Spring中用到的几种典型的设计模式
Spring 框架中用到的设计模式非常多,不下十几种。本文只挑选几种典型的来解析。
适配器模式应用在Spring MVC中
Spring MVC定义一个Controller最常用的方式是,通过@Controller注解来标记某个类是Controller类,通过@RequesMapping注解来标记函数对应的URL。不过,定义一个Controller远不止这一种方法。我们还可以通过让类实现Controller接口或者Servlet接口,来定义一个 Controller。这三种定义方式示例代码,如下所示:
//方法一:通过@Controller、@RequestMapping来定义@Controllerpublic class DemoController {@RequestMapping("/getUserName")public ModelAndView getUserName() {ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView("Greeting");model.addObject("message", "TOM");return model;}}//方法二:实现Controller接口 + xml配置文件:配置DemoController与URL的对应关系public class DemoControllerImpl implements Controller {@Overridepublic ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView("HelloWorld");model.addObject("message", "HelloWorld");return model;}}//方法三:继承HttpServlet抽象类 + xml配置文件:配置DemoExtendServletController类与URL的对应关系public class DemoExtendServletController extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {this.doPost(req, resp);}@Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {resp.getWriter().write("Hello World!");}}
在应用启动的时候,Spring容器会加载这些Controller类,并且解析出URL对应的处理函数,封装成Handler对象,存储到HandlerMapping对象中。当有请求到来的时候,DispatcherServlet从HanderMapping中,查找请求URL对应的Handler,然后调用执行Handler对应的函数代码,最后将执行结果返回给客户端。
但是不同方式定义的Controller,其函数的定义(函数名、入参、返回值等)是不统一的。方法一中的函数的定义很随意、不固定,方法二中的函数定义是 handleRequest()、方法三中的函数定义是HttpServlet的service()方法(实际上这里用到了模板方法模式,Servlet中的service()调用了doGet()或doPost()方法,DispatcherServlet调用的是service()方法)。
DispatcherServlet需要根据不同类型的Controller,调用不同的函数,下面是伪代码:
Handler handler = handlerMapping.get(URL);if (handler instanceof Controller) {((Controller)handler).handleRequest();} else if (handler instanceof Servlet) {((Servlet)handler).service(...);} else if (handler.getClass().getAnnotation(Controller.class) != null) {//反射调用RequestMapping修饰的方法...}
这种实现方式会有很多if-else分支判断,而且,如果要增加一个新的 Controller的定义方法,我们就要在DispatcherServlet类代码中,对应地增加一段如上伪代码所示的if逻辑,这显然不符合开闭原则。
可以利用是适配器模式对代码进行改造,让其满足开闭原则,能更好地支持扩展,适配器其中一个作用是“统一多个类的接口设计”。利用适配器模式,我们将不同方式定义的Controller类中的函数适配为统一的函数定义。这样,我们就能在DispatcherServlet类代码中,移除掉if-else分支判断逻辑,调用统一的函数。
来具体看下Spring的代码实现。Spring定义了统一的接口HandlerAdapter,并且对每种Controller定义了对应的适配器类。这些适配器类包括:AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter、SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter、SimpleServletHandlerAdapter等,源码如下。
//统一的controller处理器适配接口public interface HandlerAdapter {boolean supports(Object var1);ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest var1, HttpServletResponse var2, Object var3) throws Exception;long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest var1, Object var2);}// 对应实现Controller接口的Controllerpublic class SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter {public SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter() {}@Overridepublic boolean supports(Object handler) {return handler instanceof Controller;}@Overridepublic ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {return ((Controller)handler).handleRequest(request, response);}@Overridepublic long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest request, Object handler) {return handler instanceof LastModified ? ((LastModified)handler).getLastModified(request) : -1L;}}// 对应实现Servlet接口的Controllerpublic class SimpleServletHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter {public SimpleServletHandlerAdapter() {}@Overridepublic boolean supports(Object handler) {return handler instanceof Servlet;}@Overridepublic ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {((Servlet)handler).service(request, response);return null;}//省略...