Lombok使用示例详情
简介
Lombok是一个可以通过注解来帮助我们简化消除一些必须有但显得很臃肿的Java代码的一种工具,通过使用对应的注解,可以在编译源码的时候动态添加源码。
例如在实体中经常见到一堆Getter和Setter方法,这些方法是必要的不可缺少的,但是这些代码感觉却像是“垃圾”,看起来重复而臃肿,看起来也不美观,也不简洁清爽,可以使用lombok,在类上直接使用@Getter @Setter 这两个注解,那么代码在编译的时候会自动帮你生成这个类下的所有字段对应的Getter和Setter方法,实体中只有一些属性,看起来实体类变得简洁很多,虽然IDE可以很快的生成出来,但是生成之后的实体还是那么的臃肿,而且如果修改了字段的名称或者字段的类型还要重新生成,比较麻烦,使用Lombok就是消除一些含金量不高却必须要有的代码,使程序员看起来代码更加简洁、清爽。
Automatic Resource Management, automatic generation of getters, setters, equals, hashCode and toString, and more!
lombok的官方地址:https://projectlombok.org/
lombok的Github地址:https://github.com/rzwitserloot/lombok
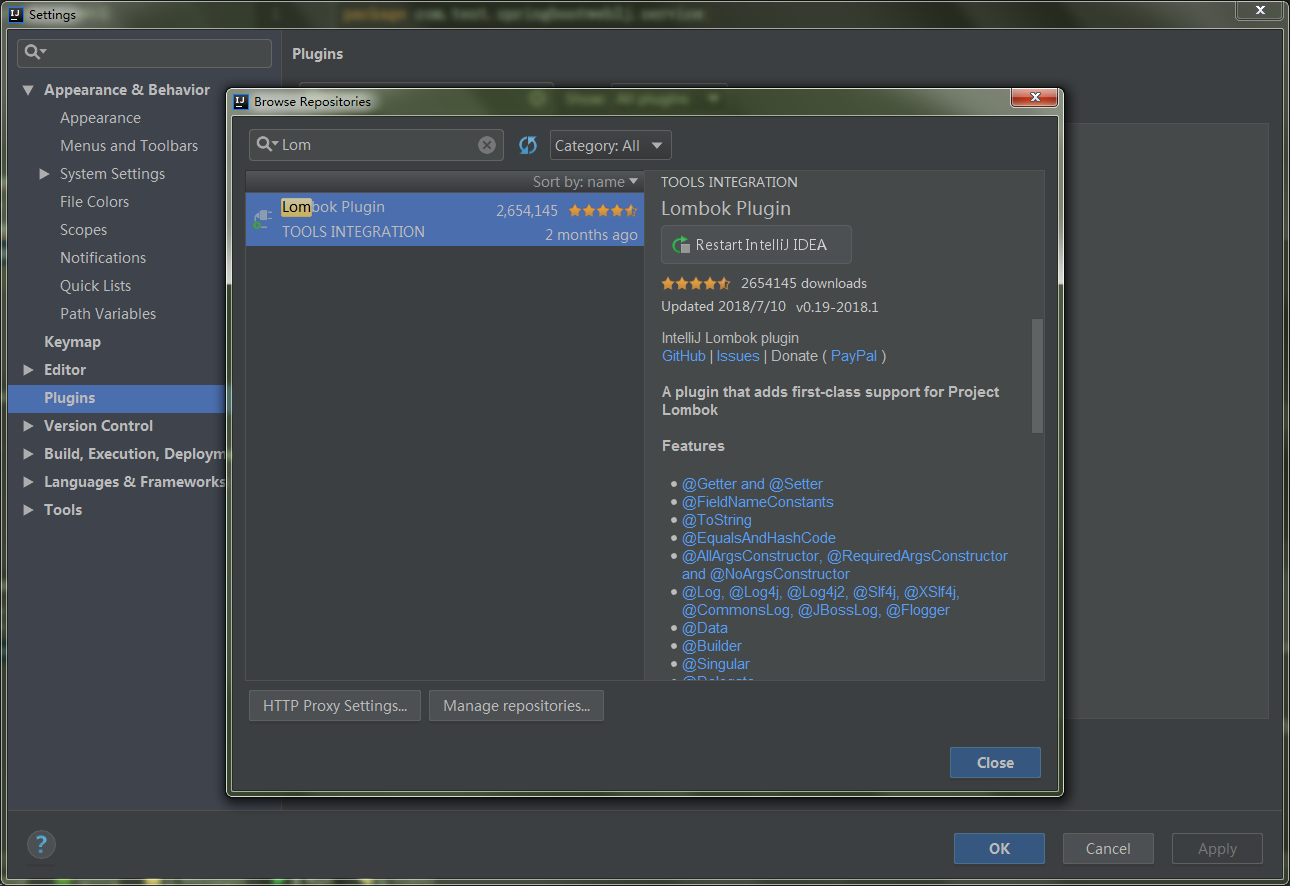
Lombok plugin 插件
Intellij idea 使用Lombok需要安装插件:Lombok plugin: Preferences —> Plugins —> 搜索 Lombok plugin — > Install
同时设置 Preferences -> Compiler -> Annotation Processors -> Enable annotation processing勾选。
使用示例
首先引入lombok依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.projectlombok/lombok --><dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId><version>1.16.20</version><scope>provided</scope></dependency>
1. @Getter/@Setter
为字段生成Getter和Setter方法,可以注解到字段或者类上(注解在类上会为类中的所有字段生成Getter和Setter方法),默认是public类型的,如果需要的话可以修改方法的访问级别。
public class User {@Getter @Setterprivate Long id;@Getter(AccessLevel.PROTECTED)private String phone;private String password;}
编译后的代码:
public class User {private Long id;private String phone;private String password;public User() {}public Long getId() {return this.id;}public void setId(Long id) {this.id = id;}protected String getPhone() {return this.phone;}}
结果解释:
id字段生成了Getter&Setter,访问修饰符是public
phone只生成了Getter方法,因为只使用了@Getter而没有使用@Setter, 并且访问修饰符是protected
password 上并没有注解,所以什么都不生成
注意:Lombok中的注解一般都会包含一个无参构造函数注解@NoArgsConstructor(用于生成无参构造函数的) ,所以还会额外生成一个无参构造函数
@Getter @Setter 注解在类上,表示为类中的所有字段生成Getter&Setter方法。
@Getter @Setterpublic class User {private Long id;private String phone;private String password;}public class User {private Long id;private String phone;private String password;public User() {}public Long getId() {return this.id;}public String getPhone() {return this.phone;}public String getPassword() {return this.password;}public void setId(Long id) {this.id = id;}public void setPhone(String phone) {this.phone = phone;}public void setPassword(String password) {this.password = password;}}
2. @NonNull
为字段赋值时(即调用字段的setter方法时),如果传的参数为null,则会抛出空异常NullPointerException,生成setter方法时会对参数是否为空检查
@Getter@Setterpublic class User {private Long id;@NonNullprivate String phone;}public class User {private Long id;@NonNullprivate String phone;public User() {}public Long getId() {return this.id;}public void setId(Long id) {this.id = id;}@NonNullpublic String getPhone() {return this.phone;}public void setPhone(@NonNull String phone) {if(phone == null) {throw new NullPointerException("phone");} else {this.phone = phone;}}}
3. @NoArgsConstructor
生成一个无参构造方法。当类中有final字段没有被初始化时,编译器会报错,此时可用@NoArgsConstructor(force = true),然后就会为没有初始化的final字段设置默认值 0 / false / null, 这样编译器就不会报错。对于具有约束的字段(例如@NonNull字段),不会生成检查或分配,因此请注意,正确初始化这些字段之前,这些约束无效。
@NoArgsConstructor(force = true)public class User {private Long id;@NonNullprivate String phone;private final Integer age;}public class User {private Long id;@NonNullprivate String phone;private final Integer age = null;public User() {}}
4. @RequiredArgsConstructor
生成构造方法(可能带参数也可能不带参数),如果带参数,这参数只能是以final修饰的未经初始化的字段,或者是以@NonNull注解的未经初始化的字段。
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = “of”)会生成一个of()的静态方法,并把构造方法设置为私有的
