sql索引优化实战总结
sql索引优化实战总结
- 一、 避免索引失效
- 1.1 全值匹配
- 1.2 最左匹配原则
- 1.3 不再索引列上做任何操作(注意不严谨)
- 1.3.1 当查询字段为 * 时索引会失效
- 1.3.1 当查询字段为count(),或者是索引字段 时索引不会失效
- 1.4 范围条件右边的索引失效
- 1.5 mysql在使用不等于(!=或者<>)索引失效
- 1.6 is not null无法使用索引
- 1.7 like以通配符开头(%qw)索引失效
- 1.8 字符串不加引号索引失效
- 1.9 使用or连接索引失效
- 1.10 尽量使用覆盖索引
- 二 排序与分组优化
- 2.1 使用order by出现Using filesort
- 2.2 使用group by出现Using temporary
- 三 大数据量分页优化
- 3.1、数据准备
- 3.2 测试一下分页数据的相应时间
- 3.3 子查询优化
- 使用id限定方案
- 四 小表驱动大表
- 4.1 表关联查询
- 4.2 in和exits查询
- 五 max函数优化
- 案例所用sql脚本
- customer表
- employee表
- department表
- testemployee
一、 避免索引失效
-- 最左匹配原则 *-- 范围条件右边的索引失效-- 不再索引列上做任何操作 *-- 使用不等于(!=或者<>)索引失效-- is not null无法使用索引-- like以通配符开头(%qw)索引失效 *-- 字符串不加引号索引失效-- 使用or连接索引失效-- 尽量使用覆盖索引
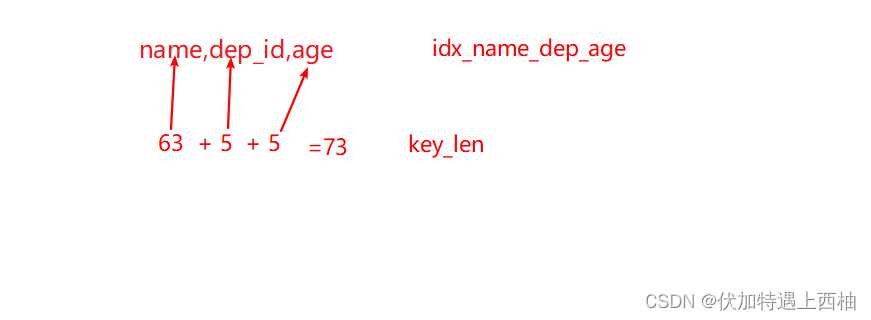
1.1 全值匹配
-- 创建组合索引create index idx_name_dep_age on employee(name,dep_id,age)-- 索引字段全部使用上explain select * from employee where name='鲁班' and dep_id=1 and age=10

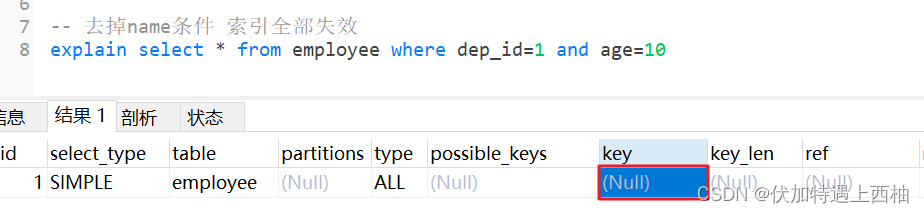
1.2 最左匹配原则
-- 去掉name条件 索引全部失效explain select * from employee where dep_id=1 and age=10
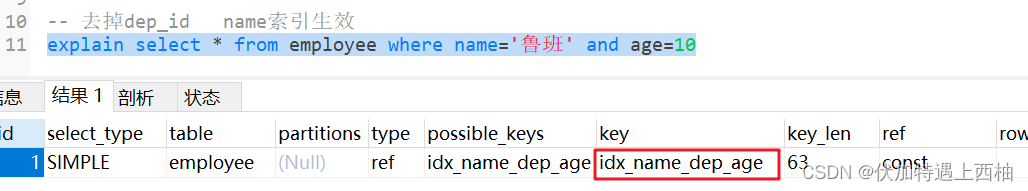
-- 去掉dep_id name索引生效explain select * from employee where name='鲁班' and age=10
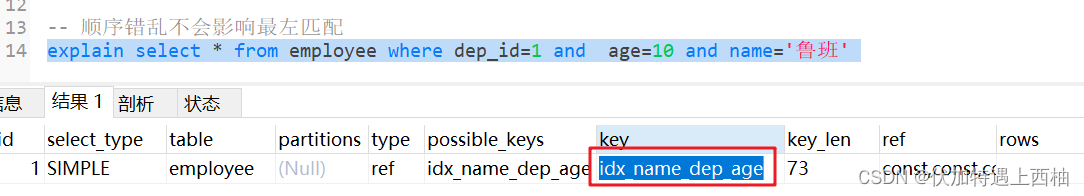
-- 顺序错乱不会影响最左匹配explain select * from employee where dep_id=1 and age=10 and name='鲁班'
1.3 不再索引列上做任何操作(注意不严谨)
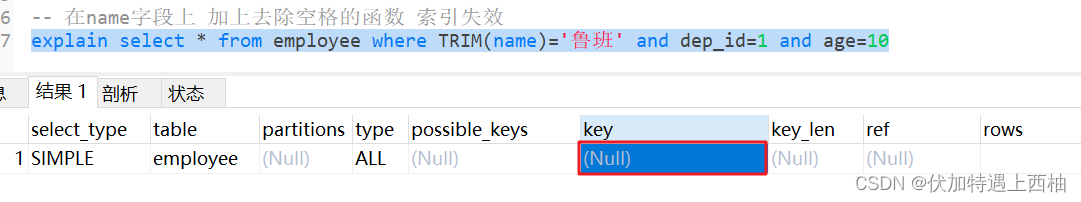
1.3.1 当查询字段为 * 时索引会失效
TRIM(name)=‘鲁班’ 没法通过索引树方式搜索,只能通过遍历索引方式去找
