【数据结构】之队列
笔者日常:
感谢孤尽(花名)大侠今天给我解答线程安全的问题,在这里推荐孤大侠书籍《码出高效》,带你深入基础,走进阿里规范!
目录
队列基本知识
队列的常见实现方式
数组实现链表实现
队列的常见分类
数组队列:基于数组的原理进行实现。链表队列:基于链表的原理进行实现。
Java对上述队列的代码实现(示例)
对(数组)顺序队列的(简单)实现对(数组)循环队列的(简单)实现对链表队列的(简单)实现
队列基本知识:
队列是一种特殊的操作受限制的线性表,它只允许在表的前端(front)进行删除操作,而在表的后端(rear)进行插入操作,**进行插入操作的端称为队尾,进行删除操作的端称为队头**。队列的插入操作称为入队,删除操作称为出队。队列就像一列进入隧道的火车,隧道就是队列,火车车厢就是元素,进入隧道就是从隧道的这头(队尾)插入元素;出隧道就是从隧道的另一头(队头)删除元素。队列具有**先进先出(FIFO—first in first out)**的特点。
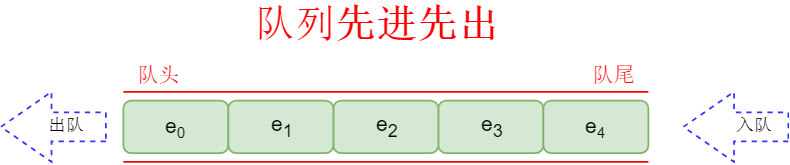
队列的常见实现方式:
队列的实现方式较多,我们常见的主要有两种,分别是数组实现与链表实现。基于数组的队列效率较高,但有长度限制(当然可以在程序内部以新建数组的方式来变相达到动态扩容的效果)。基于链表的队列,要动态创建和删除节点,效率较低,但是可以动态增长。
数组实现:

链表实现:

队列的常见分类:
分类标准不同,队列分类也不一样。按照入队出队时是否阻塞可分为阻塞队列、非阻塞队列。按照实现方式来分的话,队列可分为数组队列、链表队列等。其中,数组队列按照空间是否可以重复利用来分的话,又可分为顺序队列和循环队列。
注:对于数组队列而言,循环队列要比顺序队列实用得多。
数组队列:基于数组的原理进行实现。
相关概念之溢出(图示说明):

顺序队列(主要以图示说明):从队头删除元素,从队尾增加元素。被删除的元素空出来的位置,不会被后来增加的
元素重复利用。
第一种:队头不动,出队列时队头后的所有元素向前移动。
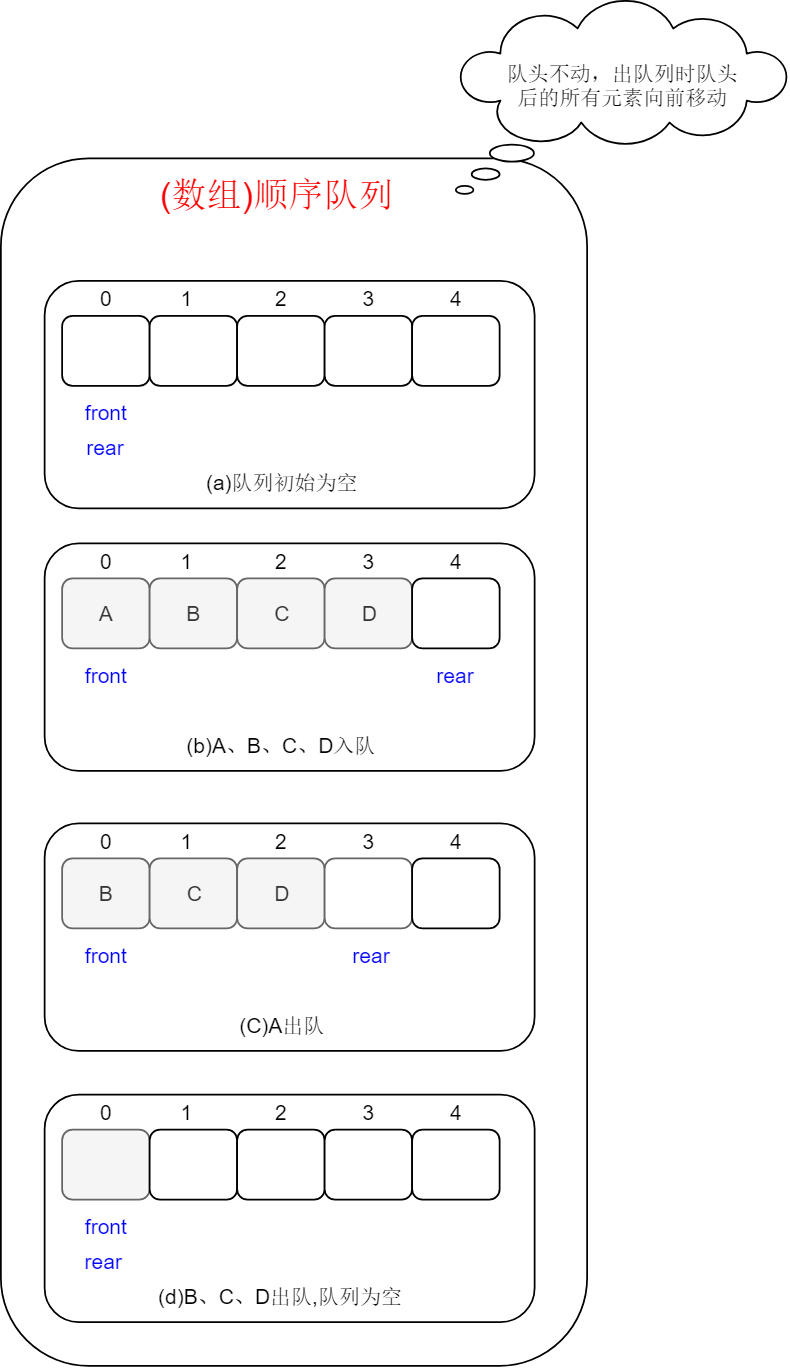
注:一旦有元素出队,那么所有元素都得移动,开销较大。
第二种:队头移动,出队列时队头向后移动一个位置。
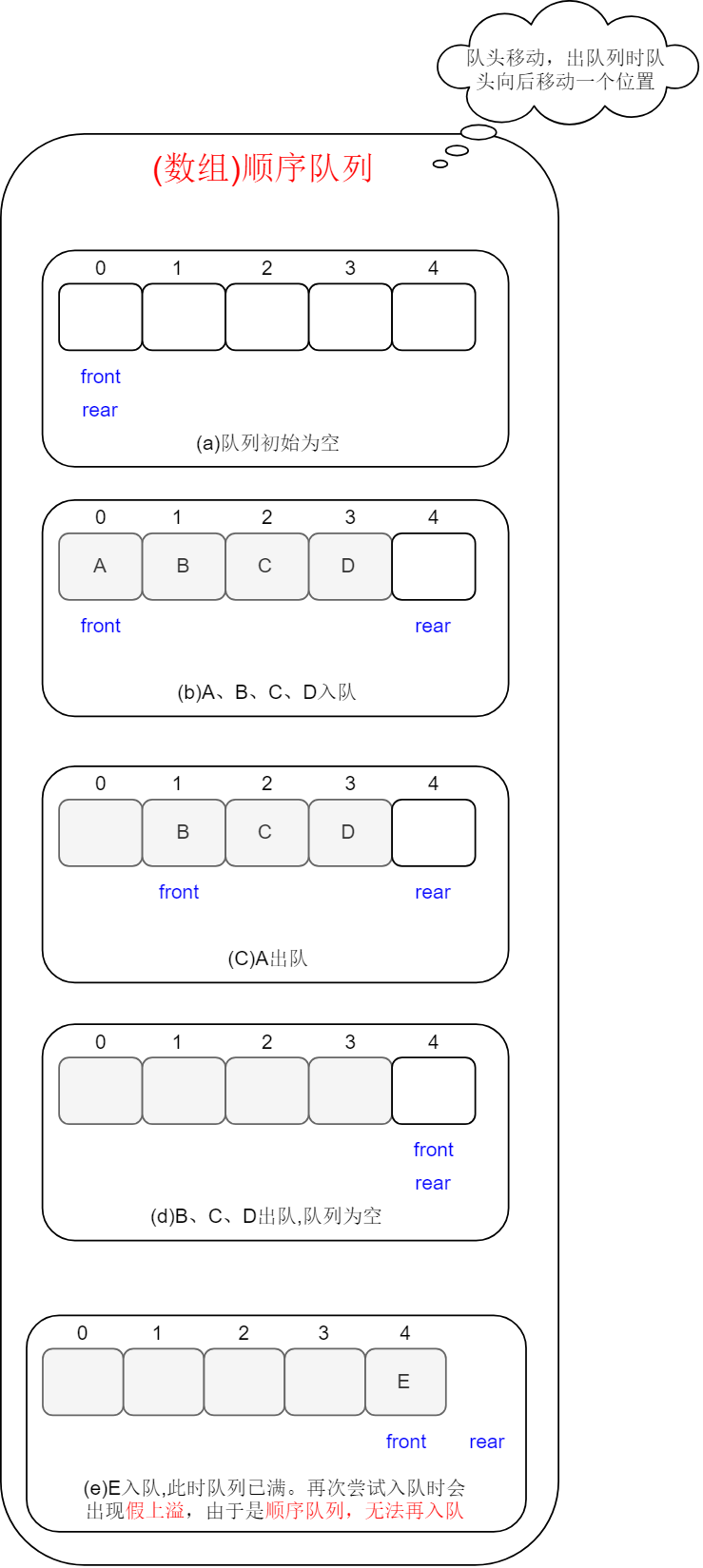
注:此方式可能出现假溢出。
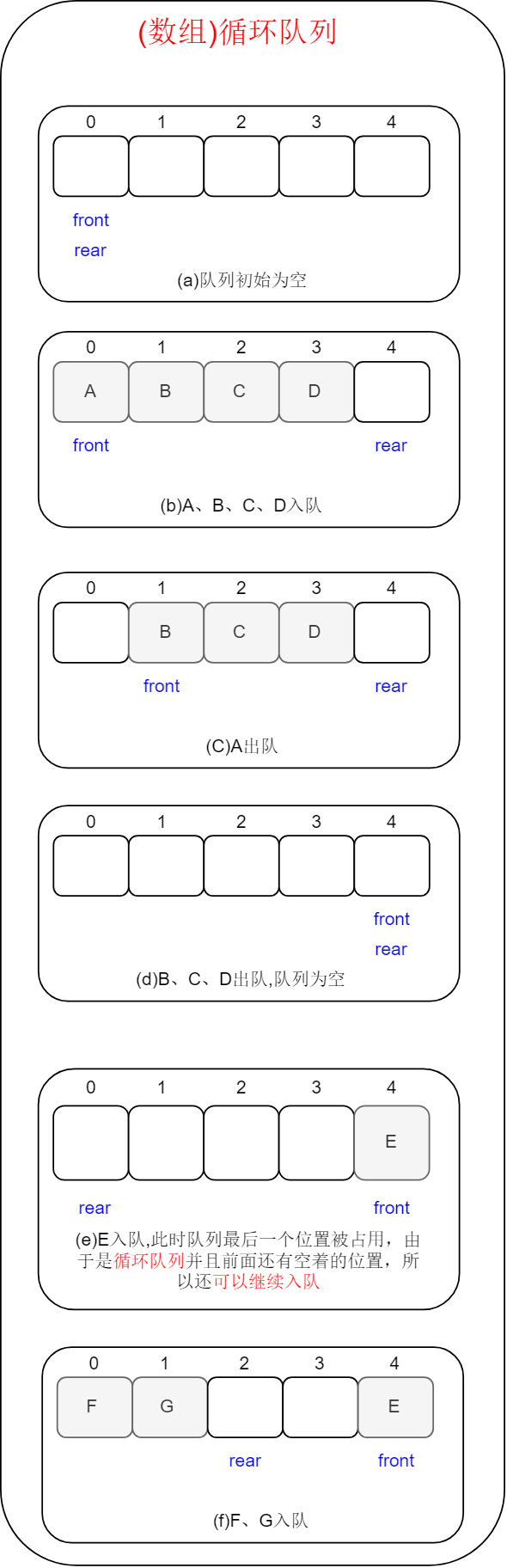
循环队列(主要以图示说明):从队头删除元素,从队尾增加元素。被删除的元素空出来的位置,会被后来增加的元素重复利用。
链表队列:基于链表的原理进行实现。
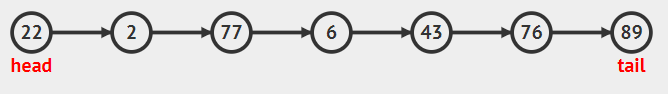
注:可结合上文中的链表实现gif动图进行理解。
Java对上述队列的代码实现(示例):
声明**:**这里只是简单的实现,如果想要了解更全面实现方式的话,推荐阅读各种阻塞非阻塞队列的源码。
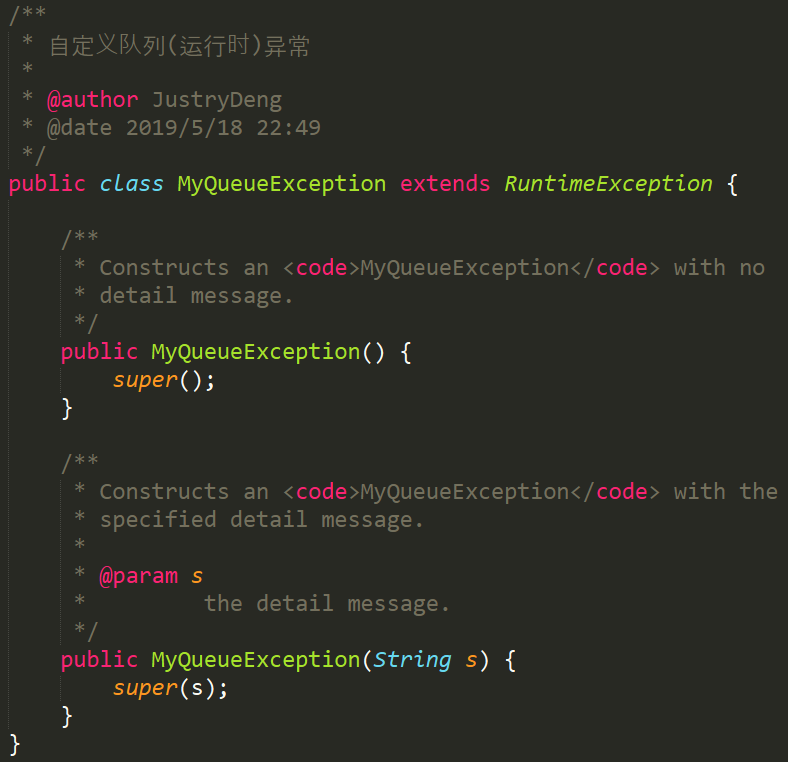
先给出一个下面三个队列实现中都会用到的异常类:
对(数组)顺序队列的(简单)实现:
import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.Arrays;/*** (简单实现)顺序队列** @author JustryDeng* @date 2019/5/18 21:19*/public class SequenceQueue<E> implements Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = -807097163996913371L;/** 元素容器 */private final Object[] items;/** 队列的容量(即:数组的长度) */private int