SpringMVC 学习笔记(二) @RequestMapping、@PathVariable等注解
1.1. @RequestMapping映射请求
SpringMVC 使用 @RequestMapping 注解为控制器指定可以处理那些URL 请求
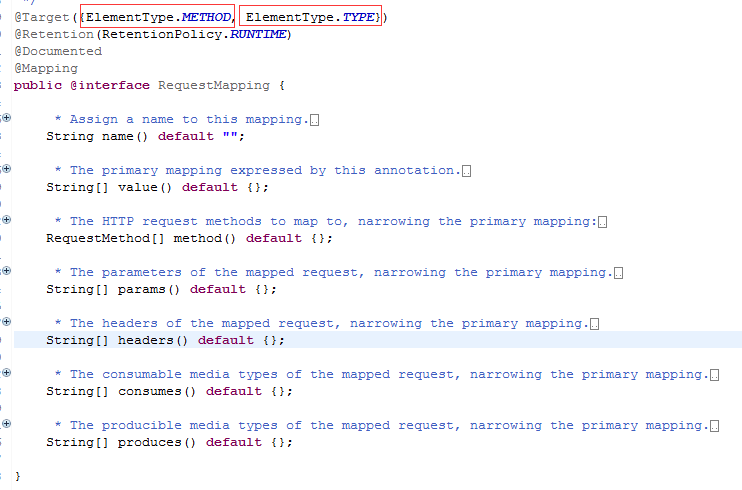
@requestMapping 可以定义在 类 和 方法 上
- package com.ibigsea.springmvc.helloworld;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
- @Controller
- public class HelloWorld {
- /**
- * 配置@RequestMapping 拦截 localhost:8080/springmvc/hello 请求
- * @return
- */
- @RequestMapping(“/hello”)
- public String helloWorld() {
- System.out.println(“hello world”);
- return “helloworld”;
- }
}
package com.ibigsea.springmvc.helloworld;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@Controller
public class HelloWorld {/*** 配置@RequestMapping 拦截 localhost:8080/springmvc/hello 请求* @return*/@RequestMapping("/hello")public String helloWorld() {System.out.println("hello world");return "helloworld";}
}
- package com.ibigsea.springmvc.helloworld;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
- @Controller
- @RequestMapping(“/hello”)
- public class HelloWorld {
- /**
- * 配置@RequestMapping 拦截 localhost:8080/springmvc/hello/world 请求
- * @return
- */
- @RequestMapping(“/world”)
- public String helloWorld(){
- System.out.println(“hello world”);
- return “helloworld”;
- }
}
package com.ibigsea.springmvc.helloworld;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@Controller
@RequestMapping(“/hello”)
public class HelloWorld {/*** 配置@RequestMapping 拦截 localhost:8080/springmvc/hello/world 请求* @return*/@RequestMapping("/world")public String helloWorld(){System.out.println("hello world");return "helloworld";}
}
@RequestMapping
– 类定义处:提供初步的请求映射信息。相对于 WEB 应用的根目录
– 方法处:提供进一步的细分映射信息。相对于类定义处的 URL。若
类定义处未标注 @RequestMapping,则方法处标记的 URL 相对于
WEB 应用的根目录
DispatcherServlet 截获请求后,就通过控制器上
@RequestMapping 提供的映射信息确定请求所对应的处理方法。
@RequestMapping 除了可以使用请求 URL 映射请求外,
还可以使用请求方法、请求参数及请求头映射请求
1.2. @RequestMapping限定请求方法、请求参数、请求头
- /**
- * 接收GET请求
- * @return
- */
- @RequestMapping(value=”/get”,method = RequestMethod.GET)
- public String get(){
- System.out.println(“get”);
- return “get”;
- }
- /**
- * 接收POST请求
- * @return
- */
- @RequestMapping(value=”/post”,method = RequestMethod.POST)
- public String post(){
- System.out.println(“post”);
- return “post”;
- }
- /**
- * 只接收 name 参数
- * @return
- */
- @RequestMapping(value=”/params”,params=”name”)
- public String params(String name){
- System.out.println(“hello “+name);
- return “helloworld”;
- }
- /**
- * 只接收请求头中 Content-Type 为 text/html;charset=UTF-8的请求
- * @return
- */
- @RequestMapping(value=”/headers”,headers=”Content-Type:text/html;charset=UTF-8”)
- public String headers(){
- System.out.println(“headers”);
- return “helloworld”;
}
/**
- 接收GET请求
- @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value=”/get”,method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String get(){
System.out.println(“get”);
return “get”;
}
/**
- 接收POST请求
- @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value=”/post”,method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String post(){
System.out.println(“post”);
return “post”;
}
/**
- 只接收 name 参数
- @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value=”/params”,params=”name”)
public String params(String name){
System.out.println(“hello “+name);
return “helloworld”;
}
/**
- 只接收请求头中 Content-Type 为 text/html;charset=UTF-8的请求
- @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value=”/headers”,headers=”Content-Type:text/html;charset=UTF-8”)
public String headers(){
System.out.println(“headers”);
return “helloworld”;
}
1.3. @RequestMapping匹配符
– ?:匹配文件名中的一个字符
– *:匹配文件名中的任意字符
– **:** 匹配多层路径
实例:
URL : /user/*/create
-- /user/bigsea/create 、 /user/sea/create 等URL
URL : /user/**/create
-- /user/big/sea/create 、 /user/sea/big/create 等URL
URL : /user/create??
