dir()函数
dir()函数
Python中有非常多的模块,但是有的时候我们会忘记一个模块有哪些功能。这个时候,我们可以用dir()函数来查看一下指定模块的功能列表。
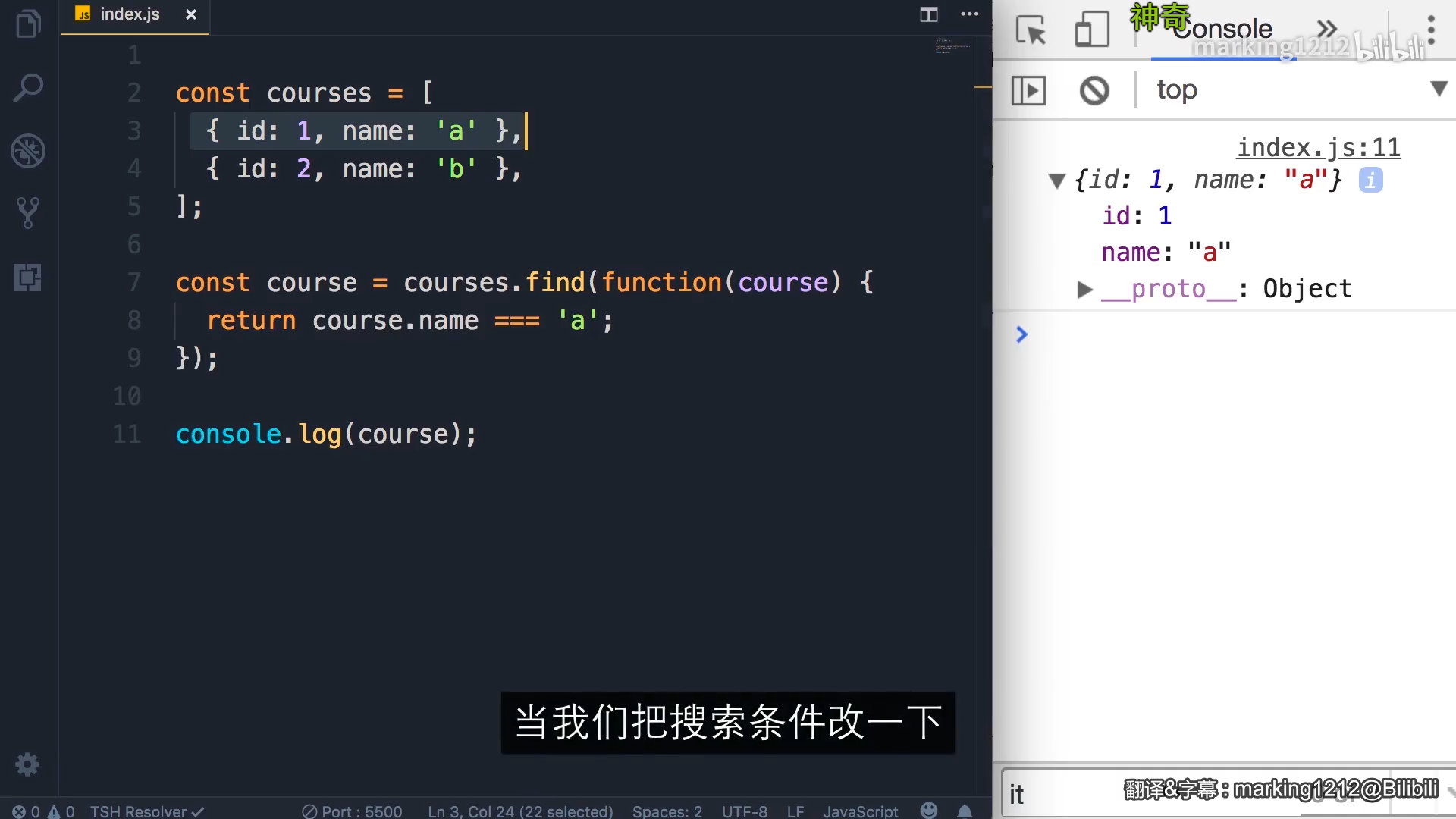
import sys#查看模块功能列表print dir(sys)#文档说明print sys.__doc__print sys.platform
输出:
C:\Python27\python.exe C:/Users/cpxiaozu-2/PycharmProjects/firstProject/ChapterTwo/list.py
[‘__displayhook__‘, ‘__doc__‘, ‘__excepthook__‘, ‘__name__‘, ‘__package__‘, ‘__stderr__‘, ‘__stdin__‘, ‘__stdout__‘, ‘_clear_type_cache’, ‘_current_frames’, ‘_getframe’, ‘_git’, ‘api_version’, ‘argv’, ‘builtin_module_names’, ‘byteorder’, ‘call_tracing’, ‘callstats’, ‘copyright’, ‘displayhook’, ‘dllhandle’, ‘dont_write_bytecode’, ‘exc_clear’, ‘exc_info’, ‘exc_type’, ‘excepthook’, ‘exec_prefix’, ‘executable’, ‘exit’, ‘flags’, ‘float_info’, ‘float_repr_style’, ‘getcheckinterval’, ‘getdefaultencoding’, ‘getfilesystemencoding’, ‘getprofile’, ‘getrecursionlimit’, ‘getrefcount’, ‘getsizeof’, ‘gettrace’, ‘getwindowsversion’, ‘hexversion’, ‘long_info’, ‘maxint’, ‘maxsize’, ‘maxunicode’, ‘meta_path’, ‘modules’, ‘path’, ‘path_hooks’, ‘path_importer_cache’, ‘platform’, ‘prefix’, ‘py3kwarning’, ‘setcheckinterval’, ‘setprofile’, ‘setrecursionlimit’, ‘settrace’, ‘stderr’, ‘stdin’, ‘stdout’, ‘subversion’, ‘version’, ‘version_info’, ‘warnoptions’, ‘winver’]
This module provides access to some objects used or maintained by the
interpreter and to functions that interact strongly with the interpreter.
Dynamic objects:
argv — command line arguments; argv[0] is the script pathname if known
path — module search path; path[0] is the script directory, else ‘’
modules — dictionary of loaded modules
displayhook — called to show results in an interactive session
excepthook — called to handle any uncaught exception other than SystemExit
To customize printing in an interactive session or to install a custom
top-level exception handler, assign other functions to replace these.
exitfunc — if sys.exitfunc exists, this routine is called when Python exits
Assigning to sys.exitfunc is deprecated; use the atexit module instead.
stdin — standard input file object; used by raw_input() and input()
stdout — standard output file object; used by the print statement
stderr — standard error object; used for error messages
By assigning other file objects (or objects that behave like files)
to these, it is possible to redirect all of the interpreter’s I/O.
last_type — type of last uncaught exception
last_value — value of last uncaught exception
last_traceback — traceback of last uncaught exception
These three are only available in an interactive session after a
traceback has been printed.
exc_type — type of exception currently being handled