}//AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter对应通过注解实现的Controller,public class AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter extends WebContentGeneratorimplements HandlerAdapter, Ordered, BeanFactoryAware {@Overridepublic boolean supports(Object handler) {return getMethodResolver(handler).hasHandlerMethods();}@Overridepublic ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)throws Exception {Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handler);Boolean annotatedWithSessionAttributes = this.sessionAnnotatedClassesCache.get(clazz);if (annotatedWithSessionAttributes == null) {annotatedWithSessionAttributes = (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(clazz, SessionAttributes.class) != null);this.sessionAnnotatedClassesCache.put(clazz, annotatedWithSessionAttributes);}if (annotatedWithSessionAttributes) {checkAndPrepare(request, response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers, true);} else {checkAndPrepare(request, response, true);}//...省略return invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handler);}//...省略}
在DispatcherServlet类中,我们就不需要区分对待不同的Controller对象了,统一调用HandlerAdapter的handle()函数就可以了,这样就没有烦人的if-else逻辑了。以下摘抄Spring-web-mvc-5.1.14.RELEASE-sources.jar中的DispatcherServlet类中与HandlerAdapter相关的部分核心代码,可以看到在容器启动后,通过调用initHandlerAdapters()函数获取context中的类型为HandlerAdapter的bean列表,在doDispatch()函数中会根据当前handler的类型,挑选出合适的适配器。
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {/** List of HandlerAdapters used by this servlet. */@Nullableprivate List<HandlerAdapter> handlerAdapters;/** Detect all HandlerAdapters or just expect "handlerAdapter" bean?. */private boolean detectAllHandlerAdapters = true;//省略大部分属性....protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);try {ModelAndView mv = null;Exception dispatchException = null;try {processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);// Determine handler for the current request.mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);if (mappedHandler == null) {noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);return;}// Determine handler adapter for the current request.HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());//中间部分省略...// Actually invoke the handler.mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());//各种catch异常的逻辑省略...}}//获取适配器,找到第一个匹配的就返回protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {if (adapter.supports(handler)) {return adapter;}}}throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");}@Overrideprotected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {initStrategies(context);}protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {//省略...initHandlerAdapters(context);//省略...}//初始化适配器列表private void initHandlerAdapters(ApplicationContext context) {this.handlerAdapters = null;if (this.detectAllHandlerAdapters) {// Find all HandlerAdapters in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.Map<String, HandlerAdapter> matchingBeans =BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerAdapter.class, true, false);if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {this.handlerAdapters = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());// We keep HandlerAdapters in sorted order.AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerAdapters);}}//以下省略...}}
