Netty内存分配
文章目录
- 基本概念
- PooledByteBufAllocator
- newDirectBuffer
- PoolThreadCache
- initCache
- PoolArena
- PoolChunkList
- PoolChunk
- memoryMap
- depthMap
- subpages
- PoolSubpage
- bitmap
- 分配原理
- ★遵循的原则
- PoolThreadCache分配内存
- PoolChunk里面分配内存
- allocate
- allocateRun
- allocateNode
- allocateSubpage
- PoolSubpage#allocate
- 回收原理
- PoolThreadCache回收内存
- 通过chunk来释放内存
- PoolChunkList#free
- PoolChunk#free
- PoolSubpage#free
- 扩充内存块
- 对比PoolArena和PoolThreadCache
基本概念
Netty内存根据使用的内存位置(堆内heap和堆外direct)和内存是否池化进行分类。
对于每个线程而言,netty会为之分配一个内存Cache;而在多个线程之间可共享一个Arena。Arena管理着相关内存,包含不同使用率的PoolChunkList、tinySubPagePools及smallSubPagePools来更好地分配内存。
内存根据大小可分为 huge、normal、small、tiny。
- huge:大于16M内存。
- normal:在8k-16M之间的内存。
- small:在512B到8K之间的内存。共有4种尺寸,分别是512B,1024B,2048B,4096B。
- tiny:小于512B的内存。最小为16B,按照16B来递增大小,区间为【16,512),共有32中尺寸。
由于初次申请内存,都是按照Chunk来申请,但是为了更高效率的使用内存,在Chunk这个级别下,还定义了Page和SubPage的内存块。
Chunk:默认大小是16M。在分配大小超过8K的内存,会从PoolChunkList中分配内存,或新增Chunk。一个Chunk会被分成2048个Page,是一个完全二叉树。一般每层节点有一个标识,标识当前节点及以下节点是否还有可用节点。
Page:默认大小是8K。通常使用subpageOverflowMask进行与运算判断一个大小是否小于8K.
SubPage: 管理小于8K的内存块(element)。
PoolSubPage:用于管理SubPage。
PooledByteBufAllocator
内存分配者。
在初始化时,会记录以下重要信息,然后在构造函数中创建数个PoolArena,后续分配内存时,其实是依靠PoolArena和PoolThreadCache。
而每个内存块最终是以Bytebuffer的实体来使用的,所以ByteBuffer中会存有对应的chunk(arena);在释放内存时,会通过PoolArena和PoolThreadCache来实现内存释放。
newDirectBuffer
protected ByteBuf newDirectBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) {//这里可能会初始化当前线程的PoolThreadCache,此时也会匹配最少使用的arena,初始化各内存块缓存PoolThreadCache cache = threadCache.get();PoolArena<ByteBuffer> directArena = cache.directArena;final ByteBuf buf;if (directArena != null) {//使用arena来分配,此内部就是结合了PoolThreadCache分配buf = directArena.allocate(cache, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);} else {buf = PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe() ?UnsafeByteBufUtil.newUnsafeDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity) :new UnpooledDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);}return toLeakAwareBuffer(buf);}
PoolThreadCache
内部主要维护了三个内存数组 tinySubPageXXXCaches,smallSubPageXXXCaches 和 normalXXXCaches。每个数组的大小分别是 32,4和3。每个数组内部存储的类型都是MemoryRegionCache,这个类里面维护了queue,用于存储内存块。
initCache
protected synchronized PoolThreadCache initialValue() {//找到使用最少的Arena(评判标准是PoolArena#numThreadCaches)final PoolArena<byte[]> heapArena = leastUsedArena(heapArenas);final PoolArena<ByteBuffer> directArena = leastUsedArena(directArenas);Thread current = Thread.currentThread();if (useCacheForAllThreads || current instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {return new PoolThreadCache(heapArena, directArena, tinyCacheSize, smallCacheSize, normalCacheSize,DEFAULT_MAX_CACHED_BUFFER_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_CACHE_TRIM_INTERVAL);}// No caching so just use 0 as sizes.return new PoolThreadCache(heapArena, directArena, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0);}PoolThreadCache(PoolArena<byte[]> heapArena, PoolArena<ByteBuffer> directArena,int tinyCacheSize, int smallCacheSize, int normalCacheSize,int maxCachedBufferCapacity, int freeSweepAllocationThreshold) {if (maxCachedBufferCapacity < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxCachedBufferCapacity: "+ maxCachedBufferCapacity + " (expected: >= 0)");}this.freeSweepAllocationThreshold = freeSweepAllocationThreshold;this.heapArena = heapArena;this.directArena = directArena;//创建tiny,small,normal cache数组if (directArena != null) {tinySubPageDirectCaches = createSubPageCaches(tinyCacheSize, PoolArena.numTinySubpagePools, SizeClass.Tiny);smallSubPageDirectCaches = createSubPageCaches(smallCacheSize, directArena.numSmallSubpagePools, SizeClass.Small);numShiftsNormalDirect = log2(directArena.pageSize);normalDirectCaches = createNormalCaches(normalCacheSize, maxCachedBufferCapacity, directArena);directArena.numThreadCaches.getAndIncrement();} else {// No directArea is configured so just null out all cachestinySubPageDirectCaches = null;smallSubPageDirectCaches = null;normalDirectCaches = null;numShiftsNormalDirect = -1;}if (heapArena != null) {// Create the caches for the heap allocationstinySubPageHeapCaches = createSubPageCaches(tinyCacheSize, PoolArena.numTinySubpagePools, SizeClass.Tiny);smallSubPageHeapCaches = createSubPageCaches(smallCacheSize, heapArena.numSmallSubpagePools, SizeClass.Small);numShiftsNormalHeap = log2(heapArena.pageSize);normalHeapCaches = createNormalCaches(normalCacheSize, maxCachedBufferCapacity, heapArena);heapArena.numThreadCaches.getAndIncrement();} else {// No heapArea is configured so just null out all cachestinySubPageHeapCaches = null;smallSubPageHeapCaches = null;normalHeapCaches = null;numShiftsNormalHeap = -1;}// Only check if there are caches in use.if ((tinySubPageDirectCaches != null || smallSubPageDirectCaches != null || normalDirectCaches != null|| tinySubPageHeapCaches != null || smallSubPageHeapCaches != null || normalHeapCaches != null)&& freeSweepAllocationThreshold < 1) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("freeSweepAllocationThreshold: "+ freeSweepAllocationThreshold + " (expected: > 0)");}}
PoolArena
我们可以理解arena是公用的一个内存缓存。其中包含了:
- 不同使用率的Chunk :qInit、q000、q025、q050、q075、q100
- Subpages: tinySubpagePools,smallSubpagePools,用于存储没有被使用的小内存块
PoolChunkList
在Arena中存储的是PoolChunkList,这是一个双向的节点。对于chunk,arena会按照不同的使用率来管理,那么不同使用率的chunkList如何连接起来,此时就出现了PoolChunkList。
每个PoolChunkList内部会记录以下信息:
nextList: 下一个PoolChunkList(使用率更高的)prevList: 前一个PoolChunkList(使用率更低的)minUsage: 最低使用率,低于该值,会移除该chunk,放到preList中maxUsage: 最高使用率,高于该值,会移除该chunk,放到nextList中maxCapacity: 最大可分配的内存大小,就是用minUsage计算的
在Arena中存在qInit、q000、q025、q050、q075和q100 六个PoolChunkList。
| prevList | nextList | minUsage | maxUsage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qInit | qInit | q000 | Integer.MIN_VALUE | 25 |
| q000 | null | q025 | 1 | 50 |
| q025 | q000 | q050 | 25 | 75 |
| q050 | q025 | q075 | 50 | 100 |
| q075 | q050 | q100 | 75 | 100 |
| q100 | q075 | null | 100 | Integer.MAX_VALUE |
对于新创建的chunk,会先加入到qInit中。
对于PoolChunkList的使用,最终还是会落到Chunk上。
PoolChunk
memoryMap
我们都知道chunk是一个二叉树,那么需要一个专门存储每一个节点的分配信息,这就是memoryMap。按照默认的规则,chunk是16M,而每个page是8k,所以会有4095个节点。把4095个节点全部记录下来,例如:{0,1,1,2,2,2,2…},用于表示每个节点下面有多少未分配的内存块。
根据memoryMap记录的值,如何看出未分配的内存呢?
