Vue 用createElement 自定义列表头
文章目录
- Vue 用createElement 自定义列表头
- 一、前言
- 二、需求实现效果
- 三、知识点
- 1、createElement 参数
- 深入 data 对象
- 2、createElement 创建元素过程
- 四、具体实现及代码
- 1、第一步:创建需要自定义列表头的table
- 二、第二步:创建自定义组件封装el-popover
- 三、局部注册组件并手写createElement
- 五、扩展知识点
- 1、Vue源码9个基础方法
Vue 用createElement 自定义列表头
一、前言
最近产品有需求,想要把一个搜索框放入到列表头中,一般的属性无法满足我们这个需求,所以我们需要使用自定义表头。
现阶段我比较常用的table有 elementUI 的 el-table、umy-ui的u-table和 vxe-table的vxe-grid。
u-table和el-table都有提供 render-header 方便我们自定义表头。而 vxe-table 则提供了更多渲染器可以方便我们进行操作,详情可以看官方文档。这里我主要用的是umy-ui的u-table。
二、需求实现效果
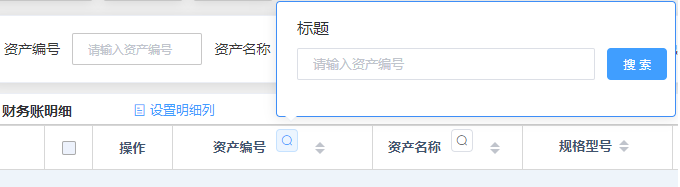
三、知识点
1、createElement 参数
createElement 参数
接下来你需要熟悉的是如何在createElement函数中生成模板。这里是createElement接受的参数:
// @returns {VNode}createElement(// {String | Object | Function}// 一个 HTML 标签字符串,组件选项对象,或者一个返回值// 类型为 String/Object 的函数,必要参数'div',// {Object}// 一个包含模板相关属性的数据对象// 这样,您可以在 template 中使用这些属性。可选参数。{// (详情见下一节)},// {String | Array}// 子节点 (VNodes),由 `createElement()` 构建而成,// 或使用字符串来生成“文本节点”。可选参数。['先写一些文字',createElement('h1', '一则头条'),createElement(MyComponent, {props: {someProp: 'foobar'}})])
深入 data 对象
有一件事要注意:正如在模板语法中,v-bind:class和v-bind:style,会被特别对待一样,在 VNode 数据对象中,下列属性名是级别最高的字段。该对象也允许你绑定普通的 HTML 特性,就像 DOM 属性一样,比如innerHTML(这会取代v-html指令)。
{// 和`v-bind:class`一样的 API'class': {foo: true,bar: false},// 和`v-bind:style`一样的 APIstyle: {color: 'red',fontSize: '14px'},// 正常的 HTML 特性attrs: {id: 'foo'},// 组件 propsprops: {myProp: 'bar'},// DOM 属性domProps: {innerHTML: 'baz'},// 事件监听器基于 `on`// 所以不再支持如 `v-on:keyup.enter` 修饰器// 需要手动匹配 keyCode。on: {click: this.clickHandler},// 仅对于组件,用于监听原生事件,而不是组件内部使用// `vm.$emit` 触发的事件。nativeOn: {click: this.nativeClickHandler},// 自定义指令。注意,你无法对 `binding` 中的 `oldValue`// 赋值,因为 Vue 已经自动为你进行了同步。directives: [{name: 'my-custom-directive',value: '2',expression: '1 + 1',arg: 'foo',modifiers: {bar: true}}],// Scoped slots in the form of// { name: props => VNode | Array<VNode> }scopedSlots: {default: props => createElement('span', props.text)},// 如果组件是其他组件的子组件,需为插槽指定名称slot: 'name-of-slot',// 其他特殊顶层属性key: 'myKey',ref: 'myRef'}
2、createElement 创建元素过程
Vue 利用 createElement 方法创建 VNode,定义在 src/core/vdom/crate-element.js 中:
// wrapper function for providing a more flexible interface
// without getting yelled at by flow
export function createElement (
context: Component,
tag: any,
data: any,
children: any,
normalizationType: any,
alwaysNormalize: boolean
): VNode | Array{
// 这些都只是判断,可以无视
if (Array.isArray(data) || isPrimitive(data)) {normalizationType = childrenchildren = datadata = undefined
}
// 这些都只是判断,可以无视
if (isTrue(alwaysNormalize)) {normalizationType = ALWAYS_NORMALIZE
}
return _createElement(context, tag, data, children, normalizationType)
}createElement 方法实际上是对 _createElement 方法的封装,它允许传入的参数更加灵活,在处理这些参数后,调用真正创建 VNode 的函数 _crateElement :