capacity;/** 队头 */private int front;/** 队尾 */private int rear;/*** 构造器** @param capacity* 队列的容量* @date 2019/5/18 21:55*/public SequenceQueue(int capacity) {this.capacity = capacity;items = new Object[capacity];front = 0;rear = 0;}/*** 入队** @param e* 入队的元素* @date 2019/5/18 22:27*/public void offer(E e) {if (e == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("arg must be not null!");}if (rear >= capacity) {throw new MyQueueException("the queue already full!");}items[rear] = e;rear++;}/*** 出队** @return 出队的那个元素* @date 2019/5/18 22:25*/public E poll() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new MyQueueException("the queue is empty!");}// 保留队列的front端的元素的值E oldValue = itemAt(front);// 释放队列的front端的元素items[front] = null;front++;return oldValue;}/*** 返回队列头元素,但不会将该元素出列** @return 队列头元素* @date 2019/5/18 22:07*/public E peek() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new MyQueueException("the queue is empty!");}return itemAt(front);}/*** 返回指定位置处的元素** @param index* 索引位置** @return 返回index位置处的元素* @date 2019/5/18 22:21*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public E itemAt(int index) {return (E) items[index];}/*** 判断队列是否为空队列** @return 是/否* @date 2019/5/18 22:04*/public boolean isEmpty() {return rear == front;}/*** 判断队列是否已满** @return 是/否* @date 2019/5/18 22:04*/public boolean isFull() {return rear >= capacity;}/*** 获取队列的实际有效大小(即:获取队列中元素的个数)** @return 获取当前队列的大小* @date 2019/5/18 21:54*/public int size() {return rear - front;}/*** 清空队列** @date 2019/5/18 22:04*/public void clear() {// 将数组所有元素赋为nullArrays.fill(items, null);// 首尾指针重置front = 0;rear = 0;}@Overridepublic String toString() {if (isEmpty()) {return "[]";} else {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");for (int i = front; i < rear; i++) {sb.append(items[i].toString()).append( ", ");}int len = sb.length();return sb.delete(len - 2, len).append("]").toString();}}/*** 测试一下** @author JustryDeng* @date 2019/5/19 1:14*/public static void main(String[] args) {SequenceQueue<String> queue = new SequenceQueue<>(5);// 入队queue.offer("A");queue.offer("B");queue.offer("C");// 出队(出队后,元素就不在队列中了)System.out.println(queue.poll());System.out.println(queue.poll());// 队列是否为空System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());// 队列中元素个数System.out.println(queue.size());// 获取队列中的头元素(此操作后,该元素仍然在队列中)System.out.println(queue.peek());// 入队queue.offer("D");queue.offer("E");// 队列是否已满System.out.println(queue.isFull());// 验证queue的toString函数System.out.println(queue);// 清空队列queue.clear();queue.offer("F");// 验证queue的toString函数System.out.println(queue);// 队列中元素个数System.out.println(queue.size());}}
注:这里以实现第二种顺序队列为例。
对(数组)循环队列的(简单)实现:
import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.Arrays;/*** (简单实现)循环队列** @author JustryDeng* @date 2019/5/18 18:58*/public class CircleQueue<E> implements Serializable {/** 元素容器 */private final Object[] items;/** 队列的容量(即:数组的长度) */private int capacity;/** 队头 */private int front;/** 队尾 */private int rear;/*** 构造器** @param capacity* 队列的容量* @date 2019/5/18 21:55*/public CircleQueue(int capacity) {this.capacity = capacity;items = new Object[capacity];front = 0;rear = 0;}/*** 入队** @param e* 入队的元素* @date 2019/5/18 22:27*/public void offer(E e) {if (e == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("arg must be not null!");}if (rear - front >= capacity) {throw new MyQueueException("the queue already full!");}int currIndex = rear % capacity;items[currIndex] = e;rear++;}/*** 出队** @return 出队的那个元素* @date 2019/5/18 22:25*/public E poll() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new MyQueueException("the queue is empty!");}int currIndex = front % capacity;E oldValue = itemAt(currIndex);items[currIndex] = null;front++;return oldValue;}/*** 返回队列头元素,但不会将该元素出列** @return 队列头元素* @date 2019/5/18 22:07*/public E peek() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new MyQueueException("the queue is empty!");}return itemAt(front % capacity);}/*** 返回指定位置处的元素** @param index* 索引位置* @return 返回index位置处的元素* @date 2019/5/18 22:21*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public E itemAt(int index) {return (E) items[index];}/*** 判断队列是否为空队列** @return 是/否* @date 2019/5/18 22:04*/public boolean isEmpty() {return rear == front;}/*** 判断队列是否已满** @return 是/否* @date 2019/5/18 22:04*/public boolean isFull() {return rear - front >= capacity;}/*** 获取队列的实际有效大小(即:获取队列中元素的个数)** @return 获取当前队列的大小* @date 2019/5/18 21:54*/public int size() {return rear - front;}/*** 清空队列** @date 2019/5/18 22:04*/public void clear() {// 将数组所有元素赋为nullArrays.fill(items, null);// 首尾指针重置front = 0;rear = 0;}@Overridepublic String toString() {if (isEmpty()) {return "[]";} else {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");int curIndex;for (int i = front; i < rear; i++) {curIndex = i % capacity;sb.append(items[curIndex].toString()).append(", ");}int len = sb.length();return sb.delete(len - 2, len).append("]").toString();}}/*** 测试一下** @author JustryDeng* @date 2019/5/19 1:14*/public static void main(String[] args) {CircleQueue<String> queue = new CircleQueue<>(5);// 入队queue.offer("A");queue.offer("B");queue.offer("C");queue.offer("D");// 