2017 ICPC 北京
E.
0 15 solved by hl
15 solved by hl
按照题意模拟即可


#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cmath>#include <cstring>#include <cstdio>#include <queue>#include <map>#include <set>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;int N,M,X;struct point{int c,t;point(int c = 0,int t = 0):c(c),t(t){}friend bool operator < (point a,point b){if(a.t == b.t) return a.c > b.c;return a.t > b.t;}};int main(){while(~scanf("%d%d%d",&N,&M,&X)){priority_queue<point>Q;for(int i = 1; i <= M ; i ++){int x; scanf("%d",&x);Q.push(point(x,0));}int sum1 = 0,sum2 = 0;while(!Q.empty() && sum1 < N){point u = Q.top(); Q.pop();u.t += u.c;sum1++;if(u.t > X) sum2++;if(u.t < X) Q.push(u);}N = max(0,N - sum1);printf("%d %d\n",N,sum2);}return 0;}
E
F.
0 05 solved by gbs
05 solved by gbs
也是模拟题


#include <iostream>#include<stdio.h>#include <string.h>using namespace std;int t,n;char sa[105][105];char ans[105][105];int nowx1,nowy1;int nowx2,nowy2;int flag1;int flag2;int newx,newy;bool judge(){if (newx<0||newx>=n)return false;if (newy<0||newy>=n)return false;return true;}bool judge2(){if (newx<0||newx>=n)return false;if (newy<0||newy>=n)return false;if (ans[newy][newx] != 0)return false;return true;}void next1(){if (flag1 == 0 ){if (nowx1 == n-1){flag1++;nowy1++;return ;}nowx1++;flag1++;return ;}else if (flag1 == 2 ){if (nowy1 == n-1){flag1++;nowx1++;return ;}nowy1++;flag1++;}else if (flag1 == 1 ){newx = nowx1-1;newy = nowy1+1;if (!judge()){flag1++;next1();}else{nowx1 = newx;nowy1 = newy;}return ;}else{newx = nowx1+1;newy = nowy1-1;if (!judge()){flag1=0;next1();}else{nowx1 = newx;nowy1 = newy;}return ;}}void next2(){newx = nowx2;newy = nowy2;if (flag2 == 0)newx++;if (flag2 == 1)newy++;if (flag2 == 2)newx--;if (flag2 == 3)newy--;if (judge2()){nowx2 = newx;nowy2 = newy;}else{flag2 = (flag2+1)%4;next2();}}int main(){while(cin >>n){;for (int i=0; i<n; i++){scanf("%s",sa[i]);}memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans));int n2 = n*n;nowx1 = nowy1 =0;nowx2 = nowy2 = 0;flag1 = flag2 = 0;for (int i=0; i<n2; i++){//cout<<nowy1<<' '<<nowx1<<endl;ans[nowy2][nowx2] = sa[nowy1][nowx1];if (i!=n2-1){next1();next2();}}for (int i=0; i<n; i++){printf("%s\n",ans[i]);}}return 0;}
F
G.披着bfs题外衣的计算几何题
难点在于判断线段穿过三角形内部
需要分三种情况
1.线段两端在三角形外
2.线段两端都在三角形内
3.线段两端一个在外一个在内
讨论一下就


