key) {if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to contains() is null");return get(key) != null;}// hash function for keys - returns value between 0 and M-1private int hash(Key key) {return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % m;}// resizes the hash table to the given capacity by re-hashing all of the keysprivate void resize(int capacity) {LinearProbingHashST<Key, Value> temp = new LinearProbingHashST<Key, Value>(capacity);for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {if (keys[i] != null) {temp.put(keys[i], vals[i]);}}keys = temp.keys;vals = temp.vals;m = temp.m;}/*** Inserts the specified key-value pair into the symbol table, overwriting the old* value with the new value if the symbol table already contains the specified key.* Deletes the specified key (and its associated value) from this symbol table* if the specified value is {@code null}.** @param key the key* @param val the value* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}*/public void put(Key key, Value val) {if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("first argument to put() is null");if (val == null) {delete(key);return;}// double table size if 50% fullif (n >= m/2) resize(2*m);int i;for (i = hash(key); keys[i] != null; i = (i + 1) % m) {if (keys[i].equals(key)) {vals[i] = val;return;}}keys[i] = key;vals[i] = val;n++;}/*** Returns the value associated with the specified key.* @param key the key* @return the value associated with {@code key};* {@code null} if no such value* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}*/public Value get(Key key) {if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to get() is null");for (int i = hash(key); keys[i] != null; i = (i + 1) % m)if (keys[i].equals(key))return vals[i];return null;}/*** Removes the specified key and its associated value from this symbol table* (if the key is in this symbol table).** @param key the key* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}*/public void delete(Key key) {if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to delete() is null");if (!contains(key)) return;// find position i of keyint i = hash(key);while (!key.equals(keys[i])) {i = (i + 1) % m;}// delete key and associated valuekeys[i] = null;vals[i] = null;// rehash all keys in same clusteri = (i + 1) % m;while (keys[i] != null) {// delete keys[i] an vals[i] and reinsertKey keyToRehash = keys[i];Value valToRehash = vals[i];keys[i] = null;vals[i] = null;n--;put(keyToRehash, valToRehash);i = (i + 1) % m;}n--;// halves size of array if it's 12.5% full or lessif (n > 0 && n <= m/8) resize(m/2);assert check();}/*** Returns all keys in this symbol table as an {@code Iterable}.* To iterate over all of the keys in the symbol table named {@code st},* use the foreach notation: {@code for (Key key : st.keys())}.** @return all keys in this symbol table*/public Iterable<Key> keys() {Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<Key>();for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)if (keys[i] != null) queue.enqueue(keys[i]);return queue;}// integrity check - don't check after each put() because// integrity not maintained during a delete()private boolean check() {// check that hash table is at most 50% fullif (m < 2*n) {System.err.println("Hash table size m = " + m + "; array size n = " + n);return false;}// check that each key in table can be found by get()for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {if (keys[i] == null) continue;else if (get(keys[i]) != vals[i]) {System.err.println("get[" + keys[i] + "] = " + get(keys[i]) + "; vals[i] = " + vals[i]);return false;}}return true;}/*** Unit tests the {@code LinearProbingHashST} data type.** @param args the command-line arguments*/public static void main(String[] args) {LinearProbingHashST<String, Integer> st = new LinearProbingHashST<String, Integer>();for (int i = 0; !StdIn.isEmpty(); i++) {String key = StdIn.readString();st.put(key, i);}// print keysfor (String s : st.keys())StdOut.println(s + " " + st.get(s));}}
注:NULL表示一簇键的结束。
delete方法比较复杂,需要在下图的哈希表中删除C,直接在该键所在的位置设为null是不行的。这样会导致其后边的S和H无法被找到,所以需要将S和H重新插入,即要删除的键同个簇中右侧的键。

和拉链法一样,线性探测法哈希表的性能也依赖于N/M的比值。
只不过意义不一样,这里是N/M是哈希表中被占用的空间比例,算法使用动态调整数组大小方法来保证使用率在1/8到1/2之间。
和拉链法一样,动态调整数组大小需要重新哈希所有键。
3、数学分析
线性探测的性能取决于元素在插入数组后聚集成的一组连续的条目,也叫键簇。
键簇短小才能保证高的效率。随着插入的键越来越多,这个要求越来越难满足,较长的键簇会越来越多。
结论:在一张大小为M,且含有N=αM个键的基于线性探测哈希表中,基于假设(算法使用的哈希函数能够将所有键均匀并独立地分布到0和M-1之间),命中和未命中查找查找所需的探测次数为分别为:
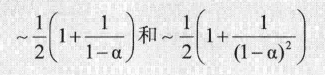
特别当α=1/2时,这两个值分别为3/2,、5/2。单α趋于1时,这些估计值精确度会下降。
不过我们不用担心这个情况,算法会保证α小于1/2。
当使用率小于1/2时,探测的预计次数在1.5和2.5之间。
在put函数和delete函数,可以看到有相应的动态调整数组大小的语句。保证α小于1/2,并大于某个值。
转载于 //www.cnblogs.com/songdechiu/p/6954038.html
//www.cnblogs.com/songdechiu/p/6954038.html



































还没有评论,来说两句吧...