首先,二叉树中每个节点都有对应的层高d。
- memoryMap[id] == d 表示该节点未分配
- memoryMap[id] > d 表示该节点已经被分配过,但是其子节点仍有未分配的
- memoryMap[id] = maxOrder + 1 表示超过最大层高(maxOrder默认是11),则说明该节点及其子节点已经被分配完
depthMap
用于存储层高信息,不会发生变化,一般用于通过memoryMapIndex来定位对应的层高
subpages
用于存储被切割的page,该处的SubPage会和Arena的tinySubpagePools、smallSubpagePools关联,并且可用于重组成Page归还到Chunk
PoolSubpage
在Chunk中,最小单位是Page,当Page还需要拆分时,此时就出现了PoolSubPage。每个PoolSubPage按照大小被PoolArena/PoolThreadCache的tinySubpagePools和smallSubpagePools管理着。
- PoolSubPage的大小是固定的(pageSize),默认是8K。
- PoolSubPage中的内存块大小都是一样的(elemSize)
由于内存块可能非常小,所以一个Page可以被切割成非常多的小内存块,于是就需要一个高效的方式(bitmap)来快速定位内存块的使用情况。 - PoolSubPage是双向节点,所以在tinySubpagePools和smallSubpagePools中就是一个数组加链表的模式存在着
bitmap
bitmap是一个long数组,每个long值的每一位代表着一个内存块的使用情况。由于一个long就64位,而每个PoolSubPage大小固定是8K,所以当存储的是tiny内存块(16B),就有 8*1024/16=512个内存块,512/64=8个long存储,也就是bitMap的长度是8。
所以当要标识一个内存块时,需要知道其在bitMap的哪个long 及 这个long中哪位。
低6位是long中的index,剩余位表示在bitMap的下标。
分配原理
★遵循的原则
1.规格化申请的内存大小,根据内存大小区分当前的需要分配的内存块种类
2.分配内存的优先级
优先从线程的内存缓存中分配
- 根据大小找到数组下标,然后从queue里面获取内存块
对应种类的内存List分配(tiny/small/qXXX)
- 根据大小找到数组下标,从head开始找到PoolSubPage/Chunk,PoolSubPage还需要再定位具体的位置(bitMap的下标及long中的位置)
- 最终方式就是新增一个Chunk
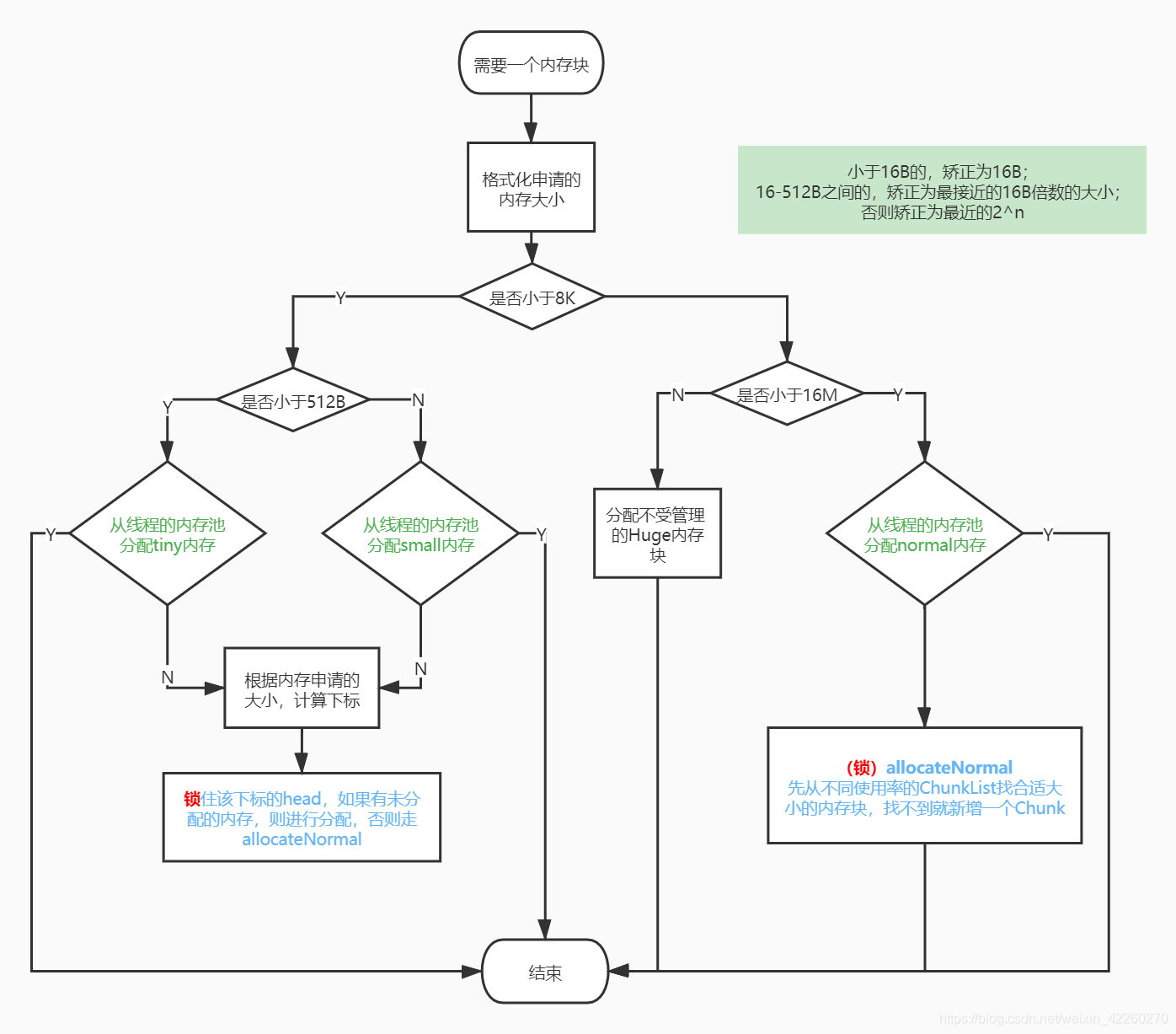
PoolThreadCache分配内存
通过allocateTiny,allocateSmall或者allocateNormal分别缓存中的内存。通过下面代码可知,都是先找到一个缓存的内存块,再进行分配。
boolean allocateTiny(PoolArena<?> area, PooledByteBuf<?> buf, int reqCapacity, int normCapacity) {return allocate(cacheForTiny(area, normCapacity), buf, reqCapacity);}boolean allocateSmall(PoolArena<?> area, PooledByteBuf<?> buf, int reqCapacity, int normCapacity) {return allocate(cacheForSmall(area, normCapacity), buf, reqCapacity);}boolean allocateNormal(PoolArena<?> area, PooledByteBuf<?> buf, int reqCapacity, int normCapacity) {return allocate(cacheForNormal(area, normCapacity), buf, reqCapacity);}
那么再看看cacheForXXX系列方法吧。根据下面的代码可以看见,都是先根据normCapacity找到在数组的下标,然后获取缓存数组对应的MemoryRegionCache。
