Spring Boot——RabbitMQ
转载自https://blog.csdn.net/lyhkmm/article/details/78772919
RabbitMq的介绍
RabbitMq的基本原理可以自行上网查阅,或者点击传送门:RabbitMQ的基本原理。
使用配置
1、老规矩,先在pom.xml中添加相关依赖:
<!--消息队列模块--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId></dependency>
2、在application.properties添加rabbitmq的相关信息:
spring.application.name=spirng-boot-rabbitmqspring.rabbitmq.host=127.0.0.1spring.rabbitmq.port=5672spring.rabbitmq.username=guestspring.rabbitmq.password=guest
端口、用户名和密码都是默认的,根据自己的实际情况配置,rabbitmq的安装教程网上很多了,这里暂时不介绍,以后有时间补上。
3、配置队列:
package com.lyh.demo;import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** @Author:linyuanhuang* @Description:队列配置,队列的名称,发送者和接受者的名称必须一致,否则接收不到消息* @Date:2017/12/11 14:50*/@Configurationpublic class RabbitMqConfig {@Beanpublic Queue Queue1() {return new Queue("lyhTest1");}}
4、发送者通过Controller类发送消息:
package com.lyh.demo.controller;import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import java.util.Date;@RestControllerpublic class SendController {@Autowiredprivate AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate;@RequestMapping("/send")public String send(){String content="Date:"+new Date();amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("lyhTest1",content);return content;}}
5、创建接受者Receiver1,新建类:
package com.lyh.demo.Receiver;import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component@RabbitListener(queues = "lyhTest1")public class Receiver1 {@RabbitHandlerpublic void receiver(String msg){System.out.println("Test1 receiver1:"+msg);}}
6、测试
浏览器访问地址:http://localhost:8080/send,如下图:
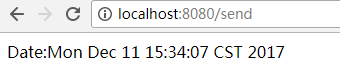
终端输出接受的内容:
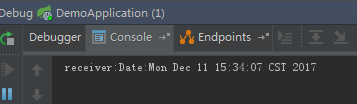
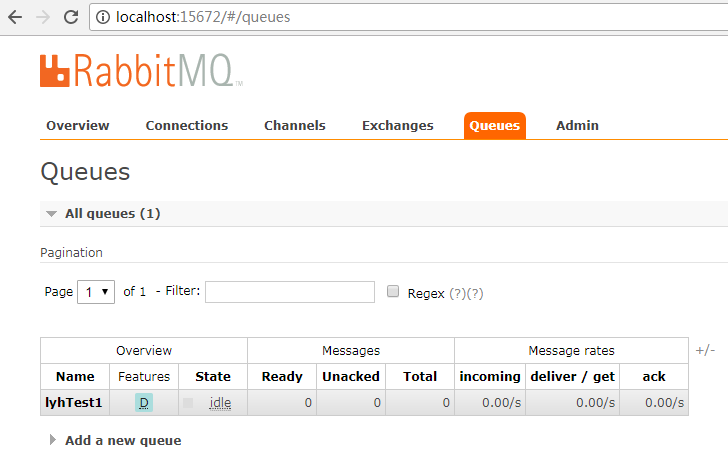
查看RabbitMQ的Web客户端http://localhost:15672,需要自己安装RabbitMQ的客户端,可以自己上网查阅相关教程。帐号密码和配置文件一样,如下图:可以在列表里看到之前创建的队列。
一对多的使用配置
1、一对多,一个发送者发送消息,多个接受者接受同一个消息,添加新的接收者Receiver2:
package com.lyh.demo.Receiver;import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component@RabbitListener(queues = "lyhTest1")public class Receiver2 {@RabbitHandlerpublic void receiver(String msg){System.out.println("Test1 receiver2:"+msg);}}
2、发送者循环发送10个消息,在SendController添加一对多发送方法:
@RequestMapping("/multiSend")public String multiSend(){StringBuilder times=new StringBuilder();for(int i=0;i<10;i++){long time=System.nanoTime();amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("lyhTest1","第"+i+"次发送的时间:"+time);times.append(time+"<br>");}return times.toString();}
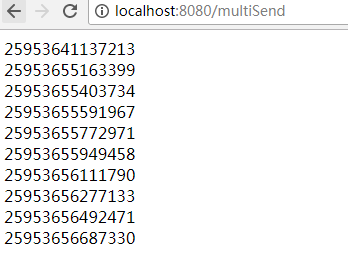
3、测试,浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/multiSend,如下图:
4、终端输出接收数据:
Test1 receiver2:第1次发送的时间:25953655163399Test1 receiver1:第0次发送的时间:25953641137213Test1 receiver2:第2次发送的时间:25953655403734Test1 receiver1:第3次发送的时间:25953655591967Test1 receiver1:第5次发送的时间:25953655949458Test1 receiver2:第4次发送的时间:25953655772971Test1 receiver1:第6次发送的时间:25953656111790Test1 receiver1:第8次发送的时间:25953656492471Test1 receiver1:第9次发送的时间:25953656687330Test1 receiver2:第7次发送的时间:25953656277133
可以看到发送者发送一个消息被多个接收者接收,注意这里的消息只能被消费一次
多对多的使用配置
1、在配置类RabbbitMqConfig添加新的队列名lyhTest2:
@Configurationpublic class RabbitMqConfig {@Beanpublic Queue Queue1() {return new Queue("lyhTest1");}@Beanpublic Queue Queue2() {return new Queue("lyhTest2");}}
2、修改Receiver2接收队列名为lyhTest2:
@Component@RabbitListener(queues = "lyhTest2")//这里的lyhTest2是多对多,如果要测试一对多改成lyhTest1public class Receiver2 {@RabbitHandlerpublic void receiver(String msg){System.out.println("Test2 receiver2:"+msg);}}
3、在SendController添加多对多发送消息的方法:
@RequestMapping("/multi2MultiSend")public String mutil2MutilSend(){StringBuilder times=new StringBuilder();for(int i=0;i<10;i++){long time=System.nanoTime();amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("lyhTest1","第"+i+"次发送的时间:"+time);amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("lyhTest2","第"+i+"次发送的时间:"+time);times.append(time+"<br>");}return times.toString();}
4、测试,浏览器访问:http://localhost:8080/multi2MultiSend,如下图:
5、终端输出接收数据:
Test1 receiver1:第0次发送的时间:27607875773748Test2 receiver2:第0次发送的时间:27607875773748Test2 receiver2:第1次发送的时间:27607882272138Test2 receiver2:第2次发送的时间:27607882429049Test1 receiver1:第1次发送的时间:27607882272138Test2 receiver2:第3次发送的时间:27607882594693Test1 receiver1:第2次发送的时间:27607882429049Test2 receiver2:第4次发送的时间:27607882897371Test1 receiver1:第3次发送的时间:27607882594693Test2 receiver2:第5次发送的时间:27607883163005Test1 receiver1:第4次发送的时间:27607882897371Test2 receiver2:第6次发送的时间:27607883319916Test2 receiver2:第7次发送的时间:27607883489777Test1 receiver1:第5次发送的时间:27607883163005Test1 receiver1:第6次发送的时间:27607883319916Test2 receiver2:第8次发送的时间:27607883957798Test2 receiver2:第9次发送的时间:27607884305953Test1 receiver1:第7次发送的时间:27607883489777Test1 receiver1:第8次发送的时间:27607883957798Test1 receiver1:第9次发送的时间:27607884305953可以看到不同的接收者接收不同发送者发送的消息,消息也可以是实体对象,这里就不做演示。
Topic Exchange的使用配置
Topic Exchange是RabbitMQ中最灵活的一种方式,它能够根据routing_key自由的绑定不同的队列,可以适用绝大部分的项目需求
1、新建RabbitMqTopicConfig配置类:
package com.lyh.demo;import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** @Author:linyuanhuang* @Description:Topic Exchange配置类* @Date:2017/12/11 17:13*/@Configurationpublic class {//只接一个topicfinal static String message = "topic.message";//接收多个topicfinal static String messages = "topic.messages";@Beanpublic Queue queueMessage() {return new Queue(RabbitMqTopicConfig.message);}@Beanpublic Queue queueMessages() {return new Queue(RabbitMqTopicConfig.messages);}@BeanTopicExchange exchange() {return new TopicExchange("exchange");}@BeanBinding bindingExchangeMessage(Queue queueMessage, TopicExchange exchange) {return BindingBuilder.bind(queueMessage).to(exchange).with("topic.message");}@BeanBinding bindingExchangeMessages(Queue queueMessages, TopicExchange exchange) {//这里的#表示零个或多个词。return BindingBuilder.bind(queueMessages).to(exchange).with("topic.#");}
2、在SendController添加发送消息方法:
@RequestMapping("/topicSend1")public String topicSend1() {String context = "my topic 1";System.out.println("发送者说 : " + context);this.amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange", "topic.message", context);return context;}@RequestMapping("/topicSend2")public String topicSend2() {String context = "my topic 2";System.out.println("发送者说 : " + context);this.amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange", "topic.messages", context);return context;
3、创建接收者的方法TopicReceiver1和TopicReceiver2:
TopicReceiver1:
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.message")public class TopicReceiver1 {@RabbitHandlerpublic void process(String msg) {System.out.println("TopicReceiver1:" + msg);}}TopicReceiver2:import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.messages")public class TopicReceiver2 {@RabbitHandlerpublic void process(String msg) {System.out.println("TopicReceiver2 :" + msg);}
4、测试:
浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/topicSend1,终端输出:
发送者说 : my topic 1TopicReceiver1:my topic 1TopicReceiver2 :my topic 1
浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/topicSend2,终端输出:
发送者说 : my topic 2TopicReceiver2 :my topic 25、总结:
这里的Topic Exchange 转发消息主要是根据通配符,队列topic.message只能匹配topic.message的路由。而topic.messages匹配路由规则是topic.#,所以它可以匹配topic.开头的全部路由。而topic.#发送的消息也只能是topic.#的接受者才能接收。
GitHub地址:https://github.com/lyhkmm/spring-boot-examples/tree/master/spring-boot-rabbitmq


























还没有评论,来说两句吧...