export function createElement (
context: Component,
tag?: string | Class| Function | Object, )) {
data?: VNodeData,
children?: any,
normalizationType?: number
): VNode | Array{
// 只是一些判断,如果出问题了,就创建一个空的元素
if (isDef(data) && isDef((data: any)._obprocess.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(`Avoid using observed data object as vnode data: ${ JSON.stringify(data)}\n + 'Always create fresh vnode data objects in each render!', context // 这里\n后面应该有个`,但是不知道为什么会导致整个页面一片红,所以去掉了)// 如果传进来的VNodeData为undefined,则返回空元素return createEmptyVNode()
}
// 获取 VNodeData类型
// object syntax in v-bind
if (isDef(data) && isDef(data.is)) {tag = data.is
}
if (!tag) {// in case of component :is set to falsy valuereturn createEmptyVNode()
}
// 一些判断,可以无视
// warn against non-primitive key
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== ‘production’ &&isDef(data) && isDef(data.key) && !isPrimitive(data.key)
) {
if (!__WEEX__ || !('@binding' in data.key)) {warn('Avoid using non-primitive value as key, ' +'use string/number value instead.',context)}
}
// support single function children as default scoped slot
if (Array.isArray(children) &&typeof children[0] === 'function'
) {
data = data || { }data.scopedSlots = { default: children[0] }children.length = 0
}
// children 的规范化
//类型不同规范的方法也就不一样,它主要是参考 render 函数是编译生成的还是用户手写的。
if (normalizationType === ALWAYS_NORMALIZE) {// 用户手写的children = normalizeChildren(children)
} else if (normalizationType === SIMPLE_NORMALIZE) {
// render 函数是编译生成children = simpleNormalizeChildren(children)
}
// 经过对 children 的规范化,children 变成了一个类型为 VNode 的 Array
let vnode, ns// 这里先对 tag 做判断,如果是 string 类型,则接着判断如果是内置的一些节点,则直接创建一个普通 VNode,
// 如果是为已注册的组件名,则通过 createComponent 创建一个组件类型的 VNode,否则创建一个未知的标签的 VNode。
//如果是 tag 一个 Component 类型,则直接调用 createComponent 创建一个组件类型的 VNode 节点。
//对于 createComponent 创建组件类型的 VNode 的过程,之后再去写,本质上它还是返回了一个 VNode。if (typeof tag === ‘string’) {
let Ctorns = (context.$vnode && context.$vnode.ns) || config.getTagNamespace(tag)if (config.isReservedTag(tag)) {// platform built-in elementsif (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && isDef(data) && isDef(data.nativeOn) && data.tag !== 'component') {warn(`The .native modifier for v-on is only valid on components but it was used on <${ tag}>.`,context)}// 如果是 string 类型,则接着判断如果是内置的一些节点,则直接创建一个普通 VNodevnode = new VNode(config.parsePlatformTagName(tag), data, children,undefined, undefined, context)} else if ((!data || !data.pre) && isDef(Ctor = resolveAsset(context.$options, 'components', tag))) {// 是为已注册的组件名,则通过 createComponent 创建一个组件类型的 VNode// componentvnode = createComponent(Ctor, data, context, children, tag)} else {// 否则创建一个未知的标签的 VNode// unknown or unlisted namespaced elements// check at runtime because it may get assigned a namespace when its// parent normalizes childrenvnode = new VNode(tag, data, children,undefined, undefined, context)}
