Spring官网阅读(十五)Spring中的格式化(Formatter)
文章目录
- Formatter
- 接口定义
- 继承树
- 注解驱动的格式化
- AnnotationFormatterFactory
- FormatterRegistry
- 接口定义
- UML类图
- FormattingConversionService
- DefaultFormattingConversionService
- FormatterRegistrar
- 配置SpringMVC中的格式化器
- 配置实现的原理
- 总结
在上篇文章中,我们已经学习过了Spring中的类型转换机制。现在我们考虑这样一个需求:在我们web应用中,我们经常需要将前端传入的字符串类型的数据转换成指定格式或者指定数据类型来满足我们调用需求,同样的,后端开发也需要将返回数据调整成指定格式或者指定类型返回到前端页面。这种情况下,Converter已经没法直接支撑我们的需求了。这个时候,格式化的作用就很明显了,这篇文章我们就来介绍Spring中格式化的一套体系。本文主要涉及官网中的
3.5及3.6小结
Formatter
接口定义
public interface Formatter<T> extends Printer<T>, Parser<T> {}
可以看到,本身这个接口没有定义任何方法,只是聚合了另外两个接口的功能
Printer
// 将T类型的数据根据Locale信息打印成指定格式,即返回字符串的格式
public interface Printer{ String print(T fieldValue, Locale locale);
}
Parser
public interface Parser
{ // 将指定的字符串根据Locale信息转换成指定的T类型数据T parse(String clientValue, Locale locale) throws ParseException;
}
从上面可以看出,这个两个接口维护了两个功能相反的方法,分别完成对String类型数据的解析以及格式化。
继承树
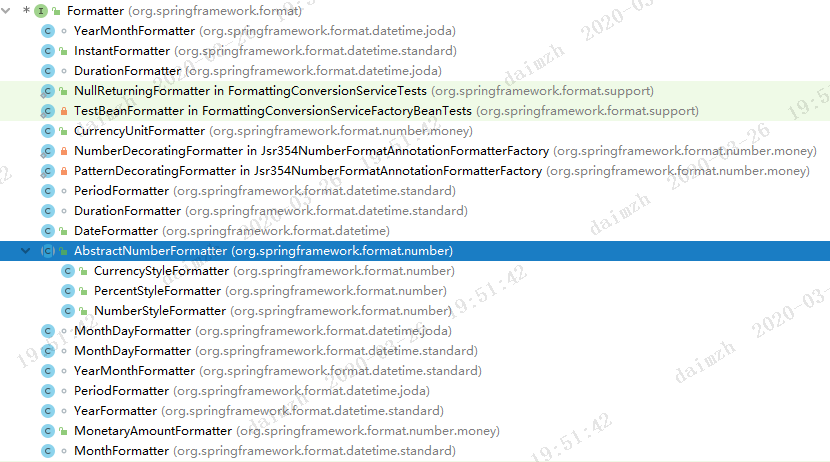
可以发现整个继承关系并不复杂,甚至可以说非常简单。只有一个抽象子类,AbstractNumberFormatter,这个类抽象了对数字进行格式化时的一些方法,它有三个子类,分别处理不同的数字类型,包括货币,百分数,正常数字。其余的子类都是直接实现了Formatter接口。其中我们比较熟悉的可能就是DateFormatter了
使用如下:
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {DateFormatter dateFormatter = new DateFormatter();dateFormatter.setIso(DateTimeFormat.ISO.DATE);System.out.println(dateFormatter.print(new Date(), Locale.CHINA));System.out.println(dateFormatter.parse("2020-03-26", Locale.CHINA));// 程序打印:// 2020-03-26// Thu Mar 26 08:00:00 CST 2020}}
注解驱动的格式化
我们在配置格式化时,除了根据类型进行格式外(比如常见的根据Date类型进行格式化),还可以根据注解来进行格式化,最常见的注解就是org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat。除此之外还有NumberFormat,它们都在format包下。
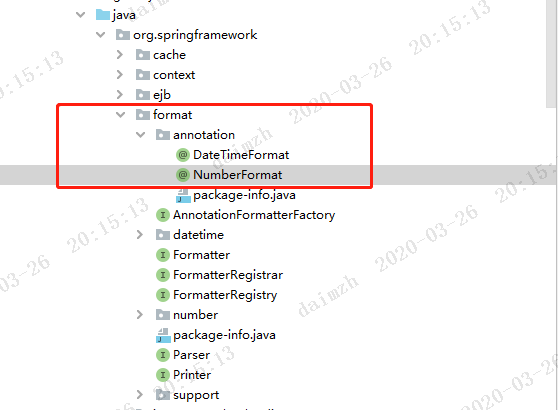
为了将一个注解绑定到指定的格式化器上,我们需要借助到一个接口AnnotationFormatterFactory
AnnotationFormatterFactory
public interface AnnotationFormatterFactory<A extends Annotation> {// 可能被添加注解的字段的类型Set<Class<?>> getFieldTypes();// 根据注解及字段类型获取一个格式化器Printer<?> getPrinter(A annotation, Class<?> fieldType);// 根据注解及字段类型获取一个解析器Parser<?> getParser(A annotation, Class<?> fieldType);}