@RequiredArgsConstructorpublic class User {private Long id;@NonNullprivate String phone;@NotNullprivate Integer status = 0;private final Integer age;private final String country = "china";}public class User {private Long id;@NonNullprivate String phone;@NotNullprivate Integer status = Integer.valueOf(0);private final Integer age;private final String country = "china";public User(@NonNull String phone, Integer age) {if(phone == null) {throw new NullPointerException("phone");} else {this.phone = phone;this.age = age;}}}
必要的构造函数只会生成final修饰的未经初始化的字段或者是以@NonNull注解的未经初始化的字段, 所以生成了public User(@NonNull String phone, Integer age)构造函数
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "of")public class User {private Long id;@NonNullprivate String phone;@NotNullprivate Integer status = 0;private final Integer age;private final String country = "china";}public class User {private Long id;@NonNullprivate String phone;@NotNullprivate Integer status = Integer.valueOf(0);private final Integer age;private final String country = "china";private User(@NonNull String phone, Integer age) {if(phone == null) {throw new NullPointerException("phone");} else {this.phone = phone;this.age = age;}}public static User of(@NonNull String phone, Integer age) {return new User(phone, age);}}
5. @AllArgsConstructor
生成一个全参数的构造方法
@AllArgsConstructorpublic class User {private Long id;@NonNullprivate String phone;@NotNullprivate Integer status = 0;private final Integer age;private final String country = "china";}public class User {private Long id;@NonNullprivate String phone;@NotNullprivate Integer status = Integer.valueOf(0);private final Integer age;private final String country = "china";public User(Long id, @NonNull String phone, Integer status, Integer age) {if(phone == null) {throw new NullPointerException("phone");} else {this.id = id;this.phone = phone;this.status = status;this.age = age;}}}
6. @ToString
生成toString()方法,默认情况下它会按顺序(以逗号分隔)打印你的类名称以及每个字段。可以这样设置不包含哪些字段,可以指定一个也可以指定多个@ToString(exclude = “id”) / @ToString(exclude = {“id”,”name”})
如果继承的有父类的话,可以设置callSuper 让其调用父类的toString()方法,例如:@ToString(callSuper = true)
@ToString(exclude = {"password", "salt"})public class User {private Long id;private String phone;private String password;private String salt;}public class User {private Long id;private String phone;private String password;private String salt;public User() {}public String toString() {return "User(id=" + this.id + ", phone=" + this.phone + ")";}}@ToString(exclude = {"password", "salt"}, callSuper = true)public class User {private Long id;private String phone;private String password;private String salt;}public class User {private Long id;private String phone;private String password;private String salt;public User() {}public String toString() {return "User(super=" + super.toString() + ", id=" + this.id + ", phone=" + this.phone + ")";}}
7. @EqualsAndHashCode
生成hashCode()和equals()方法,默认情况下,它将使用所有非静态,非transient字段。但可以通过在可选的exclude参数中来排除更多字段。或者,通过在of参数中命名它们来准确指定希望使用哪些字段。
// exclude 排除字段
@EqualsAndHashCode(exclude = {“password”, “salt”})
// of 指定要包含的字段
@EqualsAndHashCode(of = {“id”, “phone”, “password”})