-- 在name字段上 加上去除空格的函数 索引失效explain select * from employee where TRIM(name)='鲁班' and dep_id=1 and age=10
1.3.1 当查询字段为count(),或者是索引字段 时索引不会失效
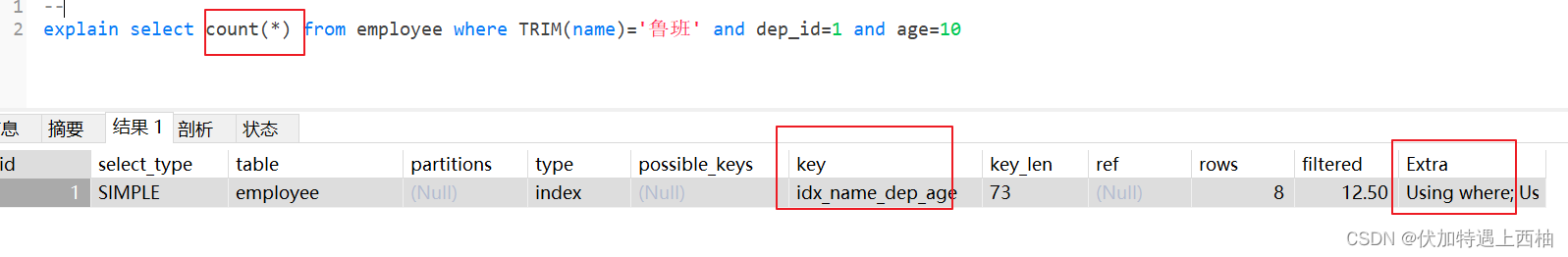
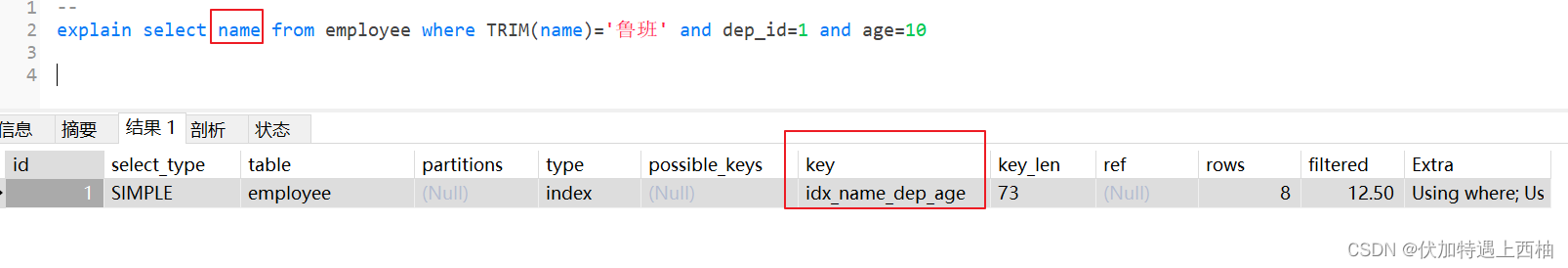
使用到了覆盖索引:
count(*),索引字段这些都不需要回表查询,只要遍历索引树就可以得到了。
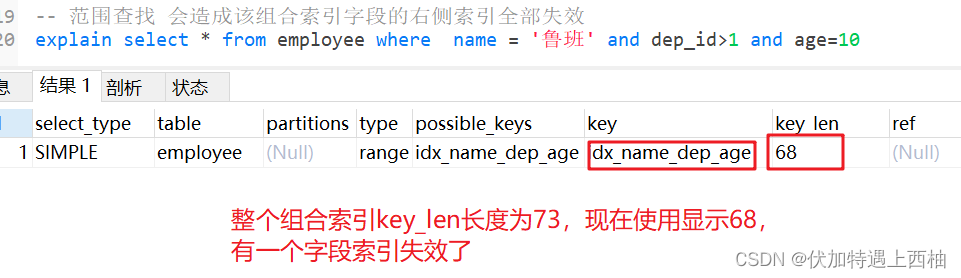
1.4 范围条件右边的索引失效
-- 范围查找 会造成该组合索引字段的右侧索引全部失效explain select * from employee where name = '鲁班' and dep_id>1 and age=10
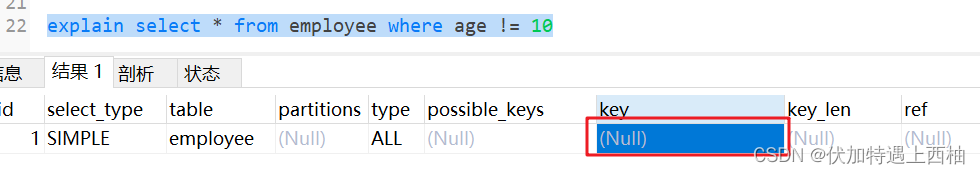
1.5 mysql在使用不等于(!=或者<>)索引失效
explain select * from employee where age != 10
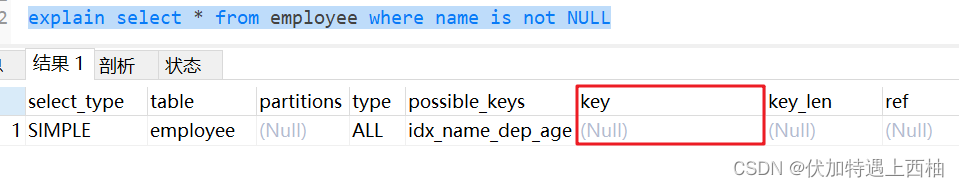
1.6 is not null无法使用索引
explain select * from employee where name is not NULL
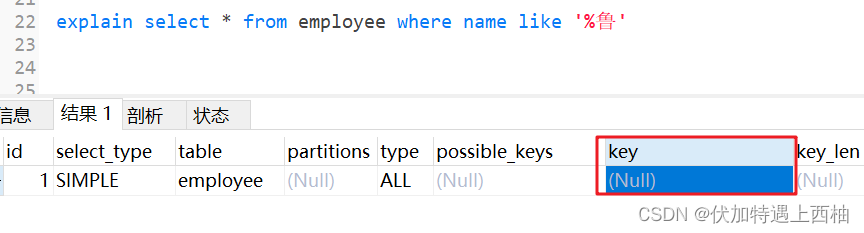
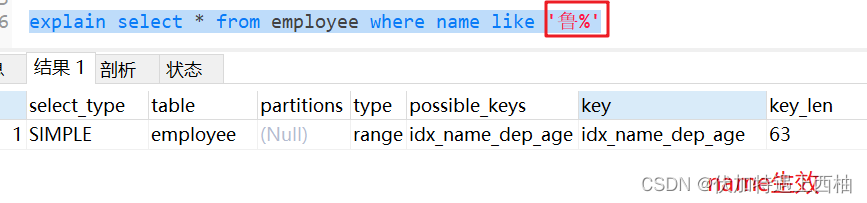
1.7 like以通配符开头(%qw)索引失效
explain select * from employee where name like '%鲁'
1.8 字符串不加引号索引失效
explain select * from employee where name = 200
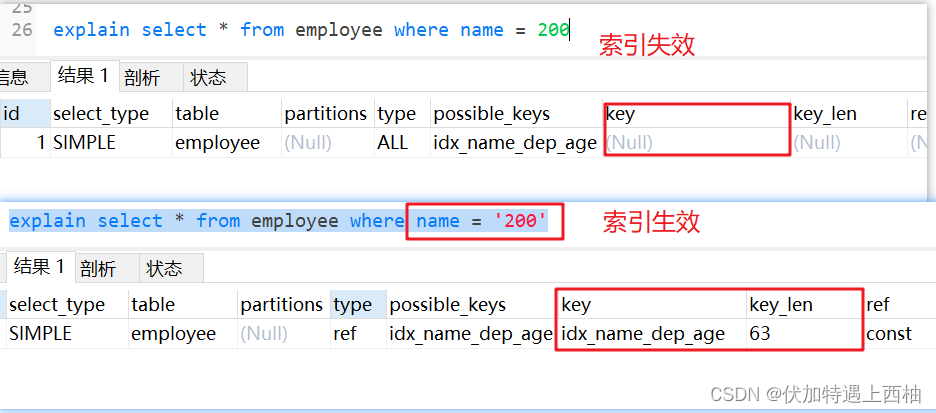
注意:如果是数字类型加上引号,索引不会失效
explain select * from employee where id = '1'
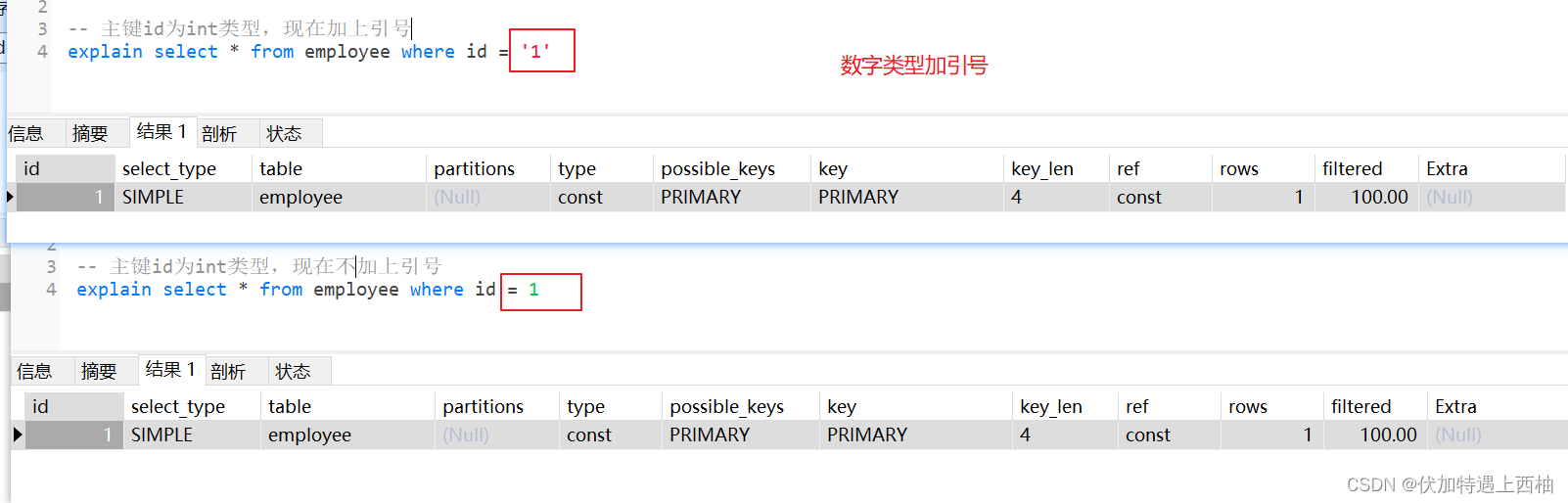
隐式类型转换规则:
当字符串类型和数字类型进行比较时候,默认字符串转数字
1.9 使用or连接索引失效
explain select * from employee where name = '鲁班' or age>10
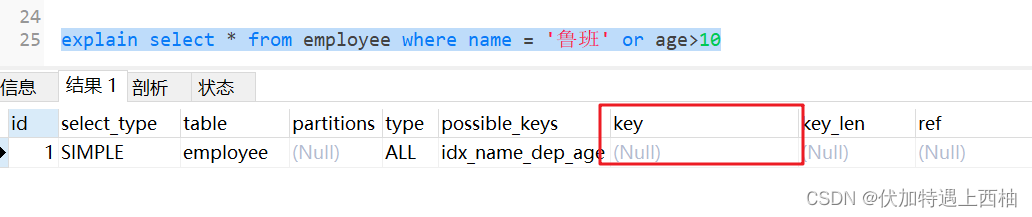
1.10 尽量使用覆盖索引
explain select * from employee where name = '鲁班' or age>10-- 覆盖索引: 要查询的字段全部是索引字段-- 上面情况会触发全表扫描,不过若使用了覆盖索引,则会只扫描索引文件explain select name,dep_id,age from employee where name = '鲁班' or age>10
二 排序与分组优化
2.1 使用order by出现Using filesort
