RabbitMQ五种消息队列学习(六)--通配符模式(路由类型:Topic)
RabbitMQ五种消息队列学习(六)–通配符模式(路由类型:Topic)
标签(空格分隔): RabbitMQ
正如上一篇文章中所描述的一种模式的升级,如果需要监听某个交换机的所有消息的话,可以通过消息队列的形式进行绑定。
队列结构图
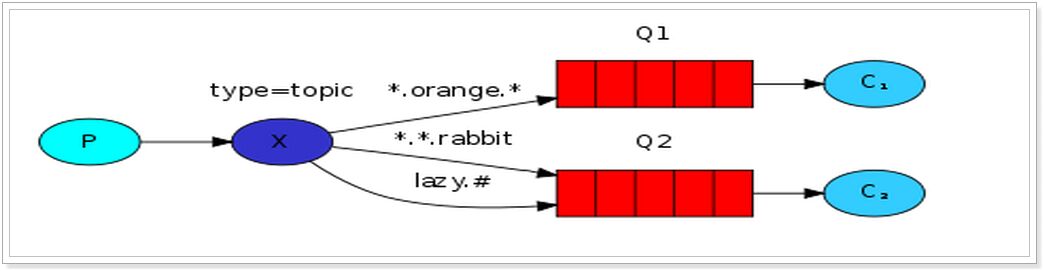
通过字符串通配符的模式匹配需要分发的消息队列
消息路径: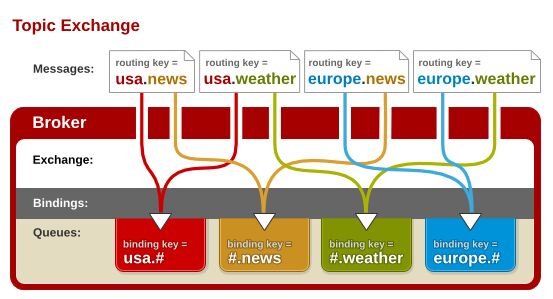
实现:
1、生产者
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_topic";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {// 获取到连接以及mq通道Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();Channel channel = connection.createChannel();// 声明exchangechannel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic");// 消息内容String message = "删除商品 id = 1000";channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, "item.delete", null, message.getBytes());System.out.println(" [x] Sent '" + message + "'");channel.close();connection.close();}
2、消费者1
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_topic_1";private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_topic";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {// 获取到连接以及mq通道Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();Channel channel = connection.createChannel();// 声明队列channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);// 绑定队列到交换机channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "item.update");channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "item.delete");// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者channel.basicQos(1);// 定义队列的消费者QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);// 监听队列,手动返回完成channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, consumer);// 获取消息while (true) {QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();String message = new String(delivery.getBody());System.out.println(" [x] Received '" + message + "'");Thread.sleep(10);channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);}}
3、消费者2
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_topic_2";private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_topic";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {// 获取到连接以及mq通道Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();Channel channel = connection.createChannel();// 声明队列channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);// 绑定队列到交换机channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "item.#");// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者channel.basicQos(1);// 定义队列的消费者QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);// 监听队列,手动返回完成channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, consumer);// 获取消息while (true) {QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();String message = new String(delivery.getBody());System.out.println(" [x] Received '" + message + "'");Thread.sleep(10);channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);}}
4、测试结果
消费者1中,明确了队列需要绑定路由器的哪些Routing Key
// 绑定队列到交换机channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "item.update");channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "item.delete");
消费者2,因为要接收item下的所有消息,所以绑定为:
// 绑定队列到交换机channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "item.#");
所有消费者2可以接收所有消息,消费者1只能接受 update\delete两种消息





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...