@EqualsAndHashCodepublic class User implements Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 6569081236403751407L;private Long id;private String phone;private transient int status;}public class User implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 6569081236403751407L;private Long id;private String phone;private transient int status;public User() {}public boolean equals(Object o) {if(o == this) {return true;} else if(!(o instanceof User)) {return false;} else {User other = (User)o;if(!other.canEqual(this)) {return false;} else {Long this$id = this.id;Long other$id = other.id;if(this$id == null) {if(other$id != null) {return false;}} else if(!this$id.equals(other$id)) {return false;}String this$phone = this.phone;String other$phone = other.phone;if(this$phone == null) {if(other$phone != null) {return false;}} else if(!this$phone.equals(other$phone)) {return false;}return true;}}}protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {return other instanceof User;}public int hashCode() {boolean PRIME = true;byte result = 1;Long $id = this.id;int result1 = result * 59 + ($id == null?43:$id.hashCode());String $phone = this.phone;result1 = result1 * 59 + ($phone == null?43:$phone.hashCode());return result1;}}
生成了 equals 、hashCode 和 canEqual 无参构造函数 四个方法
8. @Data
@Data 包含了 @ToString、@EqualsAndHashCode、@Getter / @Setter和@RequiredArgsConstructor的功能
@Datapublic class User {private Long id;private String phone;private Integer status;}public class User {private Long id;private String phone;private Integer status;public User() {}public Long getId() {return this.id;}public String getPhone() {return this.phone;}public Integer getStatus() {return this.status;}public void setId(Long id) {this.id = id;}public void setPhone(String phone) {this.phone = phone;}public void setStatus(Integer status) {this.status = status;}public boolean equals(Object o) {if(o == this) {return true;} else if(!(o instanceof User)) {return false;} else {User other = (User)o;if(!other.canEqual(this)) {return false;} else {label47: {Long this$id = this.getId();Long other$id = other.getId();if(this$id == null) {if(other$id == null) {break label47;}} else if(this$id.equals(other$id)) {break label47;}return false;}String this$phone = this.getPhone();String other$phone = other.getPhone();if(this$phone == null) {if(other$phone != null) {return false;}} else if(!this$phone.equals(other$phone)) {return false;}Integer this$status = this.getStatus();Integer other$status = other.getStatus();if(this$status == null) {if(other$status != null) {return false;}} else if(!this$status.equals(other$status)) {return false;}return true;}}}protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {return other instanceof User;}public int hashCode() {boolean PRIME = true;byte result = 1;Long $id = this.getId();int result1 = result * 59 + ($id == null?43:$id.hashCode());String $phone = this.getPhone();result1 = result1 * 59 + ($phone == null?43:$phone.hashCode());Integer $status = this.getStatus();result1 = result1 * 59 + ($status == null?43:$status.hashCode());return result1;}public String toString() {return "User(id=" + this.getId() + ", phone=" + this.getPhone() + ", status=" + this.getStatus() + ")";}}
9. @Value
@Value 将字段都变成不可变类型:使用final修饰, 同时还包含@ToString、@EqualsAndHashCode、@AllArgsConstructor 、@Getter(注意只有Getter没有Setter)