private MemoryRegionCache<?> cacheForTiny(PoolArena<?> area, int normCapacity) {//tiny是按照16的大小递增,所以normCapacity >>> 4就是对应下标int idx = PoolArena.tinyIdx(normCapacity);if (area.isDirect()) {return cache(tinySubPageDirectCaches, idx);}return cache(tinySubPageHeapCaches, idx);}private MemoryRegionCache<?> cacheForSmall(PoolArena<?> area, int normCapacity) {//small是以512B开始,按照1024B递增,所以通过 normCapacity >>> 10 就可以找到下标int idx = PoolArena.smallIdx(normCapacity);if (area.isDirect()) {return cache(smallSubPageDirectCaches, idx);}return cache(smallSubPageHeapCaches, idx);}private MemoryRegionCache<?> cacheForNormal(PoolArena<?> area, int normCapacity) {//normal是从4K开始,大小是2^n,所以计算log2就可以得到下标if (area.isDirect()) {int idx = log2(normCapacity >> numShiftsNormalDirect);return cache(normalDirectCaches, idx);}int idx = log2(normCapacity >> numShiftsNormalHeap);return cache(normalHeapCaches, idx);}
接下来从这个MemoryRegionCache的queue poll一个内存块(内存块可能为null),再根据MemoryRegionCache的allocate方法分配缓存,并且记录分配次数(如果达到freeSweepAllocationThreshold,需要释放缓存的内存块,让使用率很低的内存块回归Arena,可以使得其他线程使用)。
private boolean allocate(MemoryRegionCache<?> cache, PooledByteBuf buf, int reqCapacity) {if (cache == null) {// no cache found so just return false herereturn false;}boolean allocated = cache.allocate(buf, reqCapacity);if (++ allocations >= freeSweepAllocationThreshold) {allocations = 0;trim();}return allocated;}
再来看看trim方法是如何释放使用率低的缓存内存吧。
//这里直接看io.netty.buffer.PoolThreadCache.MemoryRegionCache#trim就行public final void trim() {//计算queue大小和分配次数之差,就能知道有多少都未曾分配过int free = size - allocations;allocations = 0;// 释放掉没有分配过的个数的缓存内存块if (free > 0) {//最终调用freeEntry,通过chunk来释放内存free(free);}}
PoolChunk里面分配内存
主要有两个规则,根据大小确定当前是分配小于8K的SubPage还是大于8K的内存
allocate
boolean allocate(PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity, int normCapacity) {//handle的低32位表示在memoryMap的位置,高32位表示在SubPage中的位置final long handle;if ((normCapacity & subpageOverflowMask) != 0) {//大于pagesize使用allocateRun分配handle = allocateRun(normCapacity);} else {//小于等于pagesize使用allocateSubpage分配handle = allocateSubpage(normCapacity);}//如果handle小于0说明没有可用的内存了if (handle < 0) {return false;}ByteBuffer nioBuffer = cachedNioBuffers != null ? cachedNioBuffers.pollLast() : null;initBuf(buf, nioBuffer, handle, reqCapacity);return true;}