} else {
// 如果是 tag 一个 Component 类型,则直接调用 createComponent 创建一个组件类型的 VNode 节点。// 这里就是通过createElement 创建组件// 本质上它还是返回了一个 VNode。// direct component options / constructorvnode = createComponent(tag, data, context, children)
}
if (Array.isArray(vnode)) {return vnode
} else if (isDef(vnode)) {
if (isDef(ns)) applyNS(vnode, ns)if (isDef(data)) registerDeepBindings(data)return vnode
} else {
return createEmptyVNode()
}
}
_createElement这个函数可以提供创建元素和创建组件两个功能。但是我们这里主要看创建元素的功能
// src/core/vdom/crate-element.js// 创建空元素export const createEmptyVNode = (text: string = '') => {const node = new VNode()node.text = textnode.isComment = truereturn node}
_createElement 方法有 5 个参数:
- context 表示 VNode 的上下文环境,它是 Component 类型;
- tag 表示标签,它可以是一个字符串,也可以是一个 Component;
- data 表示 VNode 的数据,它是一个 VNodeData 类型,可以在 flow/vnode.js 中找到他的定义;
- children 表示当前 VNode 的子节点,它是任意类型的,接下来需要被规范为标准的 VNode 数组;
- normalizationType 表示子节点规范的类型,类型不同规范的方法也就不一样,它主要是参考 render 函数是编译生成的还是用户手写的。
children 的规范化
- 由于 Virtual DOM 实际上是一个树状结构,每一个 VNode 可能会有若干个子节点,这些子节点应该也是 VNode 的类型。_createElement 接收的第 4 个参数 children 是任意类型的,因为就需要把它们规范成 VNode 类型。
这里会根据 normalizationType 的不同,调用了 normaliza(children) 和 simpleNormalizeChildren(children) 方法,定义在 src/core/vdom/helpers/normalzie-children.js 中:
// The template compiler attempts to minimize the need for normalization by
// statically analyzing the template at compile time.
//
// For plain HTML markup, normalization can be completely skipped because the
// generated render function is guaranteed to return Array. There are
// two cases where extra normalization is needed:// 1. When the children contains components - because a functional component
// may return an Array instead of a single root. In this case, just a simple
// normalization is needed - if any child is an Array, we flatten the whole
// thing with Array.prototype.concat. It is guaranteed to be only 1-level deep
// because functional components already normalize their own children.
// 当子节点包含组件时 - 因为功能组件可能返回一个数组而不是单个根节点元素。
// 在这种情况下,只需要一个简单的规范化——如果有任何子节点是一个数组,
// 我们用 Array.prototype.concat 将整个事物展平。
// 它保证只有 1 级深度,因为功能组件已经规范了他们自己的子元素。
export function simpleNormalizeChildren (children: any) {
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {if (Array.isArray(children[i])) {return Array.prototype.concat.apply([], children)}
}
return children
}// 2. When the children contains constructs that always generated nested Arrays,
// e.g. ,, v-for, or when the children is provided by user
// with hand-written render functions / JSX. In such cases a full normalization
// is needed to cater to all possible types of children values.
