Spring源代码学习系列②BeanPostProcessor执行时机与实现原理
这一篇主要学到了一种新的看源代码的方法。之前都是从最开始的代码开始,然后一步一步step into。这样会比较浪费时间,并且会因为代码多而容易搞混淆,抓不住重点。
这篇主要是看BeanPostProcessor的执行时机与相应的源代码,目前对于它是合适执行的,并不知道,但是可以明确的是我们继承的BeanPostProcessor一定会执行。因此可以完全将断点放在我们写的类MyBeanPostProcessor的函数里面。
看源码的另一种姿势
打开调试,进入断点。如下图所示:
然后逐帧查看其调用栈,慢慢找到关键代码:
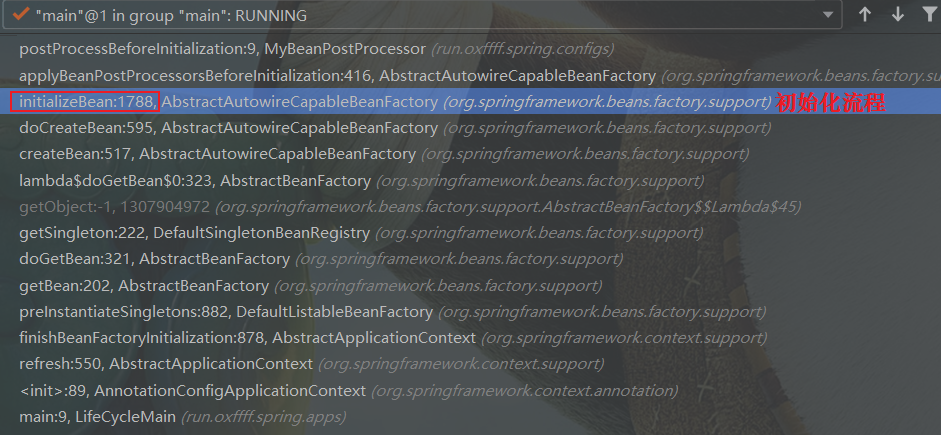
初始化流程
主要的初始化流程包括:XXXAware方法执行、BeanPostProcessor.beforeXX()、InitilizingBean、initMethod、BeanPostProcessor.afterXX()。
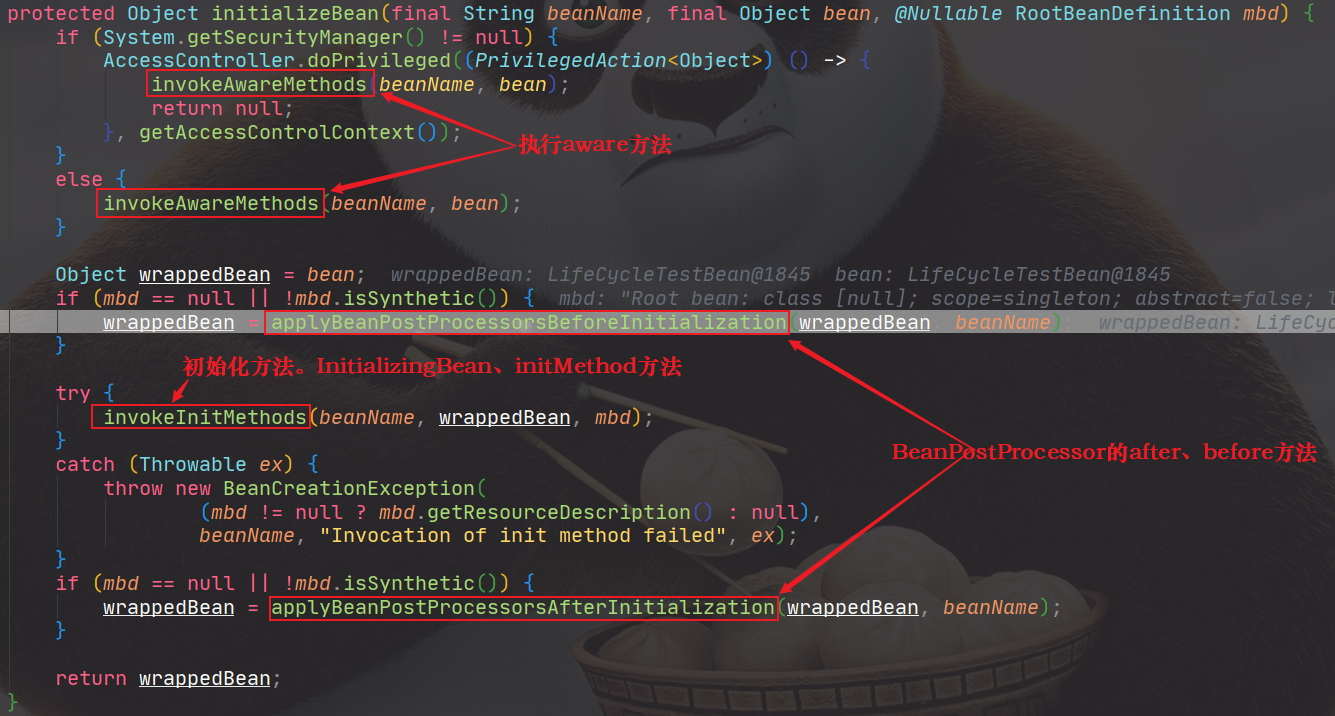
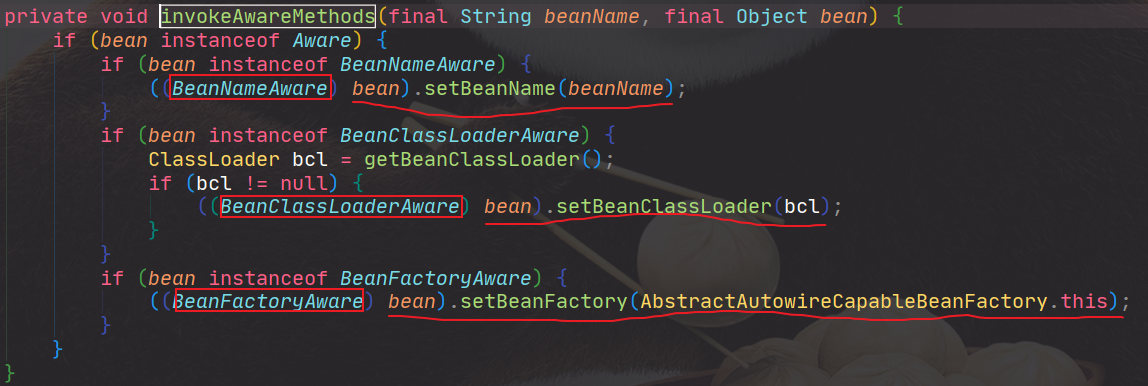
执行AwareXX的顺序如下:
执行applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization时,如果BeanPostProcessor返回的是null,那么将不会执行后续的BeanPostProcessor。
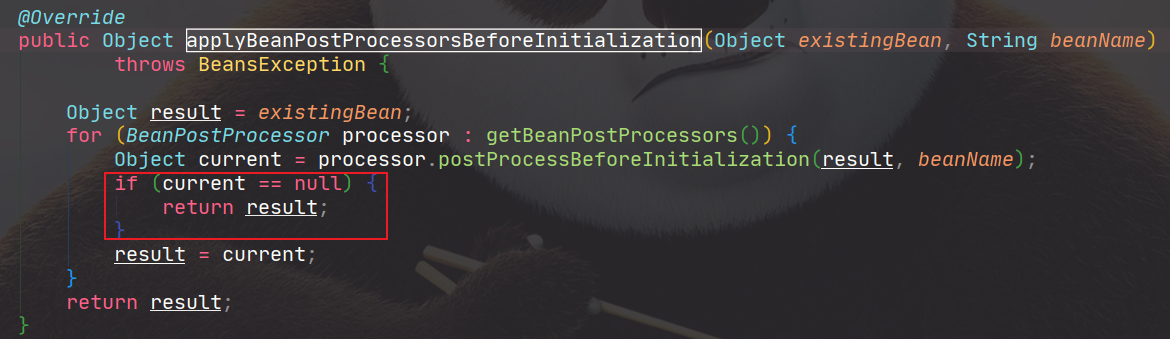
然后先执行InitializingBean,再调用自定义初始化方法initMethod。

最后执行BeanPostProcessor.afterXX(),与before的类似。
在Spring中的用途
先看两个比较简单的,会直接调用BeanPostProcessor的两个方法,达到spring的相应功能。
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
在bean中,实现ApplicationContextAware接口,这个后置处理器会在bean初始化前,设置进ApplicationContext。
@Override@Nullablepublic Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {if (!(bean instanceof EnvironmentAware || bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware ||bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware ||bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware)){return bean;}AccessControlContext acc = null;if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {acc = this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getAccessControlContext();}if (acc != null) {AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);return null;}, acc);}else {invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);}return bean;}private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());}if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);}if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);}if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);}if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);}if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);}}
BeanValidationPostProcessor
此方法默认在初始化数据之前进行数据校验。
private boolean afterInitialization = false;@Overridepublic Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {if (!this.afterInitialization) {doValidate(bean);}return bean;}@Overridepublic Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {if (this.afterInitialization) {doValidate(bean);}return bean;}protected void doValidate(Object bean) {Assert.state(this.validator != null, "No Validator set");Object objectToValidate = AopProxyUtils.getSingletonTarget(bean);if (objectToValidate == null) {objectToValidate = bean;}Set<ConstraintViolation<Object>> result = this.validator.validate(objectToValidate);if (!result.isEmpty()) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Bean state is invalid: ");for (Iterator<ConstraintViolation<Object>> it = result.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {ConstraintViolation<Object> violation = it.next();sb.append(violation.getPropertyPath()).append(" - ").append(violation.getMessage());if (it.hasNext()) {sb.append("; ");}}throw new BeanInitializationException(sb.toString());}}
InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
执行被@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解的方法,参与生命周期。
初始化方法执行
@PostConstruct执行过程比较直接,因为此类直接实现了BeanPostProcessor的初始化方法。
@Overridepublic Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass());try {// 执行初始化方法metadata.invokeInitMethods(bean, beanName);}catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex.getTargetException());}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Failed to invoke init method", ex);}return bean;}@Overridepublic Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {return bean;}
具体的初始化方法如下:
public void invokeInitMethods(Object target, String beanName) throws Throwable {Collection<LifecycleElement> checkedInitMethods = this.checkedInitMethods;Collection<LifecycleElement> initMethodsToIterate =(checkedInitMethods != null ? checkedInitMethods : this.initMethods);if (!initMethodsToIterate.isEmpty()) {for (LifecycleElement element : initMethodsToIterate) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Invoking init method on bean '" + beanName + "': " + element.getMethod());}element.invoke(target);}}}
寻找bean中初始化、销毁方法
所有的checkedInitMethods来自对initMethods中函数的遍历。包括destroy方法也是类似的。