#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cmath>#include <cstring>#include <cstdio>#include <queue>#include <map>#include <set>#include <algorithm>#define LL long longusing namespace std;#define fi first#define se second#define db doubleint ma[25][25];int vis[25][25];int dx[]={1,0,-1,0,1,-1,1,-1};int dy[]={0,1,0,-1,1,-1,-1,1};double X1,X2,X3,Y1,Y2,Y3;int n;struct Point{double x,y;Point (double x=0,double y=0):x(x),y(y){}Point operator - (const Point &b) const {return Point(x-b.x,y-b.y); }};Point t1,t2,t3;double Cross(Point a,Point b){return a.x*b.y-b.x*a.y;}double eps=1e-8;int dcmp(double x){if(x<-eps) return -1;if(x>eps) return 1;return 0;}bool SegmentProperIntersection(const Point &a1,const Point &b1,const Point &a2,const Point &b2)//两线段规范相交、即每条线段的端点分别在另一条一段的两侧{db c1=Cross(b1-a1,a2-a1),c2=Cross(b1-a1,b2-a1);db c3=Cross(b2-a2,a1-a2),c4=Cross(b2-a2,b1-a2);return dcmp(c1)*dcmp(c2)<0 && dcmp(c3)*dcmp(c4)<0;}bool in(Point a,Point t1,Point t2,Point t3){int s1=dcmp(Cross(a-t1,t2-t1));int s2=dcmp(Cross(a-t2,t3-t2));int s3=dcmp(Cross(a-t3,t1-t3));return ((s1<0&&s2<0&&s3<0)||(s1>0&&s2>0&&s3>0));}bool legle(int a,int b,int c,int d,int j){if(c<0||c>=n||d<0||d>=n||ma[c][d]==0||vis[c][d]) return false;if(in(Point(c,d),t1,t2,t3)) return false;if(in(Point(a+dx[j]*0.01,b+dy[j]*0.01),t1,t2,t3)) return false;if(in(Point(c-dx[j]*0.01,d-dy[j]*0.01),t1,t2,t3)) return false;if(SegmentProperIntersection(Point(a,b),Point(c,d),t1,t2)) return false;if(SegmentProperIntersection(Point(a,b),Point(c,d),t3,t2)) return false;if(SegmentProperIntersection(Point(a,b),Point(c,d),t1,t3)) return false;return true;}int main(){while(cin>>n){cin>>X1>>Y1>>X2>>Y2>>X3>>Y3;t1=Point(X1,Y1);t2=Point(X2,Y2);t3=Point(X3,Y3);char s[50];for(int j=n-1;j>=0;j--){scanf("%s",s);for(int i=0;i<n;i++){if(s[i]=='.'){ma[i][j]=1;}else{ma[i][j]=0;}vis[i][j]=0;}}queue<pair<int,int> > q;q.push(make_pair(0,0));vis[0][0]=1;while(!q.empty()){pair<int,int> top=q.front();q.pop();//cout<<top.fi<<' '<<top.se<<endl;for(int t=0;t<8;t++){if(legle(top.fi,top.se,top.fi+dx[t],top.se+dy[t],t)){vis[top.fi+dx[t]][top.se+dy[t]]=vis[top.fi][top.se]+1;q.push(make_pair(top.fi+dx[t],top.se+dy[t]));}}}if(!vis[n-1][n-1]||ma[0][0]==0){puts("-1");}else{printf("%d\n",vis[n-1][n-1]-1);}}return 0;}
G
H.
4 48 solved by hl
48 solved by hl
常规的子矩阵最大值之间复杂度是 n²m,即枚举上下界压缩维度之后O(m)
那么这题直接暴力的做法就是n3m2,如果n > m,就n,m互换,时间复杂度就是503 * 1502,然后通过一系列诸如从大到小枚举修改之类的大力剪枝,仰仗着数据不太硬给过了