-- 如果select * 语句未使用到索引,会出现 filesort 可使用覆盖索引解决 或 主键索引-- 组合索引不满足最左原则 会出现 filesort-- 组合索引顺序不一致(order by的后面) 会出现 filesort-- 当索引出现范围查找时 可能会出现 filesort-- 排序使用一升一降会造成filesort-- 没有使用索引排序,服务器需要额外的为数据进行排序的处理-- 如果select语句未使用到索引,会出现 filesortexplain select * from employee order by name,dep_id,age

-- 组合索引不满足最左原则 会出现 filesortexplain select * from employee where name='鲁班' order by dep_id,ageexplain select * from employee order by dep_id,age
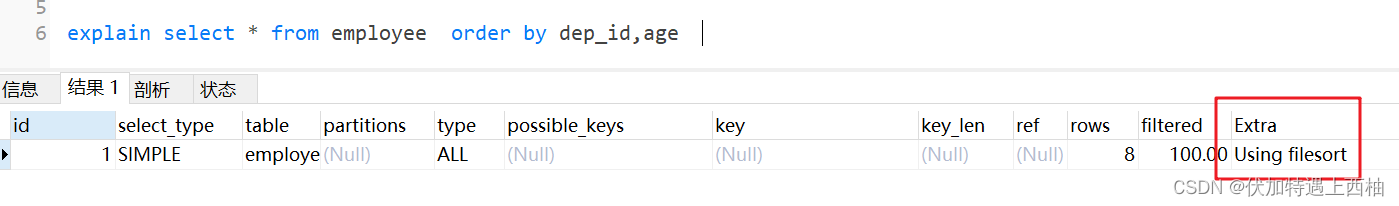
-- 组合索引顺序不一致(order by的后面) 会出现 filesortexplain select * from employee where name='鲁班' order by dep_id,ageexplain select * from employee where name='鲁班' order by age,dep_id
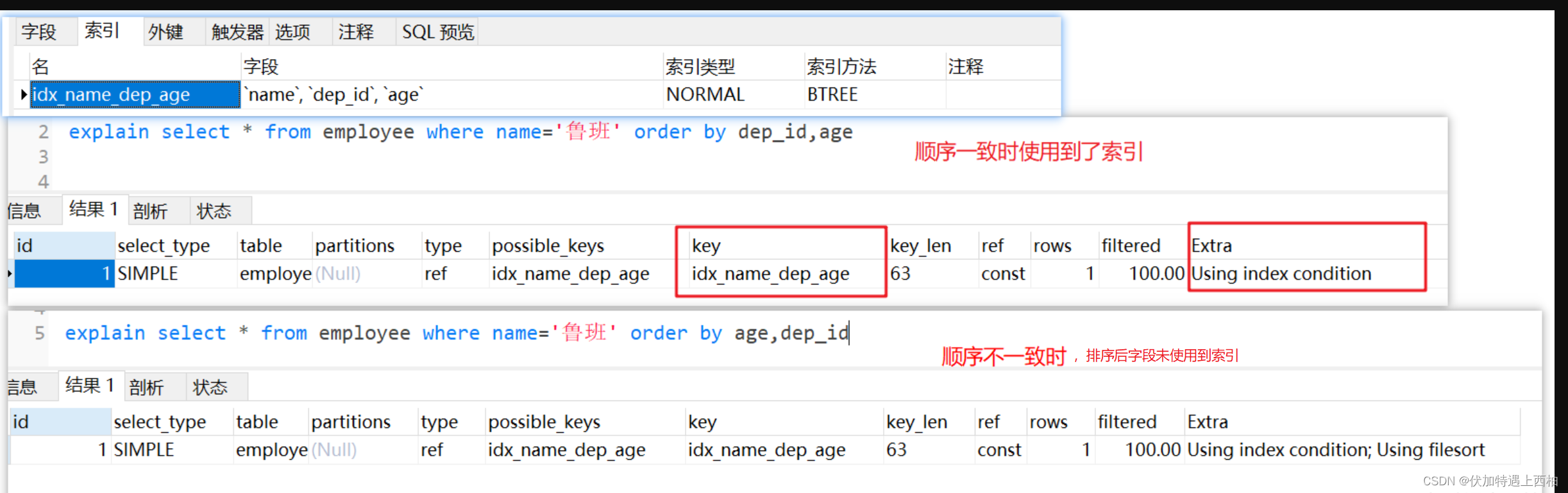
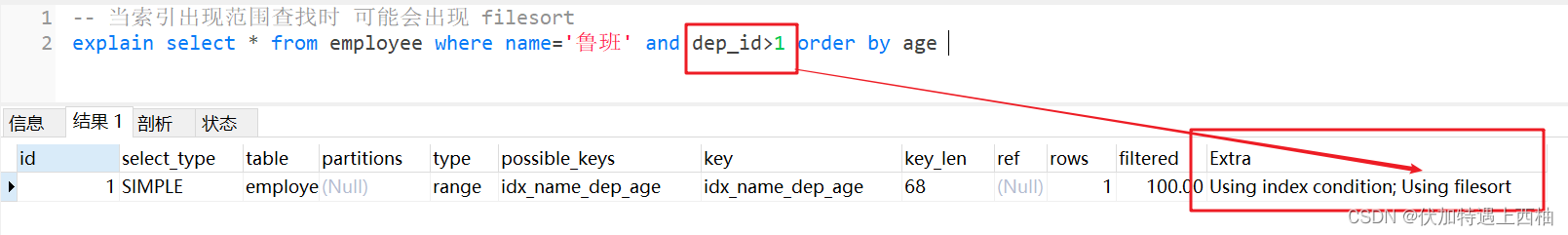
-- 当索引出现范围查找时 可能会出现 filesortexplain select * from employee where name='鲁班' and dep_id>1 order by age
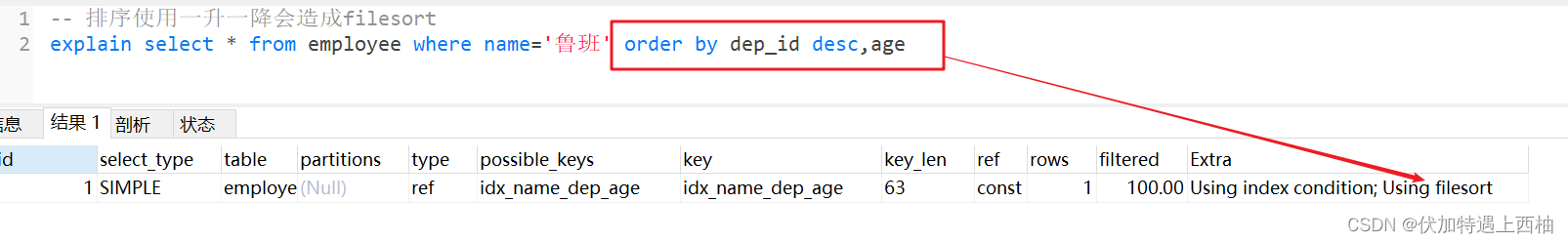
-- 排序使用一升一降会造成filesortexplain select * from employee where name='鲁班' order by dep_id desc,age
2.2 使用group by出现Using temporary
-- 同order by情况类似, 分组必定触发排序-- 组合索引不满足最左原则 会出现 filesort-- 组合索引顺序不一致(order by的后面) 会出现 filesort-- 当索引出现范围查找时 可能会出现 filesort
三 大数据量分页优化
-- 分页是我们经常使用的功能,在数据量少时单纯的使用limit m,n 不会感觉到性能的影响-- 但我们的数据达到成百上千万时 , 就会明显查询速度越来越低
3.1、数据准备
-- 使用存储过程导入数据-- 查看是否开启函数功能show variables like 'log_bin_trust_function_creators';-- 设置开启函数功能set global log_bin_trust_function_creators=1;-- 创建函数用于生成随机字符串delimiter $$create function rand_string(n int) returns varchar(255)begindeclare