以Spring内置的一个DateTimeFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory来说,这个类实现的功能就是将DateTimeFormat注解绑定到指定的格式化器,源码如下:
public class DateTimeFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory extends EmbeddedValueResolutionSupportimplements AnnotationFormatterFactory<DateTimeFormat> {private static final Set<Class<?>> FIELD_TYPES;// 只有在这些类型下加这个注解才会进行格式化static {Set<Class<?>> fieldTypes = new HashSet<>(4);fieldTypes.add(Date.class);fieldTypes.add(Calendar.class);fieldTypes.add(Long.class);FIELD_TYPES = Collections.unmodifiableSet(fieldTypes);}@Overridepublic Set<Class<?>> getFieldTypes() {return FIELD_TYPES;}@Overridepublic Printer<?> getPrinter(DateTimeFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {return getFormatter(annotation, fieldType);}@Overridepublic Parser<?> getParser(DateTimeFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {return getFormatter(annotation, fieldType);}protected Formatter<Date> getFormatter(DateTimeFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) { // 通过这个DateFormatter来完成格式化DateFormatter formatter = new DateFormatter();String style = resolveEmbeddedValue(annotation.style());if (StringUtils.hasLength(style)) {formatter.setStylePattern(style);}formatter.setIso(annotation.iso());String pattern = resolveEmbeddedValue(annotation.pattern());if (StringUtils.hasLength(pattern)) {formatter.setPattern(pattern);}return formatter;}}
使用@DateTimeFormat,我们只需要在字段上添加即可
public class MyModel {@DateTimeFormat(iso=ISO.DATE)private Date date;}
关于日期的格式化,Spring还提供了一个类似的AnnotationFormatterFactory,专门用于处理java8中的日期格式,如下
public class Jsr310DateTimeFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory extends EmbeddedValueResolutionSupportimplements AnnotationFormatterFactory<DateTimeFormat> {private static final Set<Class<?>> FIELD_TYPES;static {// 这里添加了对Java8日期的支持Set<Class<?>> fieldTypes = new HashSet<>(8);fieldTypes.add(LocalDate.class);fieldTypes.add(LocalTime.class);fieldTypes.add(LocalDateTime.class);fieldTypes.add(ZonedDateTime.class);fieldTypes.add(OffsetDateTime.class);fieldTypes.add(OffsetTime.class);FIELD_TYPES = Collections.unmodifiableSet(fieldTypes);}........