策略模式的应用
Spring中的AOP是通过动态代理来实现的。具体到代码实现,Spring支持两种动态代理实现方式,一种是JDK提供的动态代理实现方式,另一种是Cglib提供的动态代理实现方式。前者需要被代理的类有抽象的接口定义,后者不需要。针对不同的被代理类,Spring会在运行时动态地选择不同的动态代理实现方式。
动态选择代理策略,这里就用到了策略模式。策略模式包含三部分,策略的定义、创建和使用。具体到Spring中的策略模式,策略的定义这一部分很简单,我们只需要定义一个策略接口,让不同的策略类都实现这一个策略接口。对应到Spring的源码AopProxy是策略接口,JdkDynamicAopProxy、CglibAopProxy是两个实现了AopProxy接口的策略类。其中,AopProxy接口的定义如下所示:
public interface AopProxy {Object getProxy();Object getProxy(ClassLoader var1);}
策略的创建一般通过工厂方法来实现。对应到Spring源码,AopProxyFactory是一个工厂类接口,DefaultAopProxyFactory是一个默认的工厂类,用来创建AopProxy对象。两者的源码如下所示:
public interface AopProxyFactory {AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport var1) throws AopConfigException;}public class DefaultAopProxyFactory implements AopProxyFactory, Serializable {@Overridepublic AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {//optimized默认是false || proxy-target-class=true || 没有接口if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();if (targetClass == null) {throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");}//被代理类是接口,创建JDK代理if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);}else {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}}/** * Determine whether the supplied {@link AdvisedSupport} has only the * {@link org.springframework.aop.SpringProxy} interface specified * (or no proxy interfaces specified at all). */private boolean hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(AdvisedSupport config) {Class<?>[] ifcs = config.getProxiedInterfaces();return (ifcs.length == 0 || (ifcs.length == 1 && SpringProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(ifcs[0])));}}
策略模式的典型应用场景,一般是通过环境变量、状态值、计算结果等动态地决定使用哪个策略。对应到Spring源码中,我们可以参看刚刚给出的DefaultAopProxyFactory类中的createAopProxy()函数的代码实现。其中包含了多处if-else分支,用来判断要用哪种策略生成代理类。
Spring对观察者模式的实现
Java及Google Guava都提供了观察者模式的实现框架。Java 提供的框架比较简单,只包含java.util.Observable和java.util.Observer两个类。Google Guava提供的框架功能比较完善和强大:通过EventBus事件总线来实现观察者模式,可以参见之前的博文观察者模式及EventBus框架简单实现去了解Guava是怎样实现观察者模式的。
实际上,Spring中的事件驱动模型也叫作发布订阅模式,是观察者模式的一个典型的应用。Spring中实现的观察者模式包含三部分:Event事件(相当于消息)、Listener 监听者(相当于观察者)、Publisher发送者(相当于被观察者)。我们通过一个例子来看下,Spring提供的观察者模式使用代码如下所示:
// Event事件public class DemoEvent extends ApplicationEvent {private String message;public DemoEvent(Object source, String message) {super(source);}public String getMessage() {return this.message;}}// Listener监听者@Componentpublic class DemoListener implements ApplicationListener<DemoEvent> {@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(DemoEvent demoEvent) {String message = demoEvent.getMessage();System.out.println(message);}}// Publisher发送者@Componentpublic class DemoPublisher {public void publishEvent(DemoEvent demoEvent) {SpringContext.getApplicationContext.publishEvent(demoEvent);}}// 创建一个Spring上下文bean,拿到ApplicationContext@Componentpublic class SpringContext implements ApplicationContextAware {private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;@Overridepublic void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {SpringContext.applicationContext = applicationContext;}public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {return applicationContext;}}