@Valuepublic class User {private Long id;private String username;}public final class User {private final Long id;private final String username;public User(Long id, String username) {this.id = id;this.username = username;}public Long getId() {return this.id;}public String getUsername() {return this.username;}public boolean equals(Object o) {if(o == this) {return true;} else if(!(o instanceof User)) {return false;} else {User other = (User)o;Long this$id = this.getId();Long other$id = other.getId();if(this$id == null) {if(other$id != null) {return false;}} else if(!this$id.equals(other$id)) {return false;}String this$username = this.getUsername();String other$username = other.getUsername();if(this$username == null) {if(other$username != null) {return false;}} else if(!this$username.equals(other$username)) {return false;}return true;}}public int hashCode() {boolean PRIME = true;byte result = 1;Long $id = this.getId();int result1 = result * 59 + ($id == null?43:$id.hashCode());String $username = this.getUsername();result1 = result1 * 59 + ($username == null?43:$username.hashCode());return result1;}public String toString() {return "User(id=" + this.getId() + ", username=" + this.getUsername() + ")";}}
10. @Log
生成log对象,用于记录日志,可以通过topic属性来设置getLogger(String name)方法的参数 例如 @Log4j(topic = “com.xxx.entity.User”),默认是类的全限定名,即 类名.class,log支持以下几种:
- @Log java.util.logging.Logger
- @Log4j org.apache.log4j.Logger
- @Log4j2 org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger
- @Slf4j org.slf4j.Logger
- @XSlf4j org.slf4j.ext.XLogger
- @CommonsLog org.apache.commons.logging.Log
@JBossLog org.jboss.logging.Logger
@Log
private static final java.util.logging.Logger log = java.util.logging.Logger.getLogger(LogExample.class.getName());
@Log4j
private static final Logger log = org.apache.log4j.Logger.Logger.getLogger(UserService.class);
@Log4j2
private static final org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger log = org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager.getLogger(LogExample.class);
@Slf4j
private static final org.slf4j.Logger log = org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogExample.class);
@XSlf4j
private static final org.slf4j.ext.XLogger log = org.slf4j.ext.XLoggerFactory.getXLogger(LogExample.class);
@CommonsLog
private static final org.apache.commons.logging.Log log = org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory.getLog(LogExample.class);
@JBossLog
private static final org.jboss.logging.Logger log = org.jboss.logging.Logger.getLogger(LogExample.class);
@Log
public class UserService {public void addUser(){log.info("add user");}
}
import java.util.logging.Logger;public class UserService {private static final Logger log = Logger.getLogger(UserService.class.getName());public UserService() {}}
11. @SneakyThrows
使用try catch 来捕获异常, 默认捕获的是Throwable异常,也可以设置要捕获的异常
public class User {@SneakyThrowspublic void sleep(){Thread.sleep(1000);}@SneakyThrows(InterruptedException.class)public void sleep2() {Thread.sleep(1000);}}public class User {public User() {}public void sleep() {try {Thread.sleep(1000L);} catch (Throwable var2) {throw var2;}}public void sleep2() {try {Thread.sleep(1000L);} catch (InterruptedException var2) {throw var2;}}public static void main(String[] args) {}}
12. @Synchronized
给方法加上同步锁
public class User {private final Object readLock = new Object();@Synchronizedpublic static void foo(){System.out.println();}@Synchronizedpublic void bar(){System.out.println();}@Synchronized("readLock")public void test() {System.out.println();}}public class User {private static final Object $LOCK = new Object[0];private final Object $lock = new Object[0];private final Object readLock = new Object();public User() {}public static void foo() {Object var0 = $LOCK;synchronized($LOCK) {System.out.println();}}public void bar() {Object var1 = this.$lock;synchronized(this.$lock) {System.out.println();}}public void test() {Object var1 = this.readLock;synchronized(this.readLock) {System.out.println();}}}
