C++STL 常用算法
转自
[url]http://www.cnblogs.com/BeyondAnyTime/archive/2012/05/27/2520532.html\[/url\]
[align=center][size=medium][color=red][b]一、非变异算法[/b][/color][/size][/align]
是一组不破坏操作数据的模板函数,用来对序列数据进行逐个处理、元素查找、子序列搜索、统计和匹配。非变异算法具有极为广泛的适用性,基本上可应用与各种容器。
[size=medium][color=red][b]1. 查找容器元素 - find[/b][/color][/size]
[i][b]函数功能:[/b][/i]
它用于查找等于某值的元素。它在迭代器区间[first,last)(闭开区间)上查找等于value值的元素,如果迭代器i所指的元素满足*i=value,则返回迭代器i;未找到满足条件的元素,返回last。
[i][b]函数原型:[/b][/i]
#include <algorithm>template <class InputIterator, class T>InputIterator find (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const T& val);
[i][b]输入参数:[/b][/i]
[b]first, last[/b]
输入查询序列的开始和结束位置,注意:这两个参数为迭代器。
[b]val[/b]
要查询的值
[i][b]返回值:[/b][/i]
返回查询结果的迭代器
[i][b]实例:[/b][/i]
#include <vector>#include <algorithm>#include <iostream>using namespace std;void main(){//为vecIntegers添加数据vector<int> vecIntegers;for (int nNum=0; nNum<10;++nNum){vecIntegers.push_back(nNum);}//打印数据vector<int>::const_iterator iElementLocator;for (iElementLocator=vecIntegers.begin(); iElementLocator != vecIntegers.end(); ++iElementLocator){cout << *iElementLocator << ' ';}cout << endl;/*****************关键代码******************************///查找数字 3//注意:返回值为迭代器vector<int>::iterator iElementFound;iElementFound = find(vecIntegers.begin(), vecIntegers.end(), 3);if (iElementFound != vecIntegers.end()) //如果找到结果{cout << *iElementFound << endl;}else{cout << "没有找到结果!" << endl;}/****************************************************/}0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 93Press any key to continue
[size=medium][color=red][b]2. 条件查找容器元素 - find_if[/b][/color][/size]
利用返回布尔值的谓词判断pred,检查迭代器区间[first,last)(闭开区间)上的每一个元素,如果迭代器i满足pred(*i)=true,表示找到元素并返回迭代值i(找到的第一个符合条件的元素);未找到元素,返回末位置last。
函数原型:find_if(v.begin(),v.end(),divby5);#include <vector>#include <algorithm>#include <iostream>using namespace std;bool divby5(int x){return x%5 ? 0:1;}void main(){vector<int> v(20);for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++){v[i] = (i+1)*(i+3);cout << v[i] << ' ';}cout << endl;vector<int>::iterator ilocation;ilocation = find_if(v.begin(),v.end(),divby5);if(ilocation != v.end()){cout << "找到第一个能被5整除的元素:" << *ilocation << endl<< "元素的索引位置是: " << ilocation-v.begin() << endl;}}3 8 15 24 35 48 63 80 99 120 143 168 195 224 255 288 323 360 399 440找到第一个能被5整除的元素:15元素的索引位置是:2Press any key to continue
[size=medium][color=red][b]3. 统计等于某值的容器元素个数 - count[/b][/color][/size]
[i][b]函数原型:[/b][/i]
template<class InputIterator, class T>inlinesize_t count(InputIterator First,InputIterator Last,const T& Value)#include <iostream>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <string>#include <vector>void main(){using namespace std;const int VECTOR_SIZE = 8 ;// Define a template class vector of stringstypedef vector<string > StringVector ;//Define an iterator for template class vector of stringstypedef StringVector::iterator StringVectorIt ;StringVector NamesVect(VECTOR_SIZE) ; //vector containing namesstring value("Sea") ; // stores the value used// to count matching elementsStringVectorIt start, end, it ;ptrdiff_t result = 0 ; // stores count of elements// that match value.// Initialize vector NamesVectNamesVect[0] = "She" ;NamesVect[1] = "Sells" ;NamesVect[2] = "Sea" ;NamesVect[3] = "Shells" ;NamesVect[4] = "by" ;NamesVect[5] = "the" ;NamesVect[6] = "Sea" ;NamesVect[7] = "Shore" ;start = NamesVect.begin() ; // location of first// element of NamesVectend = NamesVect.end() ; // one past the location// last element of NamesVect// print content of NamesVectcout << "NamesVect { " ;for(it = start; it != end; it++){cout << *it << " " ;}cout << " }\n" << endl ;// Count the number of elements in the range [first, last +1)// that match value.result = count(start, end, value) ;// print the count of elements that match valuecout << "Number of elements that match \"Sea\" = "<< result << endl ;}NamesVect {She Sells Sea Shells by the Sea Shore}Number of elements that match "Sea" = 2Press any key to continue
[size=medium][color=red][b]4. 条件统计 - count_if[/b][/color][/size]
count_if(l.begin(),l.end(),pred)
谓词pred含义同find_if中的谓词。例子可以参考例2.