-- /user/createaa 、/user/createbb
1.4. @PathVariable 注解
带占位符的 URL 是 Spring3.0 新增的功能,该功能在SpringMVC 向 REST 目标挺进发展过程中具有里程碑的意义
通过 @PathVariable 可以将 URL 中占位符参数绑定到控制器处理方法的入参中:URL 中的 {xxx} 占位符可以通过@PathVariable(“xxx”) 绑定到操作方法的入参中。
[java] view plain copy
print ?
- /**
- * localhost:8080/springmvc/hello/pathVariable/bigsea
- * localhost:8080/springmvc/hello/pathVariable/sea
- * 这些URL 都会 执行此方法 并且将 bigsea、sea 作为参数 传递到name字段
- * @param name
- * @return
- */
- @RequestMapping(“/pathVariable/{name}“)
- public String pathVariable(@PathVariable(“name”)String name){
- System.out.println(“hello “+name);
- return “helloworld”;
}
/**
- localhost:8080/springmvc/hello/pathVariable/bigsea
- localhost:8080/springmvc/hello/pathVariable/sea
- 这些URL 都会 执行此方法 并且将 bigsea、sea 作为参数 传递到name字段
- @param name
- @return
*/
@RequestMapping(“/pathVariable/{name}”)
public String pathVariable(@PathVariable(“name”)String name){
System.out.println(“hello “+name);
return “helloworld”;
}
JSP(这里指定全路径):
pathVariable
- name is bigsea
- name is sea
pathVariable
name is bigsea
name is sea
运行结果:
- hello bigsea
hello sea
hello bigsea
hello sea

1.5. @RequestParam 绑定请求参数
在处理方法入参处使用 @RequestParam 可以把请求参数传递给请求方法
– value:参数名
– required:是否必须。默认为 true, 表示请求参数中必须包含对应的参数,若不存在,将抛出异常
- /**
- * 如果 required = true 则表示请求参数对应的 字段 必须存在.如果不存在则会抛出异常
- * @param firstName 可以为null
- * @param lastName 不能为null .为null报异常
- * @param age age字段表示如果没有 age 参数 则默认值为 0
- * @return
- */
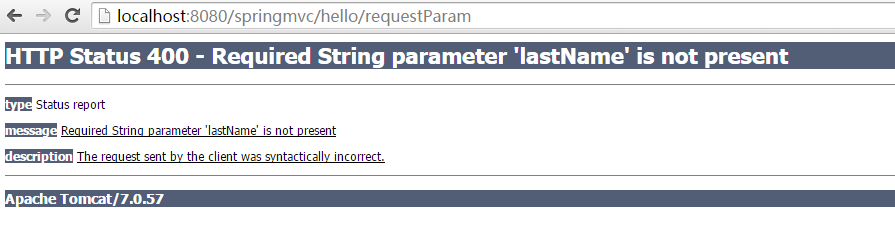
- @RequestMapping(“/requestParam”)
- public String requestParam(@RequestParam(value=”firstName”,required=false)String firstName,
- @RequestParam( value=”lastName” ,required = true) String lastName,
- @RequestParam(value=”age”,required = false ,defaultValue=”0”)int age) {
- System.out.println(“hello my name is “ + (firstName == null ? “” : firstName)
- lastName + “,” + age +” years old this year”);
- return “helloworld”;
}
/**
- 如果 required = true 则表示请求参数对应的 字段 必须存在.如果不存在则会抛出异常
- @param firstName 可以为null
- @param lastName 不能为null .为null报异常
- @param age age字段表示如果没有 age 参数 则默认值为 0
- @return
*/
@RequestMapping(“/requestParam”)
public String requestParam(@RequestParam(value=”firstName”,required=false)String firstName,
System.out.println(“hello my name is “ + (firstName == null ? “” : firstName)@RequestParam( value="lastName" ,required = true) String lastName,@RequestParam(value="age",required = false ,defaultValue="0")int age) {
return “helloworld”;+ lastName + "," + age +" years old this year");
}
- 如果 required = true 则表示请求参数对应的 字段 必须存在.如果不存在则会抛出异常
Jsp:
[java] view plain copy
print ?