13. @Cleanup
主要用来修饰 IO 流相关类, 会在 finally 代码块中对该资源进行 close();
public class CleanupExample {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {@Cleanup InputStream in = new FileInputStream(args[0]);@Cleanup OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(args[1]);byte[] b = new byte[10000];while (true) {int r = in.read(b);if (r == -1) break;out.write(b, 0, r);}}}public class CleanupExample {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {InputStream in = new FileInputStream(args[0]);try {OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(args[1]);try {byte[] b = new byte[10000];while (true) {int r = in.read(b);if (r == -1) break;out.write(b, 0, r);}} finally {if (out != null) {out.close();}}} finally {if (in != null) {in.close();}}}}
14. @Getter(lazy = true)
@Getter(lazy = true)
标注字段为懒加载字段,懒加载字段在创建对象时不会进行初始化,而是在第一次访问的时候才会初始化,后面再次访问也不会重复初始化
public class User {private final List<String> cityList = getCityFromCache();private List<String> getCityFromCache() {System.out.println("get city from cache ...");return new ArrayList<>();}}public static void main(String[] args) {User user = new User(); // 出事化对象时会会执行getCityFromCache()方法}public class User {@Getter(lazy = true)private final List<String> cityList = getCityFromCache();private List<String> getCityFromCache() {System.out.println("get city from cache ...");return new ArrayList<>();}}public class User {private final AtomicReference<Object> cityList = new AtomicReference();public User() {}private List<String> getCityFromCache() {System.out.println("get city from cache ...");return new ArrayList();}public List<String> getCityList() {Object value = this.cityList.get();if(value == null) {AtomicReference var2 = this.cityList;synchronized(this.cityList) {value = this.cityList.get();if(value == null) {List actualValue = this.getCityFromCache();value = actualValue == null?this.cityList:actualValue;this.cityList.set(value);}}}return (List)((List)(value == this.cityList?null:value));}}
@Getter(lazy = true):为懒加载字段生成一个Getter方法
public static void main(String[] args) {User user = new User(); // 创建对象时不会初始化懒加载的字段List<String> cityList = user.getCityList(); // 只有第一次访问属性时才会去初始化cityList = user.getCityList(); // 第二次就不会再次初始化了}
15. @Wither
提供了给final字段赋值的一种方法
public class User {@Witherprivate final String country;public User(String country) {this.country = country;}}public class User {private final String country;public User(String country) {this.country = country;}public User withCountry(String country) {return this.country == country?this:new User(country);}}
16. @Builder
@Builder注释为你的类生成复杂的构建器API。
@Builderpublic class User {private Long id;private String phone;}public class User {private Long id;private String phone;User(Long id, String phone) {this.id = id;this.phone = phone;}public static User.UserBuilder builder() {return new User.UserBuilder();}public static class UserBuilder {private Long id;private String phone;UserBuilder() {}public User.UserBuilder id(Long id) {this.id = id;return this;}public User.UserBuilder phone(String phone) {this.phone = phone;return this;}public User build() {return new User(this.id, this.phone);}public String toString() {return "User.UserBuilder(id=" + this.id + ", phone=" + this.phone + ")";}}}
17. @Delegate
