Data Structure--二叉树例题解析(2)--二叉树前序遍历--二叉树中序遍历--二叉树后序遍历
二叉树例题解析2
- 二叉树前序遍历 递归
- 二叉树前序遍历 非递归
- 二叉树中序遍历 非递归
- 二叉树后序遍历 非递归
这里的三种遍历方法和之前讲的 遍历方法也有关,有兴趣可以回顾一下.
二叉树前序遍历 递归
我只写了前序遍历的递归方式,但是只要你将前序的掌握了,后面两种的递归方式也是大同小异,大家自己写哦.
int getSize(struct TreeNode* root){ //求大小的函数if (root){return getSize(root->left) + getSize(root->right) + 1;}return 0;}void preorder(struct TreeNode* root, int* arr, int* idx){if (root){arr[*idx] = root->val; //核心 将值进行赋予,并进行递归的操作(*idx)++;preorder(root->left, arr, idx); //左子树preorder(root->right, arr, idx); //右子树}}int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){int sz = getSize(root); //先求长int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*sz); //动态开辟int idx = 0;preorder(root, arr, &idx); //函数调用*returnSize = idx; //更新return arr; //输出}
二叉树前序遍历 非递归
调用了栈的操作,接口我就不多描述了, 具体点击
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){int sz = getSize(root); //先求长int* arr = malloc(sizeof(int)*sz); //动态开辟stack st; //栈开辟stackInit(&st); //初始化int idx; //定义整型变量//当前遍历的节点不为空,或栈不为空while (root || !stackEmpty(&st)){//1.访问左边路径while (root){ //1.====前序arr[idx++] = root->val;//当前节点入栈stackPush(&st, root); //2.====先访问左子树root = root->left;}//2.获取栈顶元素,访问右子树root = stackTop(&st); //3.====再头结点,并出栈stackPop(&st);root = root->right; //4.====再访问右子树}*returnSize = idx;return arr; //返回值}
二叉树中序遍历 非递归
大题思路一致,只是访问的先后次序发生了变化
int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){int sz = getSize(root); //得到大小int* arr = malloc(sizeof(int)*sz); //动态开辟stack st; //创建栈stackInit(&st); //初始化int idx = 0;while (root || !stackEmpty(&st)){ //存在并不为空的条件下开始循环//1.====中序遍历//1.先遍历左边while (root){stackPush(&st, root); //2.====左子树root = root->left;}//2.获取栈顶元素root = stackTop(&st); //3.====栈顶stackPop(&st);arr[idx++] = root->val;//3.访问右子树root = root->right; //4.====右子树}*returnSize = idx;return arr;}
二叉树后序遍历 非递归
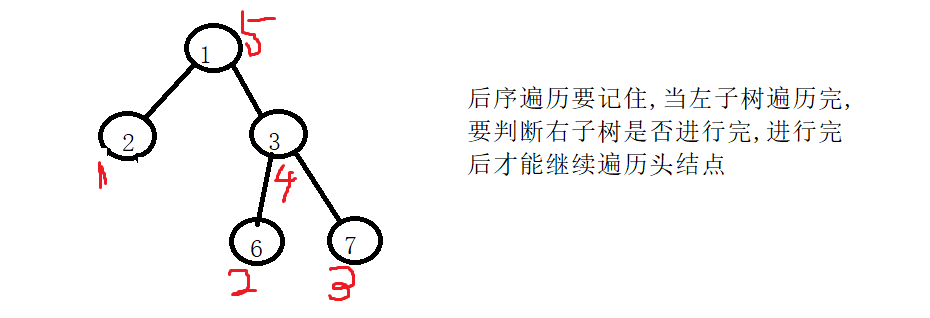
int* postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){int sz = getSize(root);int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*sz);stack st;stackInit(&st);int idx = 0;//prev:上次访问记得节点位置struct TreeNode* prev = NULL;while (root || !stackEmpty(&st)){//1.遍历左路径while (root){stackPush(&st, root); //1.====左子树root = root->left;}//top:栈顶的节点struct TreeNode* top = stackTop(&st);//这里要进行判断是否能访问栈顶//条件:没有右子树或者右子树访问完毕if (top->right == NULL || top->right == prev){ //2.====判断是否为头结点//访问栈顶元素arr[idx++] = top->val;stackPop(&st);prev = top;}else//访问右子树root = top->right; //3.====右子树}*returnSize = idx;return arr;}
主要还是这个后序遍历比较难一点,前面的都好理解,大家注意理解后序遍历访问了头结点但是没有进行出栈,而是先考虑右子树,再反回去对头结点进行出栈操作,注意理解思路.
做敲代码,大家一起加油!!!马上开学了,我们也要努力每天敲代码哦!!!





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...