[i][b]函数原型:[/b][/i]
template<class _InIt, class _Pr>inlinetypename iterator_traits<_InIt>::difference_typecount_if(_InIt _First, _InIt _Last, _Pr _Pred);
[i][b]示例:[/b][/i]
#include <iostream>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <string>#include <vector>using namespace std;// Return true if string str starts with letter 'S'int MatchFirstChar( const string& str){string s("S") ;return s == str.substr(0,1) ;}void main(){const int VECTOR_SIZE = 8 ;// Define a template class vector of stringstypedef vector<string > StringVector ;//Define an iterator for template class vector of stringstypedef StringVector::iterator StringVectorIt ;StringVector NamesVect(VECTOR_SIZE) ; //vector containing namesStringVectorIt start, end, it ;ptrdiff_t result = 0 ; // stores count of elements// that match value.// Initialize vector NamesVectNamesVect[0] = "She" ;NamesVect[1] = "Sells" ;NamesVect[2] = "Sea" ;NamesVect[3] = "Shells" ;NamesVect[4] = "by" ;NamesVect[5] = "the" ;NamesVect[6] = "Sea" ;NamesVect[7] = "Shore" ;start = NamesVect.begin() ; // location of first// element of NamesVectend = NamesVect.end() ; // one past the location// last element of NamesVect// print content of NamesVectcout << "NamesVect { " ;for(it = start; it != end; it++)cout << *it << " " ;cout << " }\n" << endl ;// Count the number of elements in the range [first, last +1)// that start with letter 'S'result = count_if(start, end, MatchFirstChar) ;// print the count of elements that start with letter 'S'cout << "Number of elements that start with letter \"S\" = "<< result << endl ;}NamesVect {She Sells Sea Shells by the Sea Shore}Number of elements that start with letter "S" = 6Press any key to continue
[color=red][b]5. 子序列搜索 - search[/b][/color]
search算法函数在一个序列中搜索与另一序列匹配的子序列。参数分别为一个序列的开始位置,结束位置和另一个序列的开始,结束位置。
函数原型:search(v1.begin(),v1.end(),v2.begin(),v2.end());#include <vector>#include <algorithm>#include <iostream>using namespace std;void main(){vector<int> v1;cout << "v1:";for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){v1.push_back(i+5);//注意:v1定义时没有给定大小,因此这里不能直接使用赋值语句。cout<<v1[i]<<' ';}cout << endl;vector<int> v2;cout << "v2:";for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++){v2.push_back(i+7);cout << v2[i] << ' ';}cout << endl;vector<int>::iterator ilocation;ilocation = search(v1.begin(),v1.end(),v2.begin(),v2.end());if (ilocation != v1.end()){cout << "v2的元素包含在v1中,起始元素为" << "v1[" << ilocation-v1.begin() << ']' << endl;}else{cout << "v2的元素不包含在v1中" << endl;}}v1: 5 6 7 8 9v2: 7 8v2的元素包含在v1中,起始元素为v1[2]
[color=red][b]6重复元素子序列搜索search_n[/b][/color]
search_n算法函数搜索序列中是否有一系列元素值均为某个给定值的子序列。
函数原型:search_n(v.begin(),v.end(),3,8),
在v中找到3个连续的元素8
#include <vector>#include <algorithm>#include <iostream>using namespace std;void main(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(8);v.push_back(8);v.push_back(8);v.push_back(6);v.push_back(6);v.push_back(8);vector<int>::iterator i;i = search_n(v.begin(),v.end(),3,8);if (i != v.end()){cout<<"在v中找到3个连续的元素8"<<endl;}else{cout<<"在v中未找到3个连续的元素8"<<endl;}}在v中找到3个连续的元素8
[color=red][b]7最后一个子序列搜索find_end[/b][/color]
函数原型find_end(v1.begin(),v1.end(),v2.begin(),v2.end());
在V1中要求的位置查找V2中要求的序列。