// 2. 当子元素包含总是生成嵌套数组的构造时,例如 、、v-for
// 或当子元素是由用户提供的手写渲染函数 / JSX 时。
// 在这种情况下,需要完全规范化以迎合所有可能类型的子值。
export function normalizeChildren (children: any): ?Array{
return isPrimitive(children)? [createTextVNode(children)] : Array.isArray(children) ? normalizeArrayChildren(children) : undefined}
simpleNormalizeChildren 方法调用了场景是 render 函数当函数是编译生成的。理论上编译生成的 children 都已经是 VNode 类型的,但是这里会有一些例外的情况,就是 functional component 函数式组件返回的是一个数组而不是一个根节点,所有会通过 Array.prototype.concat 方法把整个 children 数组打平,让它的深度只有一层。
normalizeChildren 方法的调用场景有 2 中,一个场景是 render 函数是用户手写的,当 children 只有一个节点的时候,Vue 从接口层面允许用户把 children 写成基础类型用来创建单个简单的文本节点,这种情况下回调用 createTextVNode 创建一个文本节点的 VNode;另一个场景就是当编译 slot、 v-for 的时候回产生嵌套数组的情况,回调用 normalizeArrayChildren 方法,先来看一下它是怎么实现的:
function normalizeArrayChildren (children: any, nestedIndex?: string): Array<VNode> { const res = [] let i, c, lastIndex, last for (i = 0; i < children.length; i++) { c = children[i] if (isUndef(c) || typeof c === 'boolean') continue lastIndex = res.length - 1 last = res[lastIndex] // 如果是一个数组类型,则递归调用 normalizeArrayChildren; // nested if (Array.isArray(c)) { if (c.length > 0) { c = normalizeArrayChildren(c, `${ nestedIndex || ''}_${ i}`) // merge adjacent text nodes if (isTextNode(c[0]) && isTextNode(last)) { res[lastIndex] = createTextVNode(last.text + (c[0]: any).text) c.shift() } res.push.apply(res, c) } } else if (isPrimitive(c)) { // 如果是基础类型,则通过 createTextVNode 方法转换成 VNode 类型;否则就已经是 VNode 类型了 if (isTextNode(last)) { // merge adjacent text nodes // this is necessary for SSR hydration because text nodes are // essentially merged when rendered to HTML strings res[lastIndex] = createTextVNode(last.text + c) } else if (c !== '') { // convert primitive to vnode res.push(createTextVNode(c)) } } else { // 如果 children 是一个列表并且列表还存在嵌套的情况,则根据 nestedIndex 去更新它的 key if (isTextNode(c) && isTextNode(last)) { // merge adjacent text nodes res[lastIndex] = createTextVNode(last.text + c.text) } else { // default key for nested array children (likely generated by v-for) if (isTrue(children._isVList) && isDef(c.tag) && isUndef(c.key) && isDef(nestedIndex)) { c.key = `__vlist${ nestedIndex}_${ i}__` } res.push(c) } } } return res }normalizeArrayChildren 接收 2 个参数,children 表示要规范的子节点,nestedIndex 表示嵌套的索引,因为单个 child 可能是一个数组类型。normalizeArrayCHildren 主要的逻辑就是遍历 children,获得单个节点 c,然后对 c 的类型判断
- 如果是一个数组类型,则递归调用 normalizeArrayChildren;
- 如果是基础类型,则通过 createTextVNode 方法转换成 VNode 类型;否则就已经是 VNode 类型了
- 如果 children 是一个列表并且列表还存在嵌套的情况,则根据 nestedIndex 去更新它的 key。
还有需要注意的是,在遍历过程中,对着 3 种情况都做了以下处理: 若果存在两个连续的 text 节点,会把他们合并成一个 text 节点。
经过对 children 的规范化,children 变成了一个类型为 VNode 的 Array。
四、具体实现及代码
1、第一步:创建需要自定义列表头的table
<u-table v-if="tableName === 'account'" ref="elTable" use-virtual :row-height="20" :height="getHeight()" :highlightCurrentRow="false" :data="dataList" v-loading="loading" row-key="id" @header-dragend="doLayout" :default-sort="defaultSort" :border="border" @selection-change="selectionChange" @select-all="selectAll" default-expand-all :treeConfig="treeConfig" style="border: 1px solid #ccc; width: 100%" :row-style="rowClass" > <u-table-column prop="" label=" " width="1" min-width="1" align="center" fixed="left" :tree-node="true" ></u-table-column> <u-table-column prop="No" label=" " width="50" min-width="50" fixed="left" align="center" ></u-table-column> <u-table-column type="selection" v-if="columnSelection" align="center" :selectable="selectable" fixed="left" ></u-table-column> <u-table-column header-align="center" align="center" label="操作" width="80" min-width="80" fixed="left" > <template slot-scope="scope"> <div> <el-button type="text" size="small" @click="addFn(scope.row)" :style="{ display: scope.row.isMatch === false ? 