为List类型的字段生成一大堆常用的方法,其实这些方法都是List中的方法
注意:一个类中只能使用一个@Delegate注解,因为使用多个会生成多个size()方法,从而会编译报错。
public class User {@Delegateprivate List<String> address;}public class User {private List<String> address;public User() {}public int size() {return this.address.size();}public boolean isEmpty() {return this.address.isEmpty();}public boolean contains(Object arg0) {return this.address.contains(arg0);}public Iterator<String> iterator() {return this.address.iterator();}public Object[] toArray() {return this.address.toArray();}public <T> T[] toArray(T[] arg0) {return this.address.toArray(arg0);}public boolean add(String arg0) {return this.address.add(arg0);}public boolean remove(Object arg0) {return this.address.remove(arg0);}public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> arg0) {return this.address.containsAll(arg0);}public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends String> arg0) {return this.address.addAll(arg0);}public boolean addAll(int arg0, Collection<? extends String> arg1) {return this.address.addAll(arg0, arg1);}public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> arg0) {return this.address.removeAll(arg0);}public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> arg0) {return this.address.retainAll(arg0);}public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<String> arg0) {this.address.replaceAll(arg0);}public void sort(Comparator<? super String> arg0) {this.address.sort(arg0);}public void clear() {this.address.clear();}public String get(int arg0) {return (String)this.address.get(arg0);}public String set(int arg0, String arg1) {return (String)this.address.set(arg0, arg1);}public void add(int arg0, String arg1) {this.address.add(arg0, arg1);}public String remove(int arg0) {return (String)this.address.remove(arg0);}public int indexOf(Object arg0) {return this.address.indexOf(arg0);}public int lastIndexOf(Object arg0) {return this.address.lastIndexOf(arg0);}public ListIterator<String> listIterator() {return this.address.listIterator();}public ListIterator<String> listIterator(int arg0) {return this.address.listIterator(arg0);}public List<String> subList(int arg0, int arg1) {return this.address.subList(arg0, arg1);}public Spliterator<String> spliterator() {return this.address.spliterator();}}
lombok.config
lombok.config配置文件是通过一些设置来控制代码生成的规则或者称之为习惯,配置文件的位置应放在src/mian/java,不要放置在src/main/resources。
注意配置文件和要使用注解的类要在同一套代码中,要么同时在src/main/java 要么同时在 src/test/java中
lombok.config
#lombok 默认对boolean类型字段生成的get方法使用is前缀, 通过此配置则使用get前缀,默认: falselombok.getter.noIsPrefix=true#默认的set方法返回void设置为true返回调用对象本身,这样方便使用链式来继续调用方法,默认: falselombok.accessors.chain=true#如果设置为true get和set方法将不带get,set前缀, 直接以字段名为方法名, 默认: falselombok.accessors.fluent=true#设置log类注解返回的字段名称,默认: loglombok.log.fieldName=logger@Log4j@Getter @Setterpublic class User {private String username;private boolean vip;private boolean isOldUser;}public class User {private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(User.class);private String username;private boolean vip;private boolean isOldUser;public User() {}public String username() {return this.username;}public boolean vip() {return this.vip;}public boolean isOldUser() {return this.isOldUser;}public User username(String username) {this.username = username;return this;}public User vip(boolean vip) {this.vip = vip;return this;}public User isOldUser(boolean isOldUser) {this.isOldUser = isOldUser;return this;}}


































还没有评论,来说两句吧...