@Around简单使用示例——SpringAOP增强处理
@Around的作用
- 既可以在目标方法之前织入增强动作,也可以在执行目标方法之后织入增强动作;
- 可以决定目标方法在什么时候执行,如何执行,甚至可以完全阻止目标目标方法的执行;
可以改变执行目标方法的参数值,也可以改变执行目标方法之后的返回值; 当需要改变目标方法的返回值时,只能使用Around方法;
- 虽然Around功能强大,但通常需要在线程安全的环境下使用。因此,如果使用普通的Before、AfterReturing增强方法就可以解决的事情,就没有必要使用Around增强处理了。
注解方式:如果需要对某一方法进行增强,只需要在相应的方法上添加上自定义注解即可
package com.rq.aop.common.advice;import com.rq.aop.common.annotation.MyAnnotation;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Aspect //标注增强处理类(切面类)@Component //交由Spring容器管理public class AnnotationAspect {/*可自定义切点位置,针对不同切点,方法上的@Around()可以这样写ex:@Around(value = "methodPointcut() && args(..)")@Pointcut(value = "@annotation(com.rq.aop.common.annotation.MyAnnotation)")public void methodPointcut(){}@Pointcut(value = "@annotation(com.rq.aop.common.annotation.MyAnnotation2)")public void methodPointcut2(){}*///定义增强,pointcut连接点使用@annotation(xxx)进行定义@Around(value = "@annotation(around)") //around 与 下面参数名around对应public void processAuthority(ProceedingJoinPoint point,MyAnnotation around) throws Throwable{System.out.println("ANNOTATION welcome");System.out.println("ANNOTATION 调用方法:"+ around.methodName());System.out.println("ANNOTATION 调用类:" + point.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName());System.out.println("ANNOTATION 调用类名" + point.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getSimpleName());point.proceed(); //调用目标方法System.out.println("ANNOTATION login success");}}
注解类
package com.rq.aop.common.annotation;import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;import java.lang.annotation.Retention;import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;import java.lang.annotation.Target;@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//运行时有效@Target(ElementType.METHOD)//作用于方法public @interface MyAnnotation {String methodName () default "";}
Controller
package com.rq.aop.controller;import com.rq.aop.common.annotation.MyAnnotation;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@Controller@RequestMapping("/hello")public class HelloController {@RequestMapping("/login/{name}")@MyAnnotation(methodName = "login")public void login(@PathVariable String name){System.out.println("hello!"+name);}}
运行结果: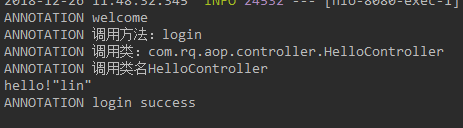
匹配方法执行连接点方式
package com.rq.aop.common.advice;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Aspect@Component@Order(0) //设置优先级,值越低优先级越高public class ExecutionAspect {@Around(value = "execution(* com.rq.aop.controller..*.*(..))")public void processAuthority (ProceedingJoinPoint point)throws Throwable{System.out.println("EXECUTION welcome");System.out.println("EXECUTION 调用方法:" + point.getSignature().getName());System.out.println("EXECUTION 目标对象:" + point.getTarget());System.out.println("EXECUTION 首个参数:" + point.getArgs()[0]);point.proceed();System.out.println("EXECUTION success");}}
eg.
- 任意公共方法的执行:execution(public * *(…))
- 任何一个以“set”开始的方法的执行:execution(* set*(…))
- AccountService 接口的任意方法的执行:execution(* com.xyz.service.AccountService.*(…))
- 定义在service包里的任意方法的执行: execution(* com.xyz.service..(…))
- 定义在service包和所有子包里的任意类的任意方法的执行:execution(* com.xyz.service….(…))
第一个表示匹配任意的方法返回值, …(两个点)表示零个或多个,第一个…表示service包及其子包,第二个表示所有类, 第三个*表示所有方法,第二个…表示方法的任意参数个数
- 定义在pointcutexp包和所有子包里的JoinPointObjP2类的任意方法的执行:execution(com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp…JoinPointObjP2.(…))”)
- pointcutexp包里的任意类: within(com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp.*)
- pointcutexp包和所有子包里的任意类:within(com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp…*)
- 实现了Intf接口的所有类,如果Intf不是接口,限定Intf单个类:this(com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp.Intf)
- 当一个实现了接口的类被AOP的时候,用getBean方法必须cast为接口类型,不能为该类的类型
- 带有@Transactional标注的所有类的任意方法: @within(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional) @target(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional)
- 带有@Transactional标注的任意方法:
@annotation(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional)
@within和@target针对类的注解,@annotation是针对方法的注解 - 参数带有@Transactional标注的方法:@args(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional)
- 参数为String类型(运行是决定)的方法: args(String)
运行结果: 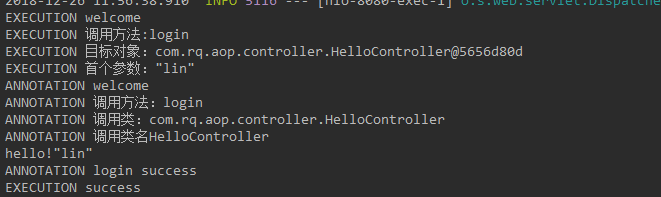
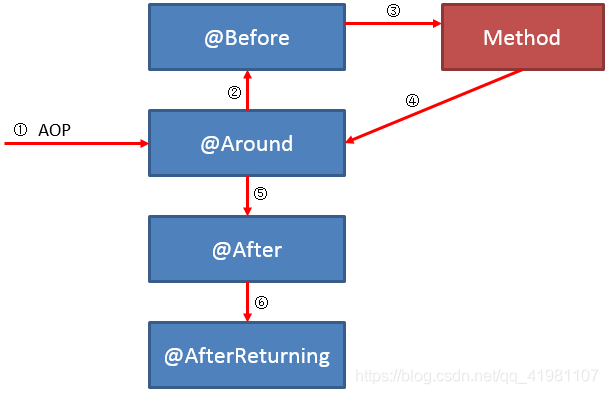
切面执行顺序:
异常: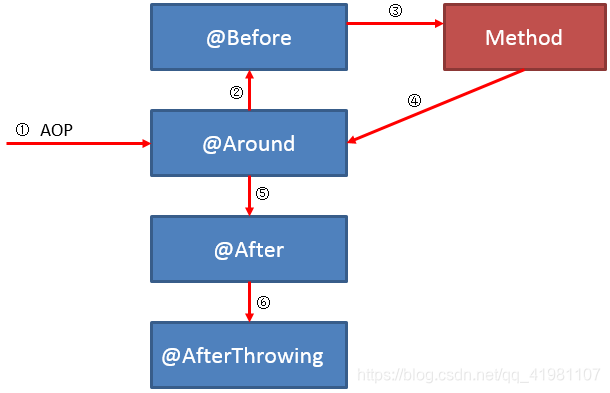































还没有评论,来说两句吧...