- name is bigsea , age is 0
- name is sea , age is 23
-
name is bigsea , age is 0
name is sea , age is 23
throws exception
运行结果:
- hello my name is bigsea,0 years old this year
hello my name is sea,23 years old this year
hello my name is bigsea,0 years old this year
hello my name is sea,23 years old this year
1.6. @RequestHeader 获取请求头
请求头包含了若干个属性,服务器可据此获知客户端的信息,通过 @RequestHeader 即可将求头中的属性值绑定到处理方法的入参中
[java] view plain copy
print ?
- /**
- * 获取请求头中的信息
- * @RequestHeader 也有 value ,required ,defaultValue 三个参数
- * @param userAgent
- * @param cookie
- * @return
- */
- @RequestMapping(“/requestHeader”)
- public String requestHeader(@RequestHeader(“User-Agent”)String userAgent,@RequestHeader(“Cookie”)String cookie){
- System.out.println(“userAgent:[“+userAgent+”]“);
- System.out.println(“cookie:[“+cookie+”]“);
- return “helloworld”;
}
/**
* 获取请求头中的信息* @RequestHeader 也有 value ,required ,defaultValue 三个参数* @param userAgent* @param cookie* @return*/@RequestMapping("/requestHeader")public String requestHeader(@RequestHeader("User-Agent")String userAgent,@RequestHeader("Cookie")String cookie){System.out.println("userAgent:["+userAgent+"]");System.out.println("cookie:["+cookie+"]");return "helloworld";}
JSP:
运行结果:
- userAgent:[Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/44.0.2383.0 Safari/537.36]
cookie:[JSESSIONID=DA3B15F559349EA2C3F08BE772FCAFD8]
userAgent:[Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/44.0.2383.0 Safari/537.36]
cookie:[JSESSIONID=DA3B15F559349EA2C3F08BE772FCAFD8]
1.7. @CookieValue 获取 cookie值
- /**
- * 使用@CookieValue 绑定cookie值
- * 注解@CookieValue 也有 value ,required ,defaultValue 三个参数
- * @param session
- * @return
- */
- public String cookieValue(@CookieValue(value = “JSESSIONID”, required= false)String session){
- System.out.println(“JESSIONID:[“+session+”]“);
- return “helloworld”;
}
/**
- 使用@CookieValue 绑定cookie值
- 注解@CookieValue 也有 value ,required ,defaultValue 三个参数
- @param session
- @return
*/
public String cookieValue(@CookieValue(value = “JSESSIONID”, required= false)String session){
System.out.println(“JESSIONID:[“+session+”]”);
return “helloworld”;
}
- 使用@CookieValue 绑定cookie值
JSP:
[java] view plain copy
print ?
