JavaScript实现继承的几种方法
JavaScript实现继承的几种方法
原型链继承
prototype原型相当于一个对象的父类,所有实例都会共享原型上的属性和方法。
constructor构造函数相当于一个创建对象的函数,同时也是对象实例的标识符。bigApple,smallApple使用Apple作为构造函数,初始化就会使用Apple方法;同时这两个实例对象也属于Apple类。
// 原型链继承// fruit水果类function Fruit() {this.name = "水果";this.color = ["green"];}Fruit.prototype.sayName = function () {console.log(this.name);}function Apple() { };// 继承Apple.prototype = new Fruit(); // 设置对象原型为FruitApple.prototype.constructor = Apple; // 将构造函数改为Applevar bigApple = new Apple();var smallApple = new Apple();bigApple.sayName(); // 水果console.log(smallApple.name); // 水果
原理:重写子类的原型对象,将父类的方法和属性继承到子类上
具体原型链如下: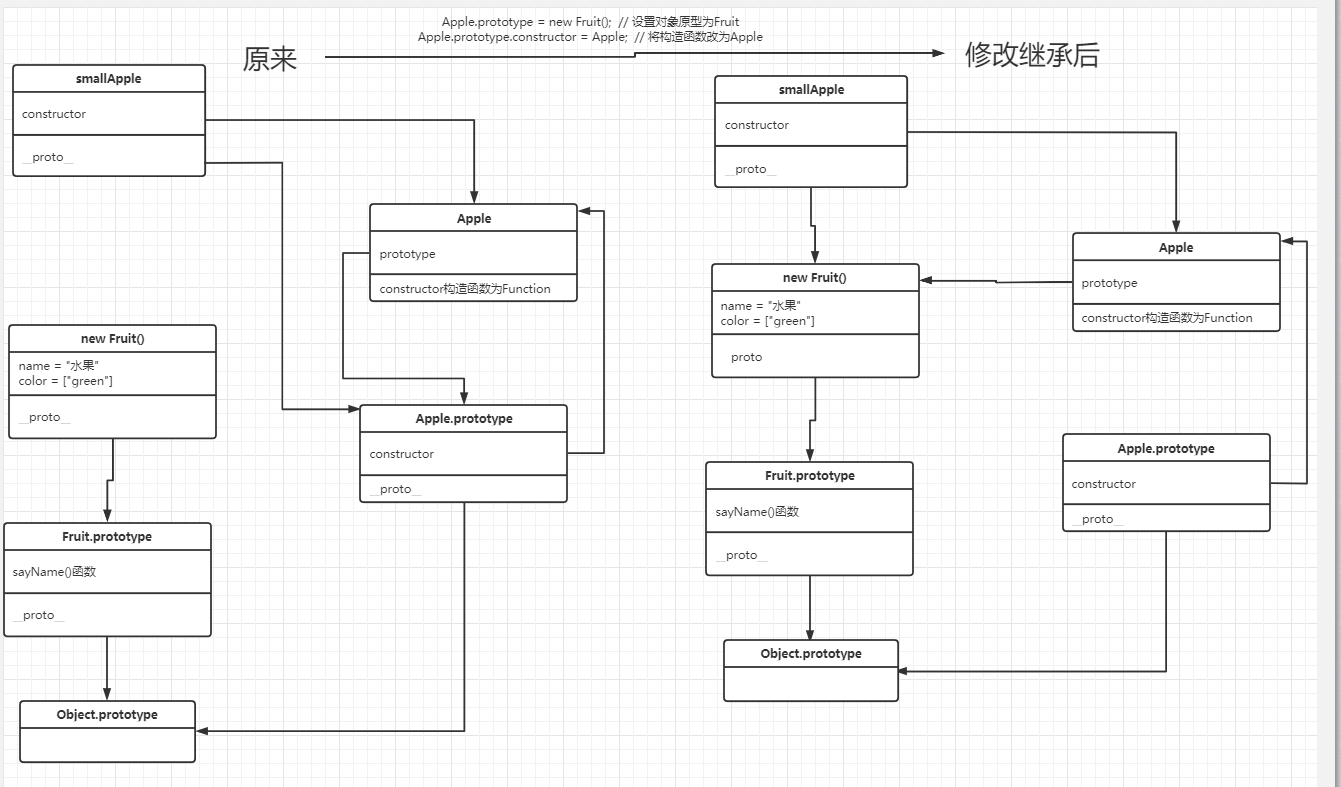
对比没有继承前和继承后的结果
缺点:
1.继承的Fruit实例会被所有Apple实例(bigApple,smallApple)所共享,如果原型上有引用类型(数组,对象),一旦修改,所有Apple实例的原型都会修改
bigApple.color.push("red");console.log(bigApple.color); // ["green", "red"]console.log(smallApple.color); // ["green", "red"]
2.创建子类实例(smallApple,bigApple)时,不能向父类传参。也就是说,子类初始化不能定制父类的属性和方法,父类对象在继承时,已经创建。每个子类实例的原型都一样。
借用构造函数继承
在子类构造函数内容调用父内构造函数方法
// 借用构造函数继承function Fruit(name) {this.name = name;this.color = ["green"];}Fruit.prototype.sayName = function () {console.log(this.name);}function Apple(name) {Fruit.call(this,name);};const bigApple = new Apple('big');const smallApple = new Apple('small');bigApple.color.push("red");console.log(bigApple.color); // ["green", "red"]console.log(smallApple.color); // ["green"]console.log(bigApple.sayName); //undefined
修改Fruit构造函数的this指向,将其指向Apple的实例对象,给Apple实例初始化
原理:改变父类函数的this指向
优点:实例的属性不会共享,子类构造函数可以传递参数给父类
缺点:父类定义的方法不能被子类继承下来
组合继承(终点)
为了解决上述,父类的方法不能被继承下来的缺点
