nginx中配置指令root与alias的区别
1.root指令
在nginx中,我们可以通过location块与root指令结合的方式,将”url”与”服务器路径”建立起对应关系,location块负责匹配url,root指令负责将匹配到的url与服务器中某个具体目录对应起来。
其实,除了root指令,还有另一个指令也能实现类似的功能,它就是alias指令,root指令和alias指令都能将url和服务器路径进行对应,但是,它们之间又存在一些区别。
先从root指令开始,我们先来看一个root指令的示例,如下:
location /demo {root /opt/test;}
上例中,location块匹配的url为/demo,root指令的路径为/opt/test,那么,根据上述配置,当我们访问http://172.5.1.1/demo这个url时,实际上访问的是服务器中/opt/test/demo路径,因此我们只需要将location中的url添加到root指令对应的路径后面,即可得到最终的服务器路径,
1.root指令示例
更改配置文件
[root@server1 conf]# vim nginx.conf48 location /demo {49 root /opt/test;50 index index.html index.htm;51 }
写入测试页面:
[root@server1 conf]# mkdir /opt/test/demo -p[root@server1 conf]# cd /opt/test/demo/[root@server1 demo]# vim index.html[root@server1 demo]# cat index.htmlwww.westos.org
重新加载nginx:
[root@server1 demo]# nginx -tnginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is oknginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful[root@server1 demo]# nginx -s reload
使用浏览器访问http://172.25.1.1/demo: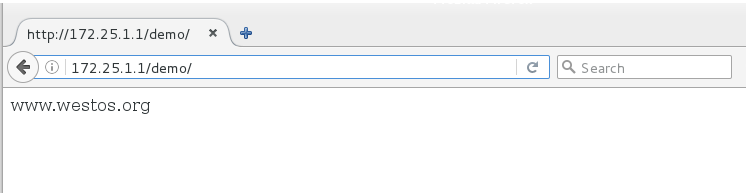
可以看到,当我们访问/demo/时,访问的其实就是/opt/test/demo/index.html。
2.alias指令
除了root指令,alias指令也能将url与服务器路径进行关联,如下:
location /demo1 {alias /opt/test;}
alias指令对应的值也是一个路径,当alias指令与location块结合时,当我们访问/demo1/1.jpg时,其实就是在访问服务器的 /opt/test/1.jpg,也就是说,当我们使用alias时,location的url是与alias的路径完全对等的。
因此,root指令和alias指令的区别就很明显了:
root指令会将location块的”url路径”带入到”root指令路径”中,将带入后的路径作为”最终路径”,使用”最终路径”与url建立对应关系。
alias指令则直接将location块的”url路径”与”alias指令路径”建立对应关系。
其实,除了上述区别,alias指令和root指令能够处于的上下文位置也不同,
alias指令只能在location块中使用,而root指令则不然。





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...