chars_str varchar(100) default 'qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnm';declare return_str varchar(255) default '';declare i int default 0;while i<n doset return_str=concat(return_str,substring(chars_str,floor(1+rand()*52),1));set i=i+1;end while;return return_str;end $$-- 创建存储过程用于插入数据delimiter $$create procedure insert_emp(in start int(10),in max_num int(10))begindeclare i int default 0;/*把autocommit设置成0*/set autocommit= 0;repeatset i=i+1;insert into testemployee(name,dep_id,age,salary,cus_id)values(rand_string(6),'2',24,3000,6);until i=max_num end repeat;commit;end $$-- 调用存储过程插入数据call insert_emp(1,1000000);
3.2 测试一下分页数据的相应时间
-- limit 0,20 时间: 0.001msselect * from testemployee limit 0,20-- limit 10000,20 时间: 0.004msselect * from testemployee limit 10000,20-- limit 100000,20 时间: 0.044msselect * from testemployee limit 100000,20-- limit 1000000,20 时间: 0.370msselect * from testemployee limit 1000000,20-- limit 3000000,20 时间: 1.068msselect * from testemployee limit 3000000,20
3.3 子查询优化
-- 子查询优化-- 通过Explain发现,之前我们没有利用到索引,这次我们利用索引查询出对应的所有ID-- 在通过关联查询,查询出对应的全部数据,性能有了明显提升-- limit 3000000,20 时间: 1.068ms -> 时间: 0.742msselect * from testemployee e,(select id from testemployee limit 3000000,20) tmp where e.id=tmp.id-- 自增ID也可以用如下方式select * from testemployee where id> (select id from testemployee t limit 3000000,1) LIMIT 10
使用id限定方案
