Notes on learning RT-Thread——线程应用示例
创建线程
/** 程序清单:创建/删除、初始化线程** 这个例子会创建两个线程,一个动态线程,一个静态线程。* 一个线程在运行完毕后自动被系统删除,另一个线程一直打印计数。*/#include <rtthread.h>#define THREAD_PRIORITY 25#define THREAD_STACK_SIZE 512#define THREAD_TIMESLICE 5static rt_thread_t tid1 = RT_NULL;/* 线程1的入口函数 */static void thread1_entry(void *parameter){rt_uint32_t count = 0;while (1){/* 线程1采用低优先级运行,一直打印计数值 */rt_kprintf("thread1 count: %d\n", count ++);rt_thread_mdelay(500);}}ALIGN(RT_ALIGN_SIZE)static char thread2_stack[1024];static struct rt_thread thread2;/* 线程2入口 */static void thread2_entry(void *param){rt_uint32_t count = 0;/* 线程2拥有较高的优先级,以抢占线程1而获得执行 */for (count = 0; count < 10 ; count++){/* 线程2打印计数值 */rt_kprintf("thread2 count: %d\n", count);}rt_kprintf("thread2 exit\n");/* 线程2运行结束后也将自动被系统删除(线程控制块和线程栈依然在idle线程中释放) */}/* 删除线程示例的初始化 */int thread_sample(void){/* 创建线程1,名称是thread1,入口是thread1_entry*/tid1 = rt_thread_create("thread1",thread1_entry, RT_NULL,THREAD_STACK_SIZE,THREAD_PRIORITY, THREAD_TIMESLICE);/* 如果获得线程控制块,启动这个线程 */if (tid1 != RT_NULL)rt_thread_startup(tid1);/* 初始化线程2,名称是thread2,入口是thread2_entry */rt_thread_init(&thread2,"thread2",thread2_entry,RT_NULL,&thread2_stack[0],sizeof(thread2_stack),THREAD_PRIORITY - 1, THREAD_TIMESLICE);rt_thread_startup(&thread2);return 0;}/* 导出到 msh 命令列表中 */MSH_CMD_EXPORT(thread_sample, thread sample);
功能:创建一个动态线程初始化一个静态线程,一个线程在运行完毕后自动被系统删除,另一个线程一直打印计数
执行效果: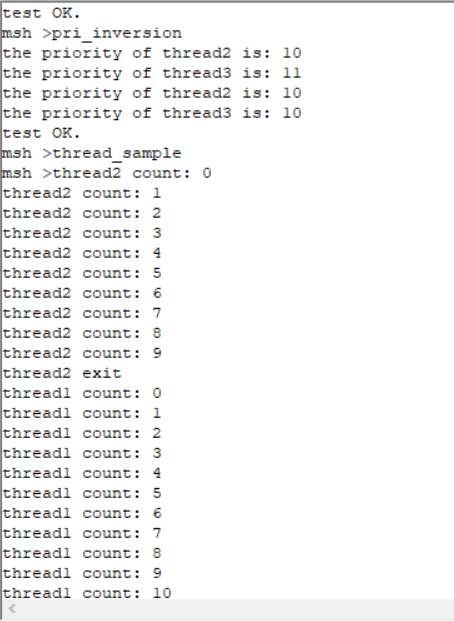 线程2在计10个数之后退出并被系统删除,而线程1一直在计数。
线程2在计10个数之后退出并被系统删除,而线程1一直在计数。
注意事项
关于删除线程:大多数线程是循环执行的,无需删除;而能运行完毕的线程,RT-Thread 在线程运行完毕后,自动删除线程,在 rt_thread_exit() 里完成删除动作。用户只需要了解该接口的作用,不推荐使用该接口(可以由其他线程调用此接口或在定时器超时函数中调用此接口删除一个线程,但是这种使用非常少)。
线程时间片轮转调度示例
/** Copyright (c) 2006-2018, RT-Thread Development Team** SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0** Change Logs:* Date Author Notes* 2018-08-24 yangjie the first version*//** 程序清单:相同优先级线程按照时间片轮番调度** 这个例子中将创建两个线程,每一个线程都在打印信息**/#include <rtthread.h>#define THREAD_STACK_SIZE 1024#define THREAD_PRIORITY 20#define THREAD_TIMESLICE 10/* 线程入口 */static void thread_entry(void* parameter){rt_uint32_t