学习到现在,对Spring的脾气大家应该都有所了解,上面这些都是定义了具体的功能实现,它们必定会有一个管理者,一个Registry,用来注册这些格式化器
FormatterRegistry
接口定义
// 继承了ConverterRegistry,所以它同时还是一个Converter注册器public interface FormatterRegistry extends ConverterRegistry {// 一系列添加格式化器的方法void addFormatterForFieldType(Class<?> fieldType, Printer<?> printer, Parser<?> parser);void addFormatterForFieldType(Class<?> fieldType, Formatter<?> formatter);void addFormatterForFieldType(Formatter<?> formatter);void addFormatterForAnnotation(AnnotationFormatterFactory<?, ?> factory);}
UML类图
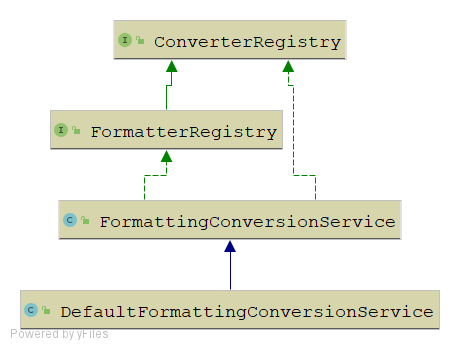
我们可以发现FormatterRegistry默认只有两个实现类
FormattingConversionService
// 继承了GenericConversionService ,所以它能对Converter进行一系列的操作// 实现了接口FormatterRegistry,所以它也可以注册格式化器了// 实现了EmbeddedValueResolverAware,所以它还能有非常强大的功能:处理占位符public class FormattingConversionService extends GenericConversionService implements FormatterRegistry, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {// ....// 最终也是交给addFormatterForFieldType去做的// getFieldType:它会拿到泛型类型。并且支持DecoratingProxy@Overridepublic void addFormatter(Formatter<?> formatter) {addFormatterForFieldType(getFieldType(formatter), formatter);}// 存储都是分开存储的 读写分离// PrinterConverter和ParserConverter都是一个GenericConverter 采用内部类实现的// 注意:他们的ConvertiblePair必有一个类型是String.class// Locale一般都可以这么获取:LocaleContextHolder.getLocale()// 在进行printer之前,会先判断是否能进行类型转换,如果能进行类型转换会先进行类型转换,之后再格式化// 在parse之后,会判断是否还需要进行类型转换,如果需要类型转换会先进行类型转换@Overridepublic void addFormatterForFieldType(Class<?> fieldType, Formatter<?> formatter) {addConverter(new PrinterConverter(fieldType, formatter, this));addConverter(new ParserConverter(fieldType, formatter, this));}// 哪怕你是一个AnnotationFormatterFactory,最终也是被适配成了GenericConverter(ConditionalGenericConverter)@Overridepublic void addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(AnnotationFormatterFactory<? extends Annotation> annotationFormatterFactory) {Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType = getAnnotationType(annotationFormatterFactory);// 若你自定义的实现了EmbeddedValueResolverAware接口,还可以使用占位符哟// AnnotationFormatterFactory是下面的重点内容if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null && annotationFormatterFactory instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) annotationFormatterFactory).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);}// 对每一种字段的type 都注册一个AnnotationPrinterConverter去处理// AnnotationPrinterConverter是一个ConditionalGenericConverter// matches方法为:sourceType.hasAnnotation(this.annotationType);// 这个判断是呼应的:因为annotationFormatterFactory只会作用在指定的字段类型上的,不符合类型条件的不用添加Set<Class<?>> fieldTypes = annotationFormatterFactory.getFieldTypes();for (Class<?