// 借用构造函数继承function Fruit(name) {this.name = name;this.color = ["green"];}Fruit.prototype.sayName = function () {console.log(this.name);}function Apple(name) {Fruit.call(this,name);};Apple.prototype = new Fruit();Apple.prototype.constructor = Apple;const bigApple = new Apple('big');const smallApple = new Apple('small');bigApple.color.push("red");console.log(bigApple.color); // ["green", "red"]console.log(smallApple.color); // ["green"]bigApple.sayName(); //big
只要子类原型对象设置为父类实例时,子类就可以继承父类原型上的方法。
注意:修改子类原型时,必须将原型上构造函数的指向子类对象。否则实例化子类对象时,会用父类的Fruit方法去构造对象;而不是Apple方法。
优点:解决了子类继承父类方法的问题
缺点:调用两次父类构造函数方法(Fruit.call(this,name);和new Fruit())
寄生组合式继承(重点)
针对上面连词使用父类构造函数方法改进
可以使用Object.create()方法替代
function Fruit(name) {this.name = name;this.color = ["green"];}Fruit.prototype.sayName = function () {console.log(this.name);}function Apple(name) {Fruit.call(this,name);};Apple.prototype = Object.create(Fruit.prototype);Apple.prototype.constructor = Apple;const bigApple = new Apple('big');const smallApple = new Apple('small');
Object.create()方法,创建一个新对象,将传入的对象Fruit.prototype作为父类
原理:将子类的原型对象 指向 父类的原型对象
多重继承
理论上js不允许一个对象继承多个对象
Object.assign(); 可以将参数二对象上的属性和方法 复制给 参数一对象
function Fruit(name) {this.name = name;this.color = ["green"];}Fruit.prototype.sayName = function () {console.log(this.name);}function Plant(){this.desc = "植物类"}Plant.prototype.sayHi = function () {console.log("hi");}function Apple(name) {Fruit.call(this,name);Plant.call(this);};Apple.prototype = Object.create(Fruit.prototype);// 将植物类原型上的属性和方法复制给Apple原型Object.assign(Apple.prototype,Plant.prototype);Apple.prototype.constructor = Apple;const bigApple = new Apple('big');bigApple.sayName(); // bigbigApple.sayHi(); // hi






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...