public void checkConfigMembers(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {Set<LifecycleElement> checkedInitMethods = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.initMethods.size());for (LifecycleElement element : this.initMethods) {String methodIdentifier = element.getIdentifier();if (!beanDefinition.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(methodIdentifier)) {beanDefinition.registerExternallyManagedInitMethod(methodIdentifier);checkedInitMethods.add(element);if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Registered init method on class [" + this.targetClass.getName() + "]: " + element);}}}Set<LifecycleElement> checkedDestroyMethods = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.destroyMethods.size());for (LifecycleElement element : this.destroyMethods) {String methodIdentifier = element.getIdentifier();if (!beanDefinition.isExternallyManagedDestroyMethod(methodIdentifier)) {beanDefinition.registerExternallyManagedDestroyMethod(methodIdentifier);checkedDestroyMethods.add(element);if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Registered destroy method on class [" + this.targetClass.getName() + "]: " + element);}}}this.checkedInitMethods = checkedInitMethods;this.checkedDestroyMethods = checkedDestroyMethods;}
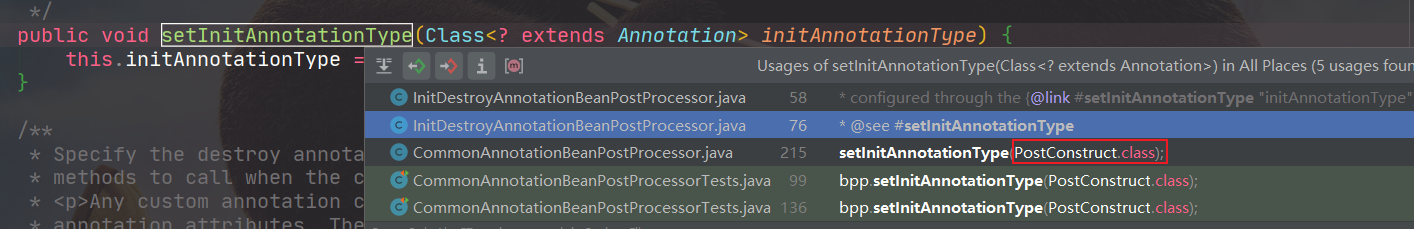
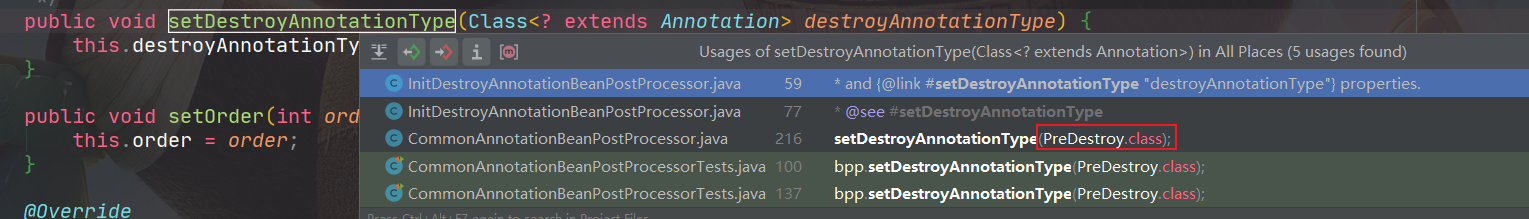
只要是被@PostConstruct注解过的函数,都会被加入到initMethods中。destroy也类似。