allocateRun
private long allocateRun(int normCapacity) {//计算层级int d = maxOrder - (log2(normCapacity) - pageShifts);//找到该层级合适的节点int id = allocateNode(d);//小于0说明已经分配完了,没有可用的内存块if (id < 0) {return id;}freeBytes -= runLength(id);return id;}
allocateNode
//d是层高private int allocateNode(int d) {int id = 1;int initial = - (1 << d); // 如果d是2,则 1<<2就是 11111100byte val = value(id);if (val > d) { // 如果根节点的value已经大于d,说明没有可用的内存了return -1;}//val小于d:表示一定有可以分配的内存//id & initial == 0:同层的节点,后续用于遍历while (val < d || (id & initial) == 0) {//左子节点id <<= 1;val = value(id);if (val > d) {//右子节点 异或:相同为0,相异为1,所以和1进行异或,除低1位之外都保留了id的值,而因为id是偶数,低一位为0,所以通过异或1,一定为奇数,得到右子节点id ^= 1;val = value(id);}}byte value = value(id);assert value == d && (id & initial) == 1 << d : String.format("val = %d, id & initial = %d, d = %d",value, id & initial, d);setValue(id, unusable); // 标记为不可用updateParentsAlloc(id); // 更新所有父节点分配信息return id;}
allocateSubpage
private long allocateSubpage(int normCapacity) {//找到arena里面对应大小内存块的头节点PoolSubpage<T> head = arena.findSubpagePoolHead(normCapacity);int d = maxOrder; //因为是SubPage,所以层数直接设置为最大层数synchronized (head) {//找到memoryMap中的下标int id = allocateNode(d);if (id < 0) {return id;}final PoolSubpage<T>[] subpages = this.subpages;final int pageSize = this.pageSize;freeBytes -= pageSize;// 计算SubPage的下标int subpageIdx = subpageIdx(id);PoolSubpage<T> subpage = subpages[subpageIdx];if (subpage == null) {//初始化一个PoolSubpage//初始化额外信息,并将此SubPage加入到head的链表中subpage = new PoolSubpage<T>(head, this, id, runOffset(id), pageSize, normCapacity);subpages[subpageIdx] = subpage;} else {//初始化额外信息,并将此SubPage加入到head的链表中subpage.init(head, normCapacity);}//返回一个long值,高32位是bitmap的数据,低32位是memoryMap的下标return subpage.allocate();}}
PoolSubpage#allocate