#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cmath>#include <cstring>#include <cstdio>#include <queue>#include <map>#include <set>#include <algorithm>#define LL long longusing namespace std;int N,M;LL p;const int maxn = 155;const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;LL MAP[maxn][maxn],MAP2[maxn][maxn];LL pre[maxn][maxn];LL a[maxn];LL Max = 0;LL solve(){for(int i = 1; i <= N ; i ++){for(int j = 1; j <= M ; j ++){pre[i][j] = pre[i - 1][j] + MAP[i][j];}}LL ans = -INF;for(int L = 1; L <= N ; L++){for(int R = L;R <= N; R++){for(int i = 1; i <= M; i ++){a[i] = pre[R][i] - pre[L - 1][i];}LL p = 0,pr = 0;for(int i = 1; i <= M ; i ++){pr += a[i];ans = max(ans,pr - p);p = min(p,pr);}}}return ans;}#define PII pair<int,int>#define fi first#define se secondPII tmp[maxn * maxn];bool cmp(PII a,PII b){return MAP[a.fi][a.se] > MAP[b.fi][b.se];}int main(){while(~scanf("%d%d%lld",&N,&M,&p)){for(int i = 1; i <= N ; i ++){for(int j = 1; j <= M ; j ++){scanf("%lld",&MAP2[i][j]);}}if(N > M){swap(N,M);for(int i = 1; i <= N ; i ++){for(int j = 1; j <= M ; j ++){MAP[i][j] = MAP2[j][i];}}}else{for(int i = 1; i <= N ; i ++){for(int j = 1; j <= M ; j ++){MAP[i][j] = MAP2[i][j];// cout << MAP[i][j] << ' ';}// cout << endl;}}LL Min = solve();LL s = Min;int cnt = 0;for(int i = 1; i <= N; i ++){for(int j = 1; j <= M ; j ++) tmp[++cnt] = make_pair(i,j);}sort(tmp + 1,tmp + 1 + cnt,cmp);for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i ++){if(s + p - MAP[tmp[i].fi][tmp[i].se] >= Min) break;LL q = MAP[tmp[i].fi][tmp[i].se];MAP[tmp[i].fi][tmp[i].se] = p;Min = min(Min,solve());MAP[tmp[i].fi][tmp[i].se] = q;}cout << Min << endl;}return 0;}
H
J.区间dp
3 14 solved by hl
14 solved by hl
dp[l][r][h]表示l到r这个区间内的石子被分为h堆需要的最小花费
然后按照枚举区间长度,枚举左端点,枚举区间堆数,枚举中间点,枚举中间点左边区间的堆数
这样的贡献,写个n5次的dp,仰仗着数据不够硬,剪了个枝就过了
不过正解是n4
也就是原来解法中枚举中间点左边区间的堆数这一层事实上是不用枚举的,这个和寻常的区间dp有些出入,从左边选择x堆右边选择y堆使得x + y = k,和左边选择k - 1堆右边选择1堆的情况是一样的,所以可以少枚举一层
也就是在源代码上这么修改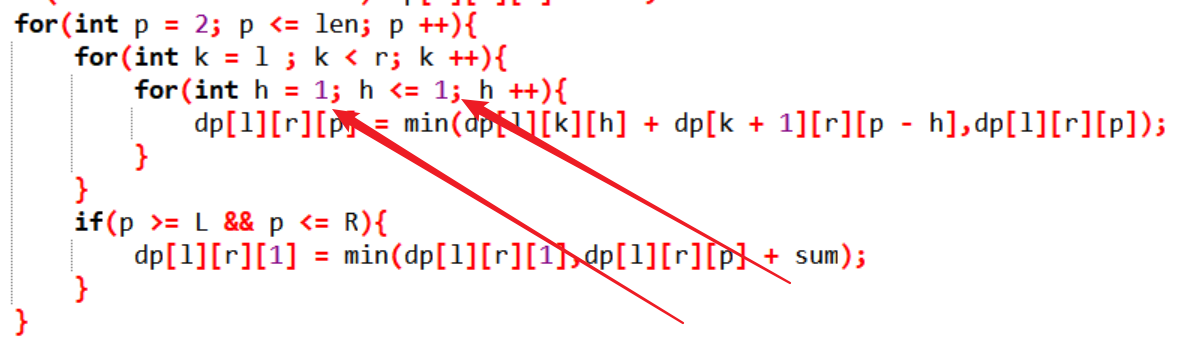 就是正解了
就是正解了


#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cmath>#include <cstring>#include <cstdio>#include <queue>#include <map>#include <set>#include <algorithm>#define LL long longusing namespace std;int N,L,R;const int maxn = 110;const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;int a[maxn];LL pre[maxn];LL dp[maxn][maxn][maxn];int main(){while(~scanf("%d%d%d",&N,&L,&R)){pre[0] = 0;for(int i = 1; i <= N ; i ++) scanf("%d",&a[i]),pre[i] = pre[i - 1] + a[i];for(int i = 1; i <= N ; i ++){for(int j = 1; j <= N ; j ++){for(int k = 0 ; k <= N; k ++){dp[i][j][k] = INF;}}dp[i][i][1] = 0;}for(int len = 1; len <= N ; len ++){for(int l = 1; l + len - 1 <= N ; l ++){int r = l + len - 1;LL sum = pre[r] - pre[l - 1];if(len >= L && len <= R) dp[l][r][1] = sum;for(int p = 2; p <= len; p ++){for(int k = l ; k < r; k ++){for(int h = max(1,p + k - r); h <= min(k - l + 1,p); h ++){dp[l][r][p] = min(dp[l][k][h] + dp[k + 1][r][p - h],dp[l][r][p]);}}if(p >= L && p <= R){dp[l][r][1] = min(dp[l][r][1],dp[l][r][p] + sum);}}}}if(dp[1][N][1] >= INF) dp[1][N][1] = 0;cout << dp[1][N][1] << endl;}return 0;}
J
转载于 //www.cnblogs.com/Hugh-Locke/p/11378901.html
//www.cnblogs.com/Hugh-Locke/p/11378901.html






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...