Spring Profile 与SpringBoot Profile使用
在实际开发中,有一个比较大的挑战就是将程序从一个环境迁移或切换到另一个环境。我们知道,测试或开发环境与正式或生产环境中的某些配置是不同的,如:数据库配置、加密算法等。所以传统的做法就是每次发布或测试时,都手动修改相关配置信息,十分繁琐和低效率,并且在发布时容易忽略修改的信息导致环境切换不正确。虽然,在早期时,我们可以在服务器存放配置信息,然后通过程序动态读取配置,但这样作的效率、灵活性及安全方面不是和好,所以鉴于这些问题,Spring在3.1版引入了BeanProfile的功能,它的产生可以完美的解决上面的问题,那么就进入正文吧!
l Profile工作原理
l Profile如何使用
一、Profile工作原理
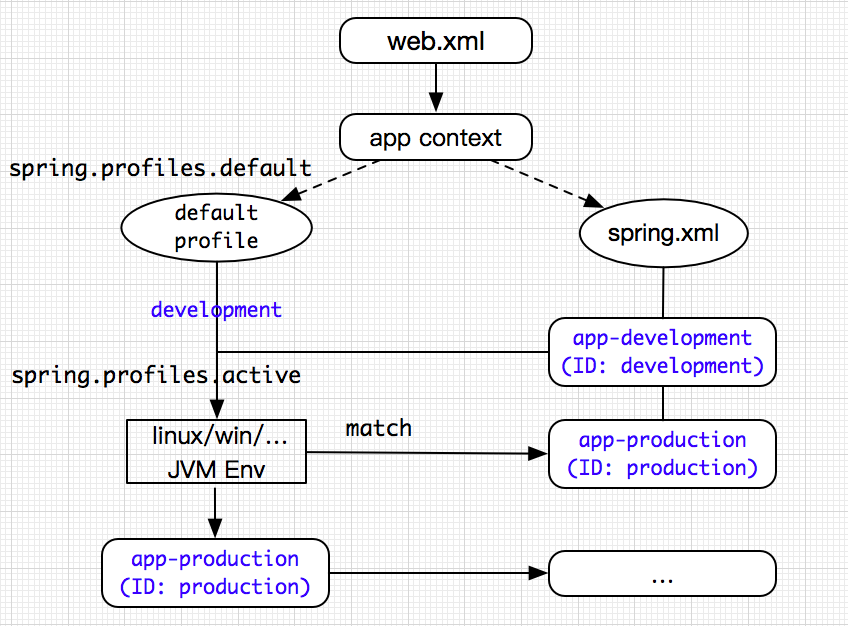
如图所示,我们以web应用为例说明,web.xml是web应用程序的入口,并且需要在这个文件中配置spring.xml和指定默认访问的profile环境属性。对于spring.xml,这里就不多做说明,它主要是一些bean的声明文件,也包括profile的bean声明,稍后在第二部分会详细说明。而对于spring.profiles.default,这里需要说明下:在Spring的Profile中,Profile存在两种状态,一种为默认加载的profile(spring.profiles.default),一种为指定激活的profile(spring.profiles.active)。如果程序未指定active状态的profile,那么执行default状态的profile,如果两种状态都指定,则优先执行或选择active状态的profile。所以如果我们在生产服务器中,指定环境变量spring.profiles.active=production,而web.xml默认为default状态的profile,所以程序不论部署到测试或生产哪个环境,程序都可以通过检索匹配对应服务器中的JVM 参数spring.profiles.active所指定的值来适配对应环境的配置信息,这就是Profile的基本原理!
二、Profile如何使用
这里不做Spring及maven的基础知识介绍,只罗列Profile的使用流程及需要注意的地方,具体如下所示:
1、web.xml
默认上下文中,添加spring.profiles.default的配置,如下:
<param-name>spring.profiles.default</param-name><param-value>development</param-value>
网上有说,需要在Servlet设置中也添加该配置,实际上不需要该操作,本人已经验证,也希望各位也自行验证下,以便牢记!
2、spring.xml
在spring容器中,添加对应profile的bean,以便程序运行时,根据环境变量设置的环境值,选择对应的profile执行,具体如下:
<context:property-placeholderlocation=*"classpath:app-development.properties"*/><util:propertiesid=*"app"*location=*"classpath:app-development.properties"*/>
<context:property-placeholderlocation=*"classpath:app-production.properties"*/><util:propertiesid=*"app"*location=*"classpath:app-production.properties"*/>
需要特别注意的是,上面的两个beans配置,需要放在其它bean配置的后面,建议将beans配置放在最下面设置。
三,SpringBoot JavaConfig 使用
Profile是什么
Profile我也找不出合适的中文来定义,简单来说,Profile就是Spring Boot可以对不同环境或者指令来读取不同的配置文件。
Profile使用
假如有开发、测试、生产三个不同的环境,需要定义三个不同环境下的配置。
基于properties文件类型
你可以另外建立3个环境下的配置文件:
applcation.properties
application-dev.properties
application-test.properties
application-prod.properties
然后在applcation.properties文件中指定当前的环境:
spring.profiles.active=test
这时候读取的就是application-test.properties文件。
基于yml文件类型
只需要一个applcation.yml文件就能搞定,推荐此方式。
spring:profiles:active: prod---spring:profiles: devserver:port: 8080---spring:profiles: testserver:port: 8081---spring.profiles: prodspring.profiles.include:- proddb- prodmqserver:port: 8082---spring:profiles: proddbdb:name: mysql---spring:profiles: prodmqmq:address: localhost
此时读取的就是prod的配置,prod包含proddb,prodmq,此时可以读取proddb,prodmq下的配置。
也可以同时激活三个配置。
spring.profiles.active: prod,proddb,prodmq
基于Java代码
在JAVA配置代码中也可以加不同Profile下定义不同的配置文件,@Profile注解只能组合使用@Configuration和@Component注解。
@Configuration@Profile("prod")public class ProductionConfiguration {// ...}
指定Profile
main方法启动方式:
// 在Eclipse Arguments里面添加--spring.profiles.active=prod
插件启动方式:
spring-boot:run -Drun.profiles=prod
jar运行方式:
java -jar xx.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod
除了在配置文件和命令行中指定Profile,还可以在启动类中写死指定,通过SpringApplication.setAdditionalProfiles方法。
SpringApplication.class
public void setAdditionalProfiles(String... profiles) {this.additionalProfiles = new LinkedHashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(profiles));}





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...