> fieldType : fieldTypes) {addConverter(new AnnotationPrinterConverter(annotationType, annotationFormatterFactory, fieldType));addConverter(new AnnotationParserConverter(annotationType, annotationFormatterFactory, fieldType));}}// .......// 持有的一个内部类private static class PrinterConverter implements GenericConverter {private final Class<?> fieldType;private final TypeDescriptor printerObjectType;@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")private final Printer printer;// 最终也是通过conversionService完成类型转换private final ConversionService conversionService;public PrinterConverter(Class<?> fieldType, Printer<?> printer, ConversionService conversionService) {this.fieldType = fieldType;this.printerObjectType =// 会通过解析Printer中的泛型获取具体类型,主要是为了判断是否需要进行类型转换TypeDescriptor.valueOf(resolvePrinterObjectType(printer));this.printer = printer;this.conversionService = conversionService;}// ......}
DefaultFormattingConversionService
类比我们上篇文中介绍的GenericConversionService跟DefaultConversionService,它相比于FormattingConversionService而言,提供了大量的默认的格式化器,源码如下:
public class DefaultFormattingConversionService extends FormattingConversionService {private static final boolean jsr354Present;private static final boolean jodaTimePresent;static {ClassLoader classLoader = DefaultFormattingConversionService.class.getClassLoader();// 判断是否导入了jsr354相关的包jsr354Present = ClassUtils.isPresent("javax.money.MonetaryAmount", classLoader);// 判断是否导入了jodajodaTimePresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("org.joda.time.LocalDate", classLoader);}// 会注册很多默认的格式化器public DefaultFormattingConversionService() {this(null, true);}public DefaultFormattingConversionService(boolean registerDefaultFormatters) {this(null, registerDefaultFormatters);}public DefaultFormattingConversionService(@Nullable StringValueResolver embeddedValueResolver, boolean registerDefaultFormatters) {if (embeddedValueResolver != null) {setEmbeddedValueResolver(embeddedValueResolver);}DefaultConversionService.addDefaultConverters(this);if (registerDefaultFormatters) {addDefaultFormatters(this);}}public static void addDefaultFormatters(FormatterRegistry formatterRegistry) {// 添加针对@NumberFormat的格式化器formatterRegistry.addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(new NumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory());// 针对货币的格式化器if (jsr354Present) {formatterRegistry.addFormatter(new CurrencyUnitFormatter());formatterRegistry.addFormatter(new MonetaryAmountFormatter());formatterRegistry.addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(new Jsr354NumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory());}new DateTimeFormatterRegistrar().registerFormatters(formatterRegistry);// 如没有导入joda的包,那就默认使用Dateif (jodaTimePresent) {// 针对Jodanew JodaTimeFormatterRegistrar().registerFormatters(formatterRegistry);}else {// 没有joda的包,是否Datenew DateFormatterRegistrar().registerFormatters(formatterRegistry);}}}