-- 使用id限定方案,将上一页的ID传递过来 根据id范围进行分页查询-- 通过程序的设计,持续保留上一页的ID,并且ID保证自增-- 时间: 0.010msselect * from testemployee where id>3000109 limit 20-- 虽然使用条件有些苛刻 但效率非常高,可以和方案一组合使用 ,跳转某页使用方案一 下一页使用方案2
四 小表驱动大表
4.1 表关联查询
explain select e.id from employee e,department d where e.dep_id=d.id
MySQL 表关联的算法是 Nest Loop Join,是通过驱动表的结果集作为循环基础数据,
然后一条一条地通过该结果集中的数据作为过滤条件到下一个表中查询数据,然后合并结果。
如果小的循环在外层,对于数据库连接来说就只连接5次,进行5000次操作,
如果1000在外,则需要进行1000次数据库连接,从而浪费资源,增加消耗。
这就是为什么要小表驱动大表。
总结:多表查询中,一定要让小表驱动大表create index idx_dep_id on testemployee(dep_id)explain select e.id from testemployee e LEFT JOIN department d on e.dep_id=d.idexplain select e.id from testemployee e RIGHT JOIN department d on e.dep_id=d.id
小表驱动大表
4.2 in和exits查询
使用in 时的explain执行计划 d的数据先被查询出来, 根据d的结果集循环查询a表数据
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-8iP7lhxZ-1653547861343)(assets/1598535713330.png)]
-- 使用in 时间: 3.292msA Bselect * from employee where dep_id in (select id from department)使用department表中数据作为外层循环 10次for( select id from department d)每次循环执行employee表中的查询for( select * from employee e where e.dep_id=d.id)
使用exits时的explain执行计划 虽然d的查询优先级高,但是当select_type为DEPENDENT_SUBQUERY时,代表当前子查询依赖外部查询,所以可以考到 e表先进行查询
-- 使用exits 时间: 14.771msA Bselect * from employee e where exists (select 1 from department d where d.id = e.dep_id)使用employee表中数据作为外层循环 3000000万次for(select * from employee e)每次循环执行department表中的查询for( select 1 from department d where d.id = e.dep_id)总结:当A表数据多于B表中的数据时,这是我们使用in优于Exists当B表数据多于A表中的数据时,这时我们使用Exists优于in如果数据量差不多,那么它们的执行性能差不多Exists子查询只返回true或false,因此子查询中的select * 可以是select 1或其它