'block' : 'none', color: scope.row.isAddFn === false ? '' : 'blue', fontWeight: scope.row.isAddFn === false ? '' : 'bold', }" >添加</el-button > </div> <div> <el-button type="text" size="small" @click="deleteFn(scope.row)" style="color: red" :style="{ display: scope.row.isMatch === false ? 'none' : 'block', }" >删除 / { { scope.row.assetIndex }}</el-button > </div> </template> </u-table-column> <!-- :formatter="column.formatter" --> <u-table-column v-if="getShow(column)" v-for="(column, index) in tableColumns" :key="index" :width="column.width" :min-width="column.width" :align="column.align" header-align="center" :label="column.label" :fixed="column.isFrozen" :render-header="column.isRenderHeader ? column.renderHeader : normalRender" sortable :prop="column.prop" > <template slot-scope="scope"> <span v-text=" fieldFormatter( scope.row, column.prop, scope.row[column.prop], column.type ) " ></span> </template> </u-table-column> </u-table>二、第二步:创建自定义组件封装el-popover
<template> <div class="tooltip"> <!--<el-tooltip effect="dark" placement="top"> <div slot="content"> <p> { { column.label}} </p> </div> <i class="el-icon-question tooltipIcon" ></i> </el-tooltip>--> <el-popover placement="top-start" title="标题" width="400" trigger="hover" v-model="visible" content="资产编码查询"> <!-- 输入类型 --> <!-- <p>{ { column}}</p> --> <el-row> <el-col :span="20"> <el-input v-model="accountParams[column.property]" :placeholder="'请输入' + `${column.label}`" @input="changeVal" clearable v-if="queryType === 1" ></el-input> <!-- 日期类型 --> <el-date-picker v-model="accountParams[column.property]" clearable type="month" value-format="yyyy-MM" placeholder="选择日期" v-if="queryType === 2" > </el-date-picker> </el-col> <el-col :span="4"> <div class="search-button"> <el-button type="primary" @click="searchAccount()" >搜 索</el-button > </div> </el-col> </el-row> <el-button slot="reference" circle style="padding: 4px; top:4px;" icon="el-icon-search" @click="click" > </el-button> </el-popover> </div> </template> <script> export default { props:{ columnIndex: { // 序号 type: Number, default: 0, }, column: { // 选择框 type: Object, default: () => [], }, queryType: { type: Number, default: 0, } }, data() { return { visible: false, accountParams: { }, isSub: false, keepSub: false, } }, methods: { click() { this.accountParams = { } this.$emit('search', '1') this.visible = !this.visible }, changeVal() { if (this.isSub) { this.isSub = '1' this.$emit('search', this.isSub) } }, searchAccount() { const emitValue = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.accountParams)); this.$emit('getValue', emitValue) if (this.isSub !== '2') { this.isSub = '2' this.$emit('search', this.isSub) } else { this.isSub = '3' this.$emit('search', this.isSub) } } }, }; </script> <style lang="scss" scope> .tooltip { top: 4px; line-height: 100% !important; } .tooltipIcon { color: #409eff; // margin-left: 5px; line-height: 100%; font-size: 15px; } .search-button { margin-left: 12px; } </style>三、局部注册组件并手写createElement
import w from "@/utils/tableWidth"; import Vue from 'vue' import columnCheckTip from './columnCheckTip' Vue.component('check-tip', columnCheckTip) const searchValue = new Object() /* 财务账明细 */ export const accountDataCol = [ { label: "资产编号", prop: "code", align: "left", isShow: true, isFrozen: false, width: w.checkTip, sortable: "custom", isRenderHeader: true, renderHeader: function(h, { column, $index }) { const _this = this return h( 'div', { style: 'line-height: 100%; display: inline-block; padding: 0px' }, [ h('span', { // style:'color:#409eff;', domProps: { innerHTML: column.label } }), h('check-tip', { props: { column: column, columnIndex: $index, queryType: 1 }, on: { getValue: function (value) { console.log(searchValue, value); Vue.set(searchValue, 'value', value) }, search(value) { console.log(searchValue, value); Vue.set(searchValue, 'search', value) } } }) ], ); } }, { label: "资产名称", prop: "name", align: "left", isShow: true, isFrozen: false, width: w.name, sortable: "custom", isRenderHeader: true, renderHeader: function(h, { column, $index }) { const _this = this return h( 'div', { style: 'line-height: 100%; display: inline-block; padding: 0px' }, [ h('span', { // style:'color:#409eff;', domProps: { innerHTML: column.label } }), h('check-tip', { props: { column: column, columnIndex: $index, queryType: 1 }, on: { getValue: function (value) { Vue.set(searchValue, 'value', value) }, search(value) { Vue.set(searchValue, 'search', value) } } }) ], ); } }, { label: "规格型号", prop: "modelDesc", align: "right", isShow: true, isFrozen: false, width: w.modelDesc, sortable: "custom" }, { label: "使用人", prop: "userUserName", align: "right", isShow: true, isFrozen: false, width: w.createUserName, sortable: "custom" }, { label: "存放地点", prop: "locationName", align: "right", isShow: true, isFrozen: false, width: w.locationName, sortable: "custom" }, { label: "取得日期", prop: "getDate", align: "center", isShow: true, isFrozen: false, width: w.createTime, type: "time", sortable: "custom" }, { label: "一级分类", prop: "maxClassName", align: "left", isShow: false, isFrozen: false, width: w.classMaxName, sortable: "custom" }, { label: "末级分类", prop: "minClassName", align: "left", isShow: false, isFrozen: false, width: w.classMaxName, sortable: "custom" }, { label: "数量", prop: "assetCount", align: "right", isShow: false, isFrozen: false, width: w.assetCount, sortable: "custom" }, { label: "使用状况", prop: "useStatus", align: "right", isShow: false, isFrozen: false, width: "130", sortable: "custom" }, { label: "使用部门", prop: "userDeptName", align: "right", isShow: false, isFrozen: false, width: w.createUserName, sortable: "custom" }, { label: "备注", prop: "comments", align: "right", isShow: false, isFrozen: false, width: "130" }, { label: "盘点日期", prop: "checkTime", align: "center", isShow: false, isFrozen: false, width: w.actionEndTime, type: "time" } ]; export { searchValue }至于具体实现,每个公司的架构不同,仅供参考
五、扩展知识点
1、Vue源码9个基础方法
基础判断
function isUndef(v) { return v === undefined || v === null } function isDef(v) { return v !== undefined && v !== null } function isTrue(v) { return v === true } function isFalse(v) { return v === false }检查是否是原始值
function isPrimitive(value) { return ( typeof value === 'string' || typeof value === 'number' || // $flow-disable-line typeof value === 'symbol' || typeof value === 'boolean' ) }快速对象检查
function isObject(obj) { return obj !== null && typeof obj === 'object' }获取值的原始类型字符串
var _toString = Object.prototype.toString; function toRawType(value) { return _toString.call(value).slice(8, -1) }严格的对象类型检查
function isPlainObject(obj) { return _toString.call(obj) === '[object Object]' }严格的正则类型检查
function isRegExp(v) { return _toString.call(v) === '[object RegExp]' }检查是否是有效的数组下标
function isValidArrayIndex(val) { var n = parseFloat(String(val)); return n >= 0 && Math.floor(n) === n && isFinite(val) }值转换为实际的字符串
function toString(val) { return val == null ? '' : Array.isArray(val) || (isPlainObject(val) && val.toString === _toString) ? JSON.stringify(val, null, 2) : String(val) }值转换为数字以进行持久化
function toNumber(val) { var n = parseFloat(val); return isNaN(n) ? val : n }






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...