STL_List使用
list构造:
<span style="font-family:Microsoft YaHei;font-size:18px;">// constructing lists#include <iostream>#include <list>int main(){std::list<int> first;// 空链表std::list<int> second(4, 100); //用4个值,全为100std::list<int> third(second.begin(), second.end()); //以第二个进行构造std::list<int> fourth(third);//以第三个构造int myints[] = { 16, 2, 77, 29 };//以数组进行构造std::list<int> fifth(myints, myints + sizeof(myints) / sizeof(int));std::cout << "The contents of fifth are: ";for (std::list<int>::iterator it = fifth.begin(); it != fifth.end(); it++)std::cout << *it << ' ';std::cout << '\n';system("pause");return 0;}</span>
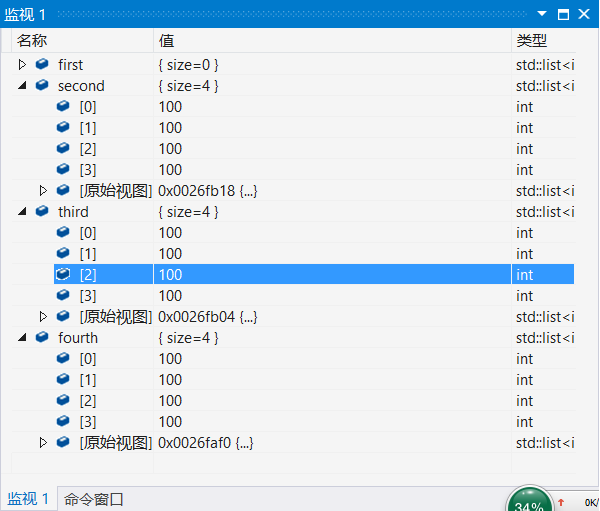
list赋值运算符重载:
<span style="font-family:Microsoft YaHei;font-size:18px;">// assignment operator with lists#include <iostream>#include <list>int main(){std::list<int> first(3); // list 用3个0std::list<int> second(5); // list 用5个0second = first;//以first赋值给second,second变为3个0first = std::list<int>(); //再以空链表赋值给firststd::cout << "Size of first: " << int(first.size()) << '\n';std::cout << "Size of second: " << int(second.size()) << '\n';system("pause");return 0;}</span>
list::begin() :指向迭代器起始位置
list::end() :指向最后一个元素的下一个位置
list::rbegin()/list::rend(): 逆向迭代器。
list::cbegin(): C++11标准, const类型迭代器
list::cend(): C++11标准,const类型迭代器
list::size():求元素个数
<span style="font-family:Microsoft YaHei;font-size:18px;">// list::size#include <iostream>#include <list>int main(){std::list<int> l;std::cout << "0. size: " << l.size() << '\n';for (int i = 0; i<10; i++)l.push_back(i);//插入10个元素,分别为0-9std::cout << "1. size: " << l.size() << '\n';l.insert(l.begin(), 10, 100);//从头开始插入,插入10个元素,全为100std::cout << "2. size: " << l.size() << '\n';l.pop_back();//尾删一个元素std::cout << "3. size: " << l.size() << '\n';//剩余19个元素system("pause");return 0;}</span>
list::front():
<span style="font-family:Microsoft YaHei;font-size:18px;">std::list<int> l;l.push_back(77);l.push_back(22);//l.front()指向第一个元素l.front() -= l.back();//77-=22-->55std::cout << "l.front() is now " << l.front() << '\n';</span>
list::back():指向链表中最后一个元素
<span style="font-family:Microsoft YaHei;font-size:18px;">std::list<int> l;l.push_back(10);while (l.back() != 0){l.push_back(l.back() - 1);//l.back()指向最后一个元素,每次减一}</span>
list::assign():重新分配空间
<span style="font-family:Microsoft YaHei;font-size:18px;">int myints[] = { 1776, 7, 4 };first.assign(myints, myints + 3); //以数组重新分配空间</span>
list::push_front(): 在头结点前插入
list::push_front():从头结点删除
list::push_back():尾插
list::pop_back():尾删
list::insert():插入
<span style="font-family:Microsoft YaHei;font-size:18px;">// inserting into a list#include <iostream>#include <list>#include <vector>int main(){std::list<int> mylist;std::list<int>::iterator it;// set some initial values:for (int i = 1; i <= 5; ++i) mylist.push_back(i); // 1 2 3 4 5it = mylist.begin();++it; // it 指向第二个 ^mylist.insert(it, 10); // 1 10 2 3 4 5// it仍然指向数字2,插入2个20,所以2 3 4 5向后挪动,然后插入2个20 ^mylist.insert(it, 2, 20); // 1 10 20 20 2 3 4 5--it; // 减减it,it指向第二个20std::vector<int> myvector(2, 30);mylist.insert(it, myvector.begin(), myvector.end());//it指向第二个20,插入2个30,所以第二个20后面的元素向后移动,然后插入2个30// 1 10 20 30 30 20 2 3 4 5// ^std::cout << "mylist contains:";for (it = mylist.begin(); it != mylist.end(); ++it)std::cout << ' ' << *it;std::cout << '\n';system("pause");return 0;}</span>
list::erase():删除
<span style="font-family:Microsoft YaHei;font-size:18px;">// erasing from list#include <iostream>#include <list>int main(){std::list<int> mylist;std::list<int>::iterator it1, it2;// set some values:for (int i = 1; i<10; ++i)mylist.push_back(i * 10);// 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90it1 = it2 = mylist.begin();advance(it2, 6); //迭代器it2向前移动6个位置。++it1; //it1后移一位---指向20//记得要用迭代器接收it1 = mylist.erase(it1); //it1指向20,erase(it1),返回下一个位置给it1it2 = mylist.erase(it2); //it2指向70,erase(it2),返回下一个位置80++it1; //指向40--it2; //指向60//10 30 40 50 60 80 90mylist.erase(it1, it2); // 10 30 60 80 90//删除40 50 (60并不删除,因为是左闭右开区间)std::cout << "mylist contains:";for (it1 = mylist.begin(); it1 != mylist.end(); ++it1)std::cout << ' ' << *it1;std::cout << '\n';system("pause");return 0;}</span>
list::remove():移除
list::unique():去重
<span style="font-family:Microsoft YaHei;font-size:18px;">// list::unique#include <iostream>#include <cmath>#include <list>// a binary predicate implemented as a function:bool same_integral_part(double first, double second){return (int(first) == int(second));}// a binary predicate implemented as a class:struct is_near {bool operator() (double first, double second){return (fabs(first - second)<5.0);}};int main(){double mydoubles[] = { 12.15, 2.72, 73.0, 12.77, 3.14,12.77, 73.35, 72.25, 15.3, 72.25 };std::list<double> mylist(mydoubles, mydoubles + 10);mylist.sort(); // 2.72, 3.14, 12.15, 12.77, 12.77,// 15.3, 72.25, 72.25, 73.0, 73.35mylist.unique(); //去重 // 2.72, 3.14, 12.15, 12.77// 15.3, 72.25, 73.0, 73.35mylist.unique(same_integral_part);//整数部分相同的去掉一个,保留第一个,去掉后面的// 2.72, 3.14, 12.15 15.3, 72.25, 73.0mylist.unique(is_near());//绝对值小于5的删除后一个 // 2.72, 12.15, 72.25std::cout << "mylist contains:";for (std::list<double>::iterator it = mylist.begin(); it != mylist.end(); ++it)std::cout << ' ' << *it;std::cout << '\n';system("pause");return 0;}</span>
list::merge():合并
list::sort():排序






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...