FormatterRegistrar
在上面DefaultFormattingConversionService的源码中,有这么几行:
new JodaTimeFormatterRegistrar().registerFormatters(formatterRegistry);new DateFormatterRegistrar().registerFormatters(formatterRegistry);
其中的JodaTimeFormatterRegistrar,DateFormatterRegistrar就是FormatterRegistrar。那么这个接口有什么用呢?我们先来看看它的接口定义:
public interface FormatterRegistrar {// 最终也是调用FormatterRegistry来完成注册void registerFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry);}
我们思考一个问题,为什么已经有了FormatterRegistry,Spring还要开发一个FormatterRegistrar呢?直接使用FormatterRegistry完成注册不好吗?
以这句代码为例:new JodaTimeFormatterRegistrar().registerFormatters(formatterRegistry),这段代码是将joda包下所有的默认的转换器已经注册器都注册到formatterRegistry中。
我们可以发现FormatterRegistrar相当于对格式化器及转换器进行了分组,我们调用它的registerFormatters方法,相当于将这一组格式化器直接添加到指定的formatterRegistry中。这样做的好处在于,如果我们对同一个类型的数据有两组不同的格式化策略,例如就以上面的日期为例,我们既有可能采用joda的策略进行格式化,也有可能采用Date的策略进行格式化,通过分组的方式,我们可以更见方便的在确认好策略后将需要的格式化器添加到容器中。
配置SpringMVC中的格式化器
@Configuration@EnableWebMvcpublic class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Overridepublic void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {// 调用registry.addFormatter添加格式化器即可}}
配置实现的原理
@EnableWebMvc注解上导入了一个DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration类@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableWebMvc {
}DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration// 继承了WebMvcConfigurationSupport
@Configuration
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();// 这个方法会注入所有的WebMvcConfigurer,包括我们的WebConfig@Autowired(required = false)public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);}}//.....,省略无关代码// 复写了父类WebMvcConfigurationSupport的方法// 调用我们配置的configurer的addFormatters方法@Overrideprotected void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {this.configurers.addFormatters(registry);}
//…..,省略无关代码
}
3.WebMvcConfigurationSupport
public class WebMvcConfigurationSupport implements ApplicationContextAware, ServletContextAware {// 这就是真相,这里会创建一个FormattingConversionService,并且是一个DefaultFormattingConversionService,然后调用addFormatters方法@Beanpublic FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService() {FormattingConversionService conversionService = new DefaultFormattingConversionService();addFormatters(conversionService);return conversionService;}protected void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {}}
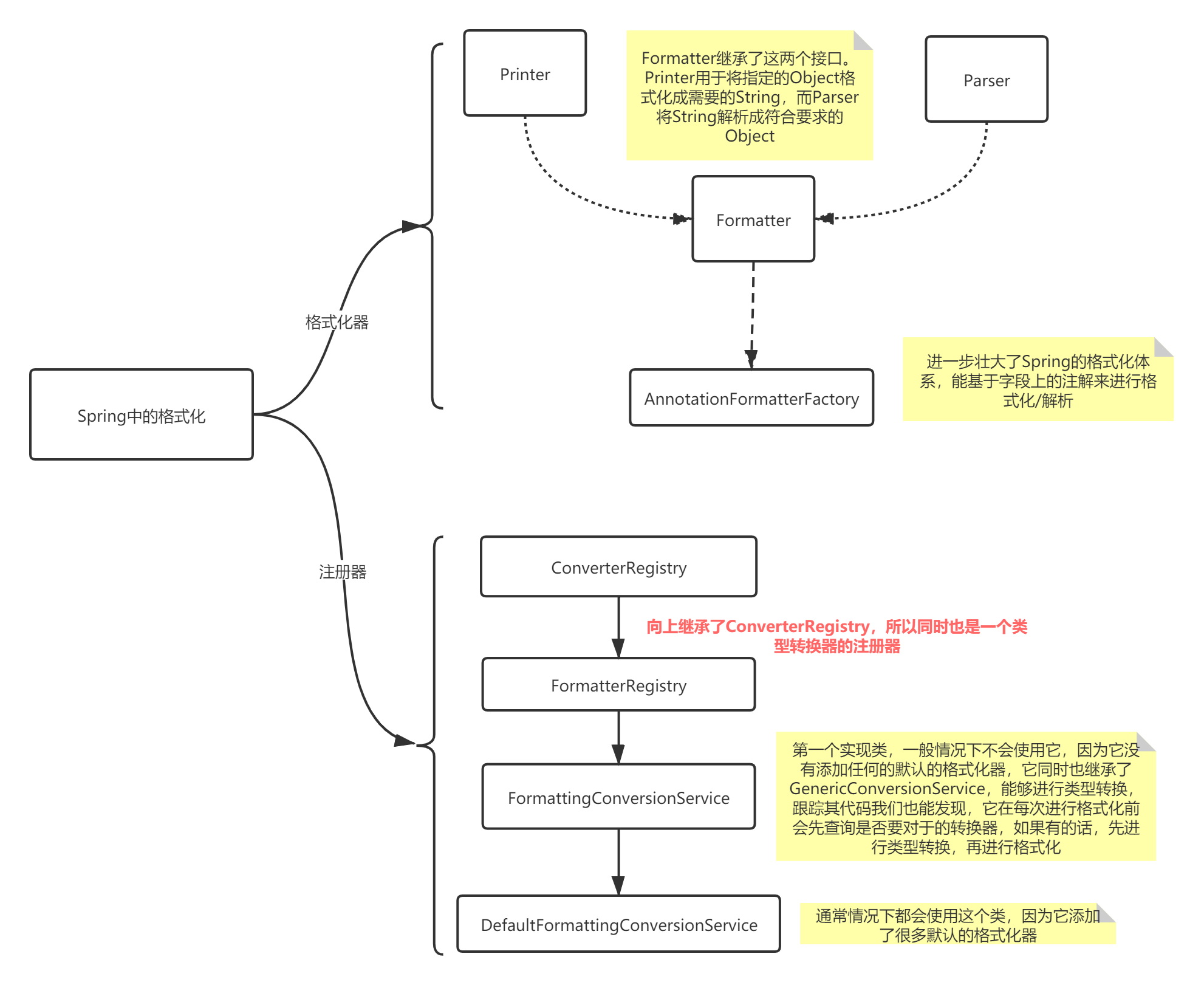
总结
Spring中的格式化到此就结束了,总结画图如下:
扫描下方二维码,关注我的公众号,更多精彩文章在等您!~~




































还没有评论,来说两句吧...