value;rt_uint32_t count = 0;value = (rt_uint32_t)parameter;while (1){if(0 == (count % 5)){rt_kprintf("thread %d is running ,thread %d count = %d\n", value , value , count);if(count > 50)return;}count++;}}int timeslice_sample(void){rt_thread_t tid;/* 创建线程1 */tid = rt_thread_create("thread1",thread_entry, (void*)1,THREAD_STACK_SIZE,THREAD_PRIORITY, THREAD_TIMESLICE);if (tid != RT_NULL)rt_thread_startup(tid);/* 创建线程2 */tid = rt_thread_create("thread2",thread_entry, (void*)2,THREAD_STACK_SIZE,THREAD_PRIORITY, THREAD_TIMESLICE-5);if (tid != RT_NULL)rt_thread_startup(tid);return 0;}/* 导出到 msh 命令列表中 */MSH_CMD_EXPORT(timeslice_sample, timeslice sample);
仿真效果: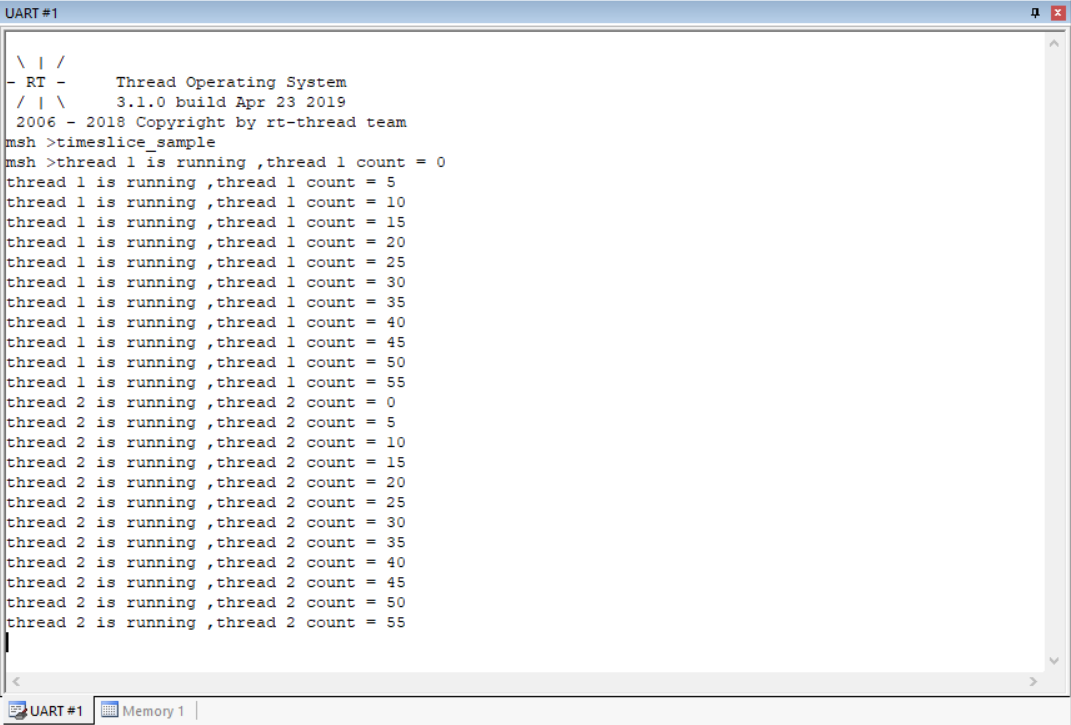 线程2运行的时间是线程1的一半。
线程2运行的时间是线程1的一半。
线程调度器钩子示例
在线程进行调度切换时,会执行调度,我们可以设置一个调度器钩子,这样可以在线程切换时,做一些额外的事情,这个例子是在调度器钩子函数中打印线程间的切换信息,如下代码:
#include <rtthread.h>#define THREAD_STACK_SIZE 1024#define THREAD_PRIORITY 20#define THREAD_TIMESLICE 10/* 针对每个线程的计数器 */volatile rt_uint32_t count[2];/* 线程 1、2 共用一个入口,但入口参数不同 */static void thread_entry(void* parameter){rt_uint32_t value;value = (rt_uint32_t)parameter;while (1){rt_kprintf("thread %d is running\n", value);rt_thread_mdelay(1000); // 延时一段时间}}static rt_thread_t tid1 = RT_NULL;static rt_thread_t tid2 = RT_NULL;static void hook_of_scheduler(struct rt_thread* from, struct rt_thread* to){rt_kprintf("from: %s --> to: %s \n", from->name , to->name);}int scheduler_hook(void){/* 设置调度器钩子 */rt_scheduler_sethook(hook_of_scheduler);/* 创建线程 1 */tid1 = rt_thread_create("thread1",thread_entry, (void*)1,THREAD_STACK_SIZE,THREAD_PRIORITY, THREAD_TIMESLICE);if (tid1 != RT_NULL)rt_thread_startup(tid1);/* 创建线程 2 */tid2 = rt_thread_create("thread2",thread_entry, (void*)2,THREAD_STACK_SIZE,THREAD_PRIORITY,THREAD_TIMESLICE - 5);if (tid2 != RT_NULL)rt_thread_startup(tid2);return 0;}/* 导出到 msh 命令列表中 */MSH_CMD_EXPORT(scheduler_hook, scheduler_hook sample);
仿真效果:
 由仿真的结果可以看出,对线程进行切换时,设置的调度器钩子函数是在正常工作的,一直在打印线程切换的信息,包含切换到空闲线程。
由仿真的结果可以看出,对线程进行切换时,设置的调度器钩子函数是在正常工作的,一直在打印线程切换的信息,包含切换到空闲线程。































还没有评论,来说两句吧...