框架使用起来并不复杂,主要包含三部分工作:定义一个继承 ApplicationEvent的事件(DemoEvent);定义一个实现了 ApplicationListener的监听器(DemoListener);定义一个发送者(DemoPublisher),发送者调用ApplicationContext来发送事件消息。其中,ApplicationEvent和ApplicationListener的代码实现都非常简单,内部并不包含太多属性和方法。实际上,它们最大的作用是做类型标识之用:继承自ApplicationEvent的类是事件,实现了ApplicationListener的类是监听器。
在观察者模式中,观察者是需要事先注册到被观察者中的。那在Spring的实现中,观察者注册到了哪里呢?又是如何注册的呢?Spring把观察者注册到了ApplicationContext对象中。这里的ApplicationContext就相当于Google EventBus框架中的“事件总线”。不过ApplicationContext这个类并不只是为观察者模式服务的。它底层依赖BeanFactory(IOC 的主要实现类),提供应用启动、运行时的上下文信息。具体到源码来说,ApplicationContext只是一个接口,具体的代码实现包含在它的实现类AbstractApplicationContext中,该类中事件相关的代码摘抄如下:
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoaderimplements ConfigurableApplicationContext, DisposableBean {//....省略/** Helper class used in event publishing */private ApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster;/** Statically specified listeners */private final Set<ApplicationListener<?>> applicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<ApplicationListener<?>>();@Overridepublic void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {publishEvent(event, null);}@Overridepublic void publishEvent(Object event) {publishEvent(event, null);}protected void publishEvent(Object event, ResolvableType eventType) {Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Publishing event in " + getDisplayName() + ": " + event);}// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessaryApplicationEvent applicationEvent;if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;} else {applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<Object>(this, event);if (eventType == null) {eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();}}// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initializedif (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);} else {getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);}// Publish event via parent context as well...if (this.parent != null) {if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);} else {this.parent.publishEvent(event);}}}@Overridepublic void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {Assert.notNull(listener, "ApplicationListener must not be null");if (this.applicationEventMulticaster != null) {this.applicationEventMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);} else {this.applicationListeners.add(listener);}}// ApplicationEventMulticaster初始化protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {this.applicationEventMulticaster = beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");}} else {this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Unable to locate ApplicationEventMulticaster with name '" +APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME +"': using default [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");}}}protected void registerListeners() {// Register statically specified listeners first.for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);}// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);}// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) {for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);}}}//....省略}
从上面的代码中,我们发现,真正的消息发送以及观察者注册实际上是通过 ApplicationEventMulticaster这个类来完成的。这个类的源码我只摘抄最关键的一部分,也就是multicastEvent()这个消息发送函数。部分关键代码如下,它通过线程池,支持异步非阻塞、同步阻塞这两种类型的观察者模式。