do {final List<LifecycleElement> currInitMethods = new ArrayList<>();final List<LifecycleElement> currDestroyMethods = new ArrayList<>();ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {// 被initAnnotationType注解if (this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)) {LifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method);currInitMethods.add(element);if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Found init method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);}}// 被destroyAnnotationType注解if (this.destroyAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.destroyAnnotationType)) {currDestroyMethods.add(new LifecycleElement(method));if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Found destroy method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);}}});initMethods.addAll(0, currInitMethods);destroyMethods.addAll(currDestroyMethods);targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();}while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);return (initMethods.isEmpty() && destroyMethods.isEmpty() ? this.emptyLifecycleMetadata :new LifecycleMetadata(clazz, initMethods, destroyMethods));
具体的类型为:
init
destroy
销毁方法执行
对@PreDestroy注解方法的执行,逻辑都放在了DisposableBeanAdapter中,它实现了DisposableBean,
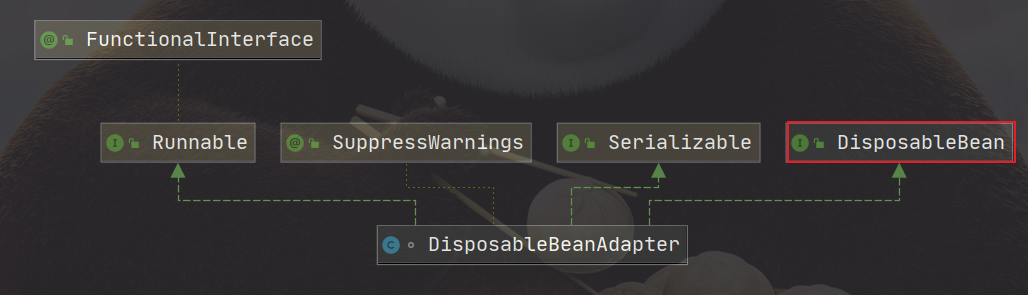
并实现了destroy()方法,执行所有的DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor方法。
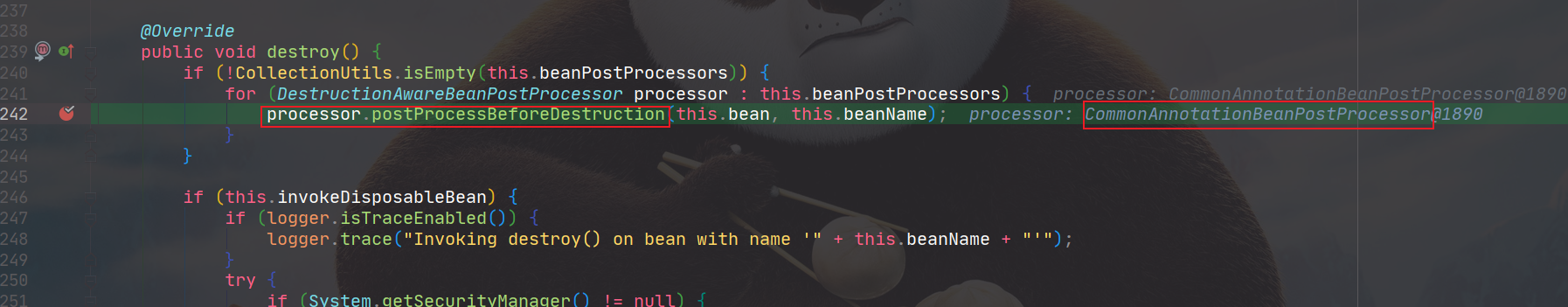
进入InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeDestruction,它完成了对所有的销毁方法的调用。
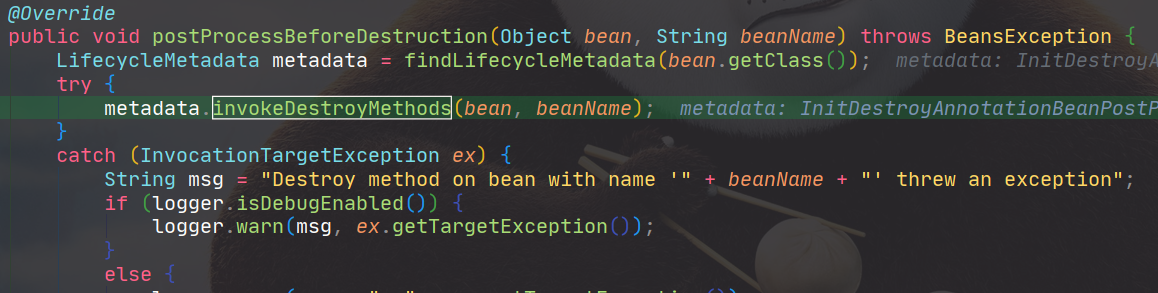
具体的执行销毁方法的逻辑与初始化类似






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...