五 max函数优化
-- 给max函数中的字段添加索引select max(age) from testemployee
案例所用sql脚本
customer表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `customer`;CREATE TABLE `customer` (`id` int(11) NOT NULL,`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;-- ------------------------------ Records of customer-- ----------------------------INSERT INTO `customer` VALUES (1, 'zs');SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
employee表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `employee`;CREATE TABLE `employee` (`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`name` varchar(20) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,`dep_id` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,`age` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,`salary` decimal(10, 2) NULL DEFAULT NULL,`cus_id` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE,INDEX `idx_name_dep_age`(`name`, `dep_id`, `age`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 109 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;-- ------------------------------ Records of employee-- ----------------------------INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES (1, '鲁班', 1, 10, 1000.00, 1);INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES (2, '后裔', 1, 20, 2000.00, 1);INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES (3, '孙尚香', 1, 20, 2500.00, 1);INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES (4, '凯', 4, 20, 3000.00, 1);INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES (5, '典韦', 4, 40, 3500.00, 2);INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES (6, '貂蝉', 6, 20, 5000.00, 1);INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES (7, '孙膑', 6, 50, 5000.00, 1);INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES (8, '蔡文姬', 30, 35, 4000.00, 1);SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
department表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `department`;CREATE TABLE `department` (`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`deptName` varchar(30) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,`address` varchar(40) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 6 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;-- ------------------------------ Records of department-- ----------------------------INSERT INTO `department` VALUES (1, '研发部(RD)', '2层');INSERT INTO `department` VALUES (2, '人事部(HR)', '3层');INSERT INTO `department` VALUES (3, '市场部(MK)', '4层');INSERT INTO `department` VALUES (4, '后勤部(MIS)', '5层');INSERT INTO `department` VALUES (5, '财务部(FD)', '6层');SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
testemployee