#include <vector>#include <algorithm>#include <iostream>using namespace std;void main(){vector<int> v1;v1.push_back(-5);v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(-6);v1.push_back(-8);v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(-11);vector<int> v2;v2.push_back(1);v2.push_back(2);vector<int>::iterator i;i = find_end(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end());if (i != v1.end()){cout << "v1中找到最后一个匹配v2的子序列,位置在" << "v1[" << i-v1.begin() << "]" << endl;}}"v1中找到最后一个匹配v2的子序列,位置在v1[5]
[align=center][size=medium][color=red][b]二、变异算法[/b][/color][/size][/align]
是一组能够修改容器元素数据的模板函数。copy(v.begin(),v.end(),l.begin());将v中的元素复制到l中。
[color=red][b]1元素复制copy[/b][/color]
#include <vector>#include <list>#include <algorithm>#include <iostream>using namespace std;void main(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(5);list<int> l;l.push_back(2);l.push_back(4);l.push_back(6);l.push_back(8);l.push_back(10);copy(v.begin(),v.end(),l.begin());list<int>::iterator i;for(i=l.begin();i!=l.end();i++)cout<<*i<<' ';cout<<endl;}
[color=red][b]2元素变换transform改变[/b][/color]
函数原型:transform(v.begin(),v.end(),l.begin(),square);
也是复制,但是要按某种方案复制。
#include <vector>#include <list>#include <algorithm>#include <iostream>using namespace std;int square(int x){return x*x;}void main(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(5);v.push_back(15);v.push_back(25);list<int> l(3);transform(v.begin(),v.end(),l.begin(),square);list<int>::iterator i;for(i=l.begin();i!=l.end();i++)cout<<*i<<' ';cout<<endl;}
[color=red][b]3替换replace[/b][/color]
replace算法将指定元素值替换为新值。
#include <vector>#include <algorithm>#include <iostream>using namespace std;void main(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(13);v.push_back(25);v.push_back(27);v.push_back(25);v.push_back(29);replace(v.begin(),v.end(),25,100);vector<int>::iterator i;for(i=v.begin();i!=v.end();i++)cout<<*i<<' ';cout<<endl;}13 100 27 100 29
[color=red][b]4条件替换replace_if[/b][/color]
函数原型:replace_if(v.begin(),v.end(),odd,100);#include <vector>#include <algorithm>#include <iostream>using namespace std;bool odd(int x){return x%2;}void main(){vector<int> v;for(int i=1;i<10;i++)v.push_back(i);replace_if(v.begin(),v.end(),odd,100);vector<int>::iterator ilocation;for(ilocation=v.begin();ilocation!=v.end();ilocation++)cout<<*ilocation<<' ';cout<<endl;}
[color=red][b]5n次填充fill_n[/b][/color]
函数原型fill_n(v.begin(),5,-1);向从v.begin开始的后面5个位置跳入-1
#include <vector>#include <algorithm>#include <iostream>using namespace std;void main(){vector<int> v(10);fill_n(v.begin(),5,-1);vector<int>::iterator ilocation;for(ilocation=v.begin();ilocation!=v.end();ilocation++)cout<<*ilocation<<' ';cout<<endl;}输出结果:-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 0 0 0 0 0
6随机生成n个元素generate
函数原型:generate_n(v.begin(),5,rand);向从v.begin开始的后面5个位置随机填写数据。
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void main()
{
vector
generate_n(v.begin(),5,rand);
vector
for(ilocation=v.begin();ilocation!=v.end();ilocation++)
cout<<*ilocation<<’ ‘;
cout<<endl;
}
7条件移除remove_if
返回值相当于移除满足条件的元素后形成的新向量的end()值。
函数原型:remove_if(v.begin(),v.end(),even);
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
bool even(int x)
{
return x%2?0:1;
}
void main()
{
vector
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++)
v.push_back(i);
vector
cout<<”移除前:”;
for(ilocation=v.begin();ilocation!=v.end();ilocation++)
cout<<*ilocation<<’ ‘;
cout<<endl;
result=remove_if(v.begin(),v.end(),even);
cout<<”移除后:”;