long allocate() {//每个内存块的大小为0,则直接返回一个handleif (elemSize == 0) {return toHandle(0);}if (numAvail == 0 || !doNotDestroy) {return -1;}//在bitmap中找到有未分配的longfinal int bitmapIdx = getNextAvail();//低6位是long中的index,剩余位表示在bitMap的下标int q = bitmapIdx >>> 6;int r = bitmapIdx & 63;assert (bitmap[q] >>> r & 1) == 0;//标记该位置内存块已使用bitmap[q] |= 1L << r;//如果没有可用的内存块了,直接移除该PoolSubPageif (-- numAvail == 0) {removeFromPool();}return toHandle(bitmapIdx);}
回收原理
优先回收到线程的内存缓存中,缓存回收不了就用PoolChunkList来回收,否则最终被释放掉
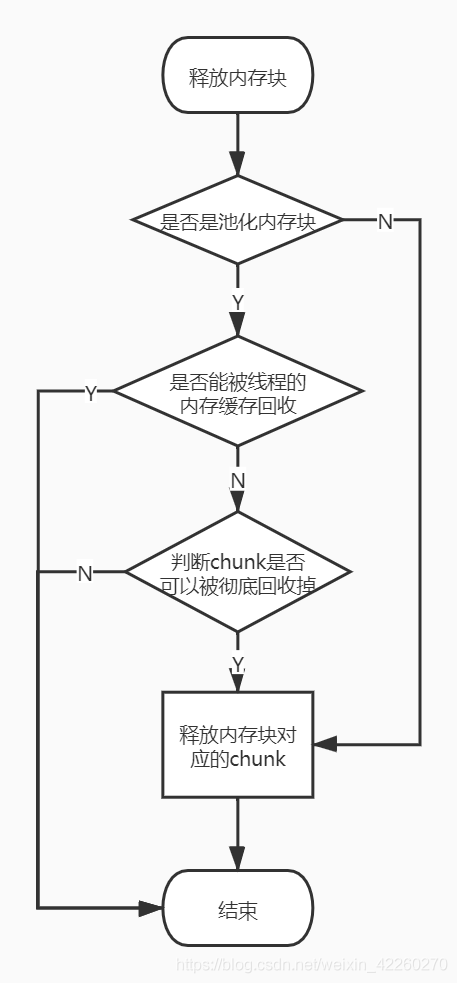
PoolThreadCache回收内存
通过add方法,将内存块缓存起来。
boolean add(PoolArena<?> area, PoolChunk chunk, ByteBuffer nioBuffer,long handle, int normCapacity, SizeClass sizeClass) {//先根据大小找到不同类型内存块的数组坐标,找到对应大小的MemoryRegionCacheMemoryRegionCache<?> cache = cache(area, normCapacity, sizeClass);if (cache == null) {return false;}//往MemoryRegionCache的queue里面添加内存块return cache.add(chunk, nioBuffer, handle);}
通过chunk来释放内存
PoolChunkList#free
boolean free(PoolChunk<T> chunk, long handle, ByteBuffer nioBuffer) {chunk.free(handle, nioBuffer);//如果小于最小使用率,需要移除该chunkif (chunk.usage() < minUsage) {remove(chunk);// 添加到preList(PoolChunkList)中,如果没有添加成功此时返回false,会触发该chunk的销毁return move0(chunk);}return true;}
PoolChunk#free
找到该内存块在memoryMap的下标 及 在bitmap的哪一个long值的哪一位来知道其下标
void free(long handle, ByteBuffer nioBuffer) {int memoryMapIdx = memoryMapIdx(handle);int bitmapIdx = bitmapIdx(handle);// 如果bitmapIdx不为0,说明该内存块是一个SubPageif (bitmapIdx != 0) {//获取到对应的SubPagePoolSubpage<T> subpage = subpages[subpageIdx(memoryMapIdx)];assert subpage != null && subpage.doNotDestroy;//获取该SubPage对应的head节点PoolSubpage<T> head = arena.findSubpagePoolHead(subpage.elemSize);synchronized (head) {//释放结果为false,说明已经从SubPage池移除,此时需要归还到chunk中if (subpage.free(head, bitmapIdx & 0x3FFFFFFF)) {return;}}}//增加空闲空间的计数freeBytes += runLength(memoryMapIdx);//更新memoryMapsetValue(memoryMapIdx, depth(memoryMapIdx));updateParentsFree(memoryMapIdx);if (nioBuffer != null && cachedNioBuffers != null &&cachedNioBuffers.size() < PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT_MAX_CACHED_BYTEBUFFERS_PER_CHUNK) {cachedNioBuffers.offer(nioBuffer);}}