运行结果
JESSIONID:[A4196EEDFD829B40CC1975F029A61328]
JESSIONID:[A4196EEDFD829B40CC1975F029A61328]
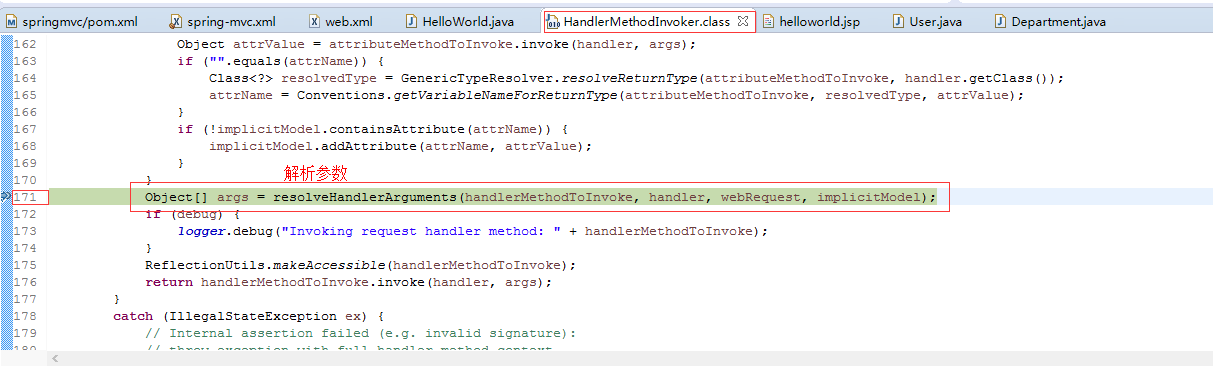
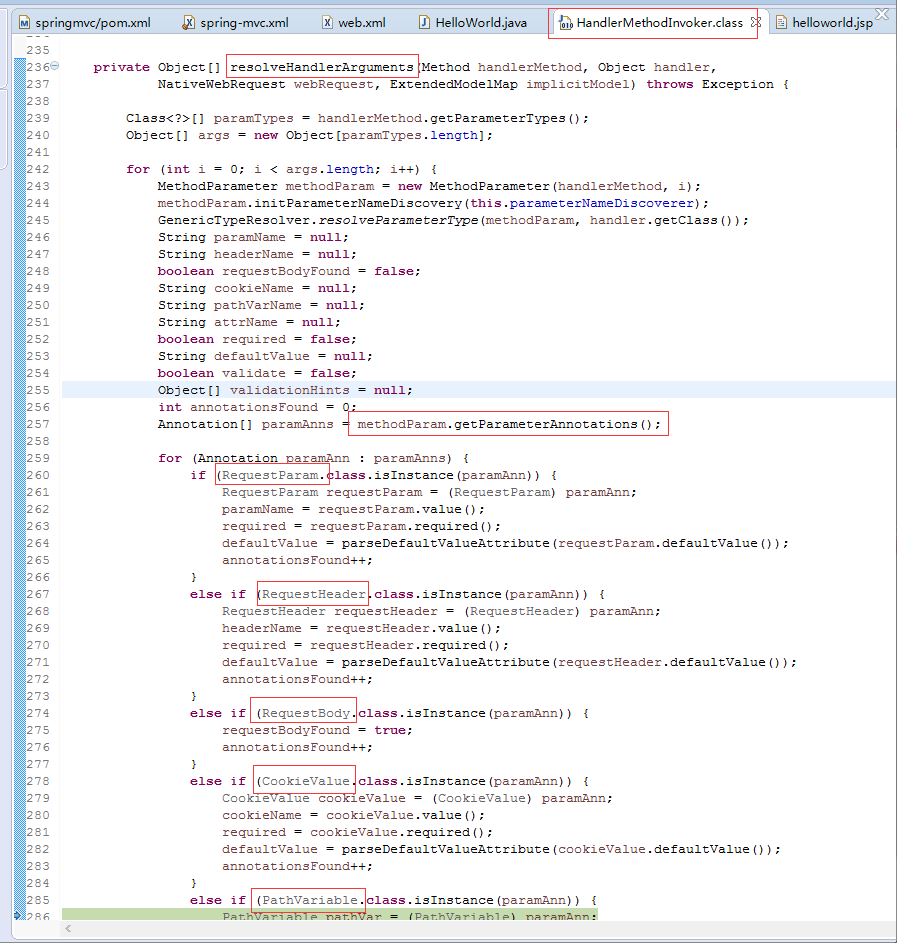