public class SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster extends AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster {private Executor taskExecutor;public SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster() {}public void setTaskExecutor(Executor taskExecutor) {this.taskExecutor = taskExecutor;}protected Executor getTaskExecutor() {return this.taskExecutor;}@Overridepublic void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));}@Overridepublic void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));for (final ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();if (executor != null) {executor.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {invokeListener(listener, event);}});} else {invokeListener(listener, event);}}}}
借助Spring提供的观察者模式的骨架代码,如果我们要在Spring下实现某个事件的发送和监听,只需要做很少的工作:定义事件、定义监听器、往ApplicationContext中发送事件就可以了。剩下的工作都由Spring框架来完成。这体现了Spring框架的扩展性,也就是在不需要修改任何代码的情况下,扩展新的事件和监听。在Spring boot中可支持直接使用@EnableAsync、@EventListener等注解定义异步或同步监听器。
模板方法模式的应用
Java IO类库中的很多类都用到了模板方法模式,许多xxxxTemplate类都用到了回调模式,详情见模板方法模式与回调函数这篇博客。
职责链模式实现Spring Interceptor
职责链模式:将能够处理同一类请求的对象连成一条链,使这些对象都有机会处理请求,所提交的请求沿着链传递。从而避免请求的发送者和接受者之间的耦合关系。链上的对象逐个判断是否有能力处理该请求,如果能则就处理,如果不能,则传给链上的下一个对象,直到有一个对象处理它为止。
用一张生动一些的图来描述一下,就是下面这样。在公司中不同的岗位拥有不同的职责与权限。以上述的请假流程为例,当员工请 1天假时,只要组长审批就可以了,不需要流转到主管和总监。如果职责链上的某个环节无法处理当前的请求,在含有下个环节时,则会把请求转交给下个环节来处理。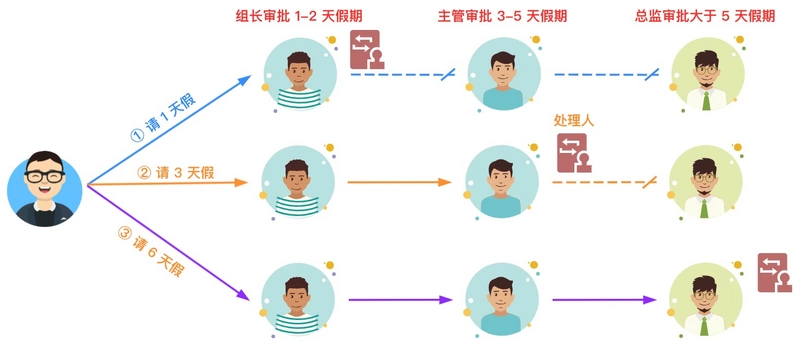
职责链的UML图如下: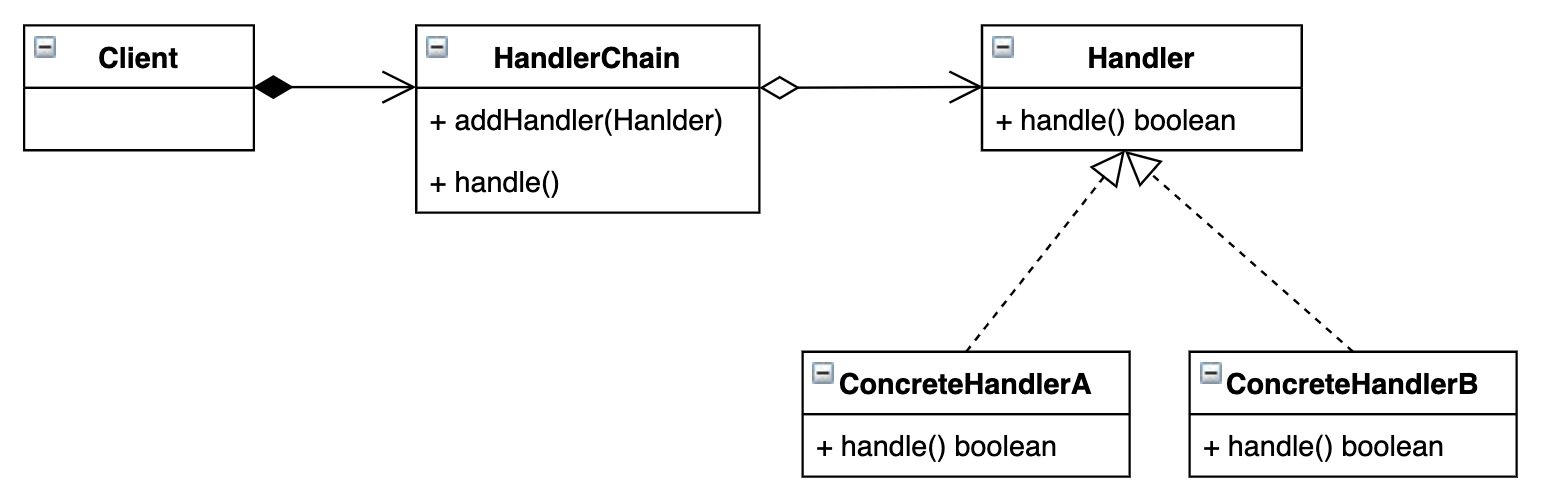
职责链模式的典型示例代码如下:
public interface IHandler {boolean handle();}public class HandlerA implements IHandler {@Overridepublic boolean handle() {boolean handleResult = false;//...return handleResult;}}public class HandlerB implements IHandler {@Overridepublic boolean handle() {boolean handleResult = false;//...return handleResult;}}public class HandlerChain {private List<IHandler> handlers = new ArrayList<>();public void addHandler(IHandler handler) {this.handlers.add(handler);}public void handle() {for (IHandler handler : handlers) {boolean handleResult = handler.handle();if (handleResult) {break;}}}}// 使用举例public class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {HandlerChain chain = new HandlerChain();chain.addHandler(new HandlerA());chain.addHandler(new HandlerB());chain.handle();}}
Spring框架中的Interceptor用来实现对HTTP请求进行拦截处理。它与Servlet Filter有所不同,Servlet Filter是Servlet规范的一部分,实现依赖于Web容器。Spring Interceptor是Spring MVC框架的一部分,由Spring MVC来提供实现。客户端发送的请求,会先经过Servlet Filter,然后再经过Spring Interceptor,最后到达具体的业务代码中。具体处理流程如下图所示:
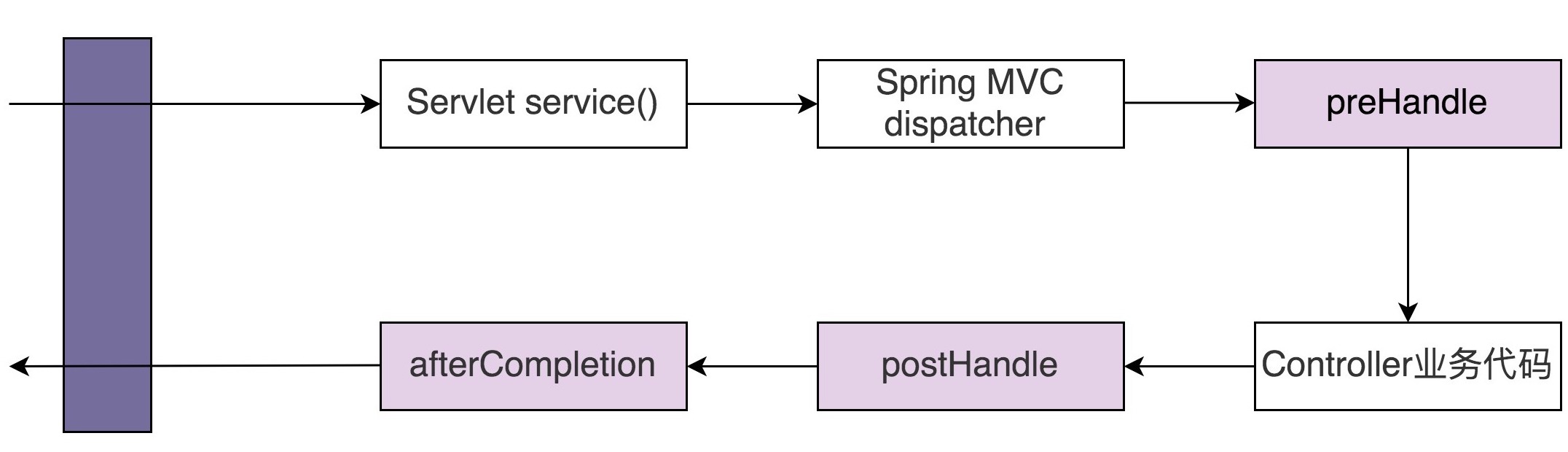
对应到Spring Interceptor的源码就是HandlerInterceptor接口和 HandlerExecutionChain。HandlerInterceptor接口源码如下, 对请求的拦截定义为preHandle()方法,对响应的拦截定义为postHandle()方法。
public interface HandlerInterceptor {boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)throws Exception;void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView)throws Exception;void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex)throws Exception;}
以下示例代码,写一个ControllerInterceptor类去实现HandlerInterceptor接口。
@Componentpublic class ControllerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {@Overridepublic boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {System.out.println("拦截客户端发送来的请求.");return true; // 继续后续的处理}@Overridepublic void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {System.out.println("拦截发送给客户端的响应.");}@Overridepublic void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {System.out.println("这里总是被执行.");}}
向Spring MVC框架配置自定义的ControllerInterceptor。