for(ilocation=v.begin();ilocation!=result;ilocation++)
cout<<*ilocation<<’ ‘;
cout<<endl;
}
8剔除连续重复元素unique
函数原型:unique(v.begin(),v.end());
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void main()
{
vector
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(6);
v.push_back(6);
v.push_back(6);
v.push_back(9);
v.push_back(6);
v.push_back(3);
vector
result=unique(v.begin(),v.end());
for(ilocation=v.begin();ilocation!=result;ilocation++)
cout<<*ilocation<<’ ‘;
cout<<endl;
}
输出结果:2 6 9 6 3
[align=center][size=medium][color=red][b]三、排序算法[/b][/color][/size][/align]
[b]1、创建堆make_heap[/b]
[b]2、元素入堆push_heap(默认插入最后一个元素)[/b]
[b]3、元素出堆pop_heap(与push_heap一样,pop_heap必须对堆操作才有意义)[/b]
#include <vector>#include <algorithm>#include <iostream>using namespace std;void main(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(5);v.push_back(6);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(8);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(7);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(9);make_heap(v.begin(), v.end());v.push_back(20);push_heap(v.begin(), v.end());vector<int>::iterator ilocation;for(ilocation = v.begin(); ilocation != v.end(); ilocation++){cout << *ilocation << ' ';}cout << endl;pop_heap(v.begin(), v.end());for (ilocation = v.begin(); ilocation != v.end(); ilocation++){cout << *ilocation << ' ';}cout << endl;}20 9 7 6 8 3 4 1 5 29 8 7 6 2 3 4 1 5 20
[size=medium][color=red][b]4. 堆排序 - sort_heap[/b][/color][/size]
使用:
make_heap(v.begin(),v.end());sort_heap(v.begin(),v.end());#include <vector>#include <algorithm>#include <iostream>using namespace std;void main(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(3);v.push_back(9);v.push_back(6);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(17);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(12);vector<int>::iterator ilocation;for (ilocation = v.begin(); ilocation != v.end(); ilocation++){cout << *ilocation << ' ';}cout << endl;make_heap(v.begin(),v.end());sort_heap(v.begin(),v.end());for (ilocation = v.begin(); ilocation != v.end(); ilocation++){cout << *ilocation << ' ';}cout << endl;}3 9 6 3 17 20 123 3 6 9 12 17 20
[size=medium][color=red][b]5. 排序 - sort[/b][/color][/size]
sort详细解释参考link[url]http://www.cppblog.com/mzty/archive/2005/12/15/1770.html\[/url\]
[i][b]函数说明:[/b][/i]
这个函数可以传两个参数或三个参数。第一个参数是要排序的区间首地址,第二个参数是区间 尾地址的下一地址。也就是说,排序的区间是[a,b)。简单来说,有一个数组int a[100],要对从a[0]到a[99]的元素进行排序,只要写sort(a,a+100)就行了,默认的排序方式是升序。
[i][b]函数原型:[/b][/i]
template<class RanIt>void sort(RanIt fist, RanIt last);template<class RanIt, class Pred>void sort(RanIt fist, RanIt last, Pred pr);#include <vector>#include <algorithm>#include <iostream>using namespace std;void main(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(2);v.push_back(8);v.push_back(-15);v.push_back(90);v.push_back(26);v.push_back(7);v.push_back(23);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(-27);v.push_back(39);v.push_back(55);vector<int>::iterator ilocation;for (ilocation = v.begin(); ilocation != v.end(); ilocation++){cout << *ilocation << ' ';}cout << endl;sort(v.begin(), v.end());//比较函数默认for (ilocation = v.begin(); ilocation != v.end(); ilocation++){cout << *ilocation << ' ';}cout << endl;}2 8 -15 90 26 7 23 30 -27 39 55-27 -15 2 7 8 23 26 30 39 55 90




























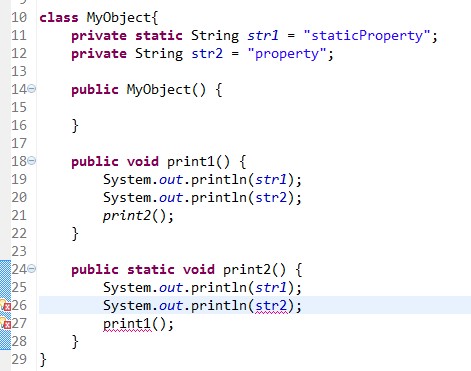




还没有评论,来说两句吧...