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `testemployee`;CREATE TABLE `testemployee` (`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`name` varchar(20) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,`dep_id` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,`age` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,`salary` decimal(10, 2) NULL DEFAULT NULL,`cus_id` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE,INDEX `idx_age`(`age`) USING BTREE,INDEX `idx_dep_id`(`dep_id`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 2000109 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;-- 使用存储过程导入数据-- 查看是否开启函数功能show variables like 'log_bin_trust_function_creators';-- 设置开启函数功能set global log_bin_trust_function_creators=1;-- 创建函数用于生成随机字符串delimiter $$create function rand_string(n int) returns varchar(255)begindeclare chars_str varchar(100) default 'qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnm';declare return_str varchar(255) default '';declare i int default 0;while i<n doset return_str=concat(return_str,substring(chars_str,floor(1+rand()*52),1));set i=i+1;end while;return return_str;end $$-- 创建存储过程用于插入数据delimiter $$create procedure insert_emp(in start int(10),in max_num int(10))begindeclare i int default 0;/*把autocommit设置成0*/set autocommit= 0;repeatset i=i+1;insert into testemployee(name,dep_id,age,salary,cus_id)values(rand_string(6),'2',24,3000,6);until i=max_num end repeat;commit;end $$-- 调用存储过程插入数据call insert_emp(1,1000000);





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...