@Configurationpublic class WebMvcConfigurer extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {@Resourceprivate ControllerInterceptor controllerInterceptor;@Overridepublic void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {registry.addInterceptor(controlToolInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/**");super.addInterceptors(registry);}}
Spring Interceptor也是基于职责链模式实现的,HandlerExecutionChain类就是职责链模式中的处理器链。它的实现不需要使用递归,主要是因为它将请求和响应的拦截工作,拆分到了两个函数中去实现。HandlerExecutionChain的关键源码摘抄如下:
public class HandlerExecutionChain {private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(HandlerExecutionChain.class);private final Object handler;private HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors;private List<HandlerInterceptor> interceptorList;private int interceptorIndex = -1;public HandlerExecutionChain(Object handler) {this(handler, (HandlerInterceptor[]) null);}public HandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HandlerInterceptor... interceptors) {if (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain) {HandlerExecutionChain originalChain = (HandlerExecutionChain) handler;this.handler = originalChain.getHandler();this.interceptorList = new ArrayList<HandlerInterceptor>();CollectionUtils.mergeArrayIntoCollection(originalChain.getInterceptors(), this.interceptorList);CollectionUtils.mergeArrayIntoCollection(interceptors, this.interceptorList);} else {this.handler = handler;this.interceptors = interceptors;}}public void addInterceptor(HandlerInterceptor interceptor) {initInterceptorList().add(interceptor);}public void addInterceptors(HandlerInterceptor... interceptors) {if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {CollectionUtils.mergeArrayIntoCollection(interceptors, initInterceptorList());}}private List<HandlerInterceptor> initInterceptorList() {if (this.interceptorList == null) {this.interceptorList = new ArrayList<HandlerInterceptor>();if (this.interceptors != null) {// An interceptor array specified through the constructorCollectionUtils.mergeArrayIntoCollection(this.interceptors, this.interceptorList);}}this.interceptors = null;return this.interceptorList;}boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) {HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) {triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);return false;}this.interceptorIndex = i;}}return true;}void applyPostHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ModelAndView mv) throws Exception {HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {for (int i = interceptors.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];interceptor.postHandle(request, response, this.handler, mv);}}}void triggerAfterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Exception ex)throws Exception {HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {for (int i = this.interceptorIndex; i >= 0; i--) {HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];try {interceptor.afterCompletion(request, response, this.handler, ex);}catch (Throwable ex2) {logger.error("HandlerInterceptor.afterCompletion threw exception", ex2);}}}}}
在Spring框架中,DispatcherServlet的doDispatch()方法用来分发请求,它在真正的业务逻辑执行前后,会执行HandlerExecutionChain中的 applyPreHandle()和applyPostHandle()函数,用来实现对请求与响应的拦截功能。
职责链模式常用在框架开发中,用来实现框架的过滤器、拦截器功能,让框架的使用者在不需要修改框架源码的情况下,添加新的过滤拦截功能,体现了对扩展开放、对修改关闭的设计原则。





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...