PoolSubpage#free
boolean free(PoolSubpage<T> head, int bitmapIdx) {if (elemSize == 0) {return true;}int q = bitmapIdx >>> 6;int r = bitmapIdx & 63;assert (bitmap[q] >>> r & 1) != 0;//标记bitmap中该SubPage为未分配状态bitmap[q] ^= 1L << r;setNextAvail(bitmapIdx);//之前被移除掉的SubPage,需要归还到arena SubPage的链表中if (numAvail ++ == 0) {addToPool(head);return true;}if (numAvail != maxNumElems) {return true;} else {//如果没有正在使用的内存块了if (prev == next) {// 如果只是一个内存块则无需删除该SubPagereturn true;}// 从SubPage池中移除并归还到正常pagedoNotDestroy = false;removeFromPool();return false;}}
扩充内存块
当向ByteBuffer写数据发现内存块不够用了,会怎么操作呢?
首先得计算出保证需求的内存块大小
- 对于小于4M的内存申请,则以64B翻倍找到刚好满足需求的大小
- 对于等于4M的内存申请,则直接返回4M大小
- 剩余情况,返回需求大小加4M或最大内存大小
然后重新找一个合适大小的内存块,进行标记后,再把数据拷贝过来,释放旧的内存。
void reallocate(PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int newCapacity, boolean freeOldMemory) {if (newCapacity < 0 || newCapacity > buf.maxCapacity()) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("newCapacity: " + newCapacity);}int oldCapacity = buf.length;if (oldCapacity == newCapacity) {return;}PoolChunk<T> oldChunk = buf.chunk;ByteBuffer oldNioBuffer = buf.tmpNioBuf;long oldHandle = buf.handle;T oldMemory = buf.memory;int oldOffset = buf.offset;int oldMaxLength = buf.maxLength;int readerIndex = buf.readerIndex();int writerIndex = buf.writerIndex();//分配一个合适大小的内存块allocate(parent.threadCache(), buf, newCapacity);//数据拷贝if (newCapacity > oldCapacity) {memoryCopy(oldMemory, oldOffset,buf.memory, buf.offset, oldCapacity);} else if (newCapacity < oldCapacity) {if (readerIndex < newCapacity) {if (writerIndex > newCapacity) {writerIndex = newCapacity;}memoryCopy(oldMemory, oldOffset + readerIndex,buf.memory, buf.offset + readerIndex, writerIndex - readerIndex);} else {readerIndex = writerIndex = newCapacity;}}buf.setIndex(readerIndex, writerIndex);//释放旧的内存if (freeOldMemory) {free(oldChunk, oldNioBuffer, oldHandle, oldMaxLength, buf.cache);}
}
对比PoolArena和PoolThreadCache
































还没有评论,来说两句吧...