出队(出队后,元素就不在队列中了)System.out.println(queue.poll());System.out.println(queue.poll());// 队列是否为空System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());// 队列中元素个数System.out.println(queue.size());// 获取队列中的头元素(此操作后,该元素仍然在队列中)System.out.println(queue.peek());// 入队queue.offer("E");queue.offer("F");queue.offer("G");// 验证queue的toString函数System.out.println(queue);// 队列是否已满System.out.println(queue.isFull());// 清空队列queue.clear();// 验证queue的toString函数System.out.println(queue);// 队列是否已满System.out.println(queue.isFull());}}
对链表队列的(简单)实现:
import java.io.Serializable;/*** (简单实现)链式(链表)队列** @author JustryDeng* @date 2019/5/19 1:32*/public class LinkQueue<E> implements Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 3748038449750184916L;/*** 定义一个内部类Node,Node实例代表链队列的节点** @author JustryDeng* @date 2019/5/19 1:31*/private class Node {/** 此节点的数据 */private E data;/** 指向下个节点的引用 */private Node next;/** 全参构造 */private Node(E data, Node next) {this.data = data;this.next = next;}}/** 头节点 */private Node front;/** 尾节点 */private Node rear;/** 此链式队列中已包含的节点数 */private int size;/*** 空链队列 构造*/public LinkQueue() {front = null;rear = null;size = 0;}/*** 入队** @param e* 入队的元素* @date 2019/5/19 1:36*/public void offer(E e) {// 如果该链队列还是空链队列if (front == null) {if (e == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("arg must be not null!");}front = new Node(e, null);// 只有一个节点,front、rear都指向该节点rear = front;} else {// 创建新节点Node newNode = new Node(e, null);// 让当前尾节点的next指向新增的节点rear.next = newNode;// 更新尾节点引用,以新节点作为新的尾节点rear = newNode;}size++;}/*** 出队** @return 出队的那个元素* @date 2019/5/18 22:25*/public E poll() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new