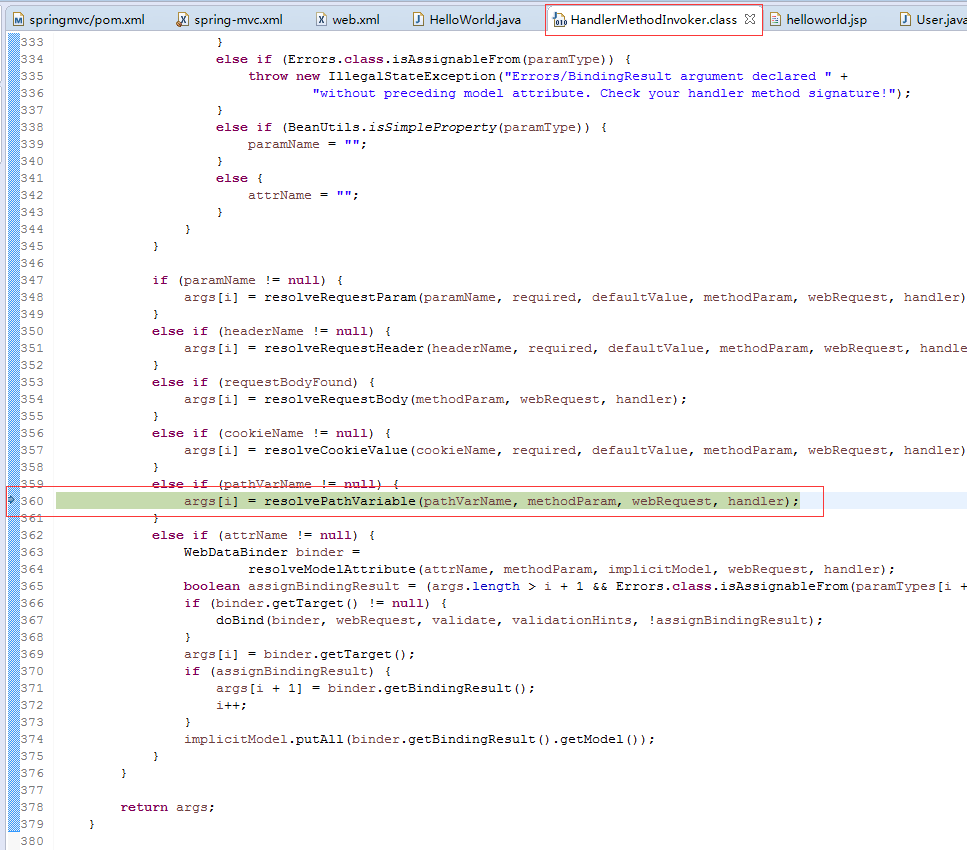
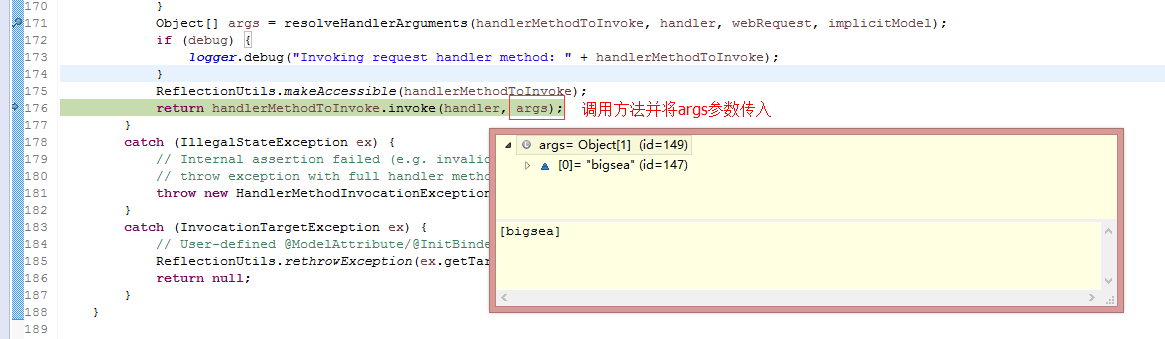
1.8. 源码分析































还没有评论,来说两句吧...