exc_value — value of exception currently being handled
exc_traceback — traceback of exception currently being handled
The function exc_info() should be used instead of these three,
because it is thread-safe.
Static objects:
float_info — a dict with information about the float inplementation.
long_info — a struct sequence with information about the long implementation.
maxint — the largest supported integer (the smallest is -maxint-1)
maxsize — the largest supported length of containers.
maxunicode — the largest supported character
builtin_module_names — tuple of module names built into this interpreter
version — the version of this interpreter as a string
version_info — version information as a named tuple
hexversion — version information encoded as a single integer
copyright — copyright notice pertaining to this interpreter
platform — platform identifier
executable — absolute path of the executable binary of the Python interpreter
prefix — prefix used to find the Python library
exec_prefix — prefix used to find the machine-specific Python library
float_repr_style — string indicating the style of repr() output for floats
dllhandle — [Windows only] integer handle of the Python DLL
winver — [Windows only] version number of the Python DLL
__stdin__ — the original stdin; don’t touch!
__stdout__ — the original stdout; don’t touch!
__stderr__ — the original stderr; don’t touch!
__displayhook__ — the original displayhook; don’t touch!
__excepthook__ — the original excepthook; don’t touch!
Functions:
displayhook() — print an object to the screen, and save it in __builtin__._
excepthook() — print an exception and its traceback to sys.stderr
exc_info() — return thread-safe information about the current exception
exc_clear() — clear the exception state for the current thread
exit() — exit the interpreter by raising SystemExit
getdlopenflags() — returns flags to be used for dlopen() calls
getprofile() — get the global profiling function
getrefcount() — return the reference count for an object (plus one :-)
getrecursionlimit() — return the max recursion depth for the interpreter
getsizeof() — return the size of an object in bytes
gettrace() — get the global debug tracing function
setcheckinterval() — control how often the interpreter checks for events
setdlopenflags() — set the flags to be used for dlopen() calls
setprofile() — set the global profiling function
setrecursionlimit() — set the max recursion depth for the interpreter
settrace() — set the global debug tracing function
win32
Process finished with exit code 0































还没有评论,来说两句吧...