MyQueueException("the queue is empty!");}Node oldFront = front;front = front.next;oldFront.next = null;size--;return oldFront.data;}/*** 返回队列头元素,但不会将该元素出列** @return 队列头元素* @date 2019/5/18 22:07*/public E peek() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new MyQueueException("the queue is empty!");}return front.data;}/*** 判断队列是否为空队列** @return 是/否* @date 2019/5/18 22:04*/public boolean isEmpty() {return size == 0;}/*** 获取此链式队列中已包含的节点数** @return 此链式队列中已包含的节点数* @date 2019/5/19 1:36*/public int size() {return size;}/*** 清空队列** @date 2019/5/18 22:04*/public void clear() {front = null;rear = null;size = 0;}@Overridepublic String toString() {// 链队列为空链队列时if (isEmpty()) {return "[]";} else {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");for (Node current = front; current != null; current = current.next) {sb.append(current.data.toString()).append(", ");}int len = sb.length();return sb.delete(len - 2, len).append("]").toString();}}/*** 测试一下** @author JustryDeng* @date 2019/5/19 1:14*/public static void main(String[] args) {LinkQueue<String> queue = new LinkQueue<>();// 入队queue.offer("A");queue.offer("B");queue.offer("C");// 出队(出队后,元素就不在队列中了)System.out.println(queue.poll());System.out.println(queue.poll());// 队列是否为空queue.offer("D");queue.offer("E");System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());// 队列中元素个数System.out.println(queue.size());// 获取队列中的头元素(此操作后,该元素仍然在队列中)System.out.println(queue.peek());// 入队queue.offer("F");queue.offer("G");// 验证queue的toString函数System.out.println(queue);// 清空队列queue.clear();// 验证queue的toString函数System.out.println(queue);// 队列中元素个数System.out.println(queue.size());}}





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...