【C++】C++ primer plus第二章练习题
问答题
- c++程序的模块叫什么?
函数。
- 下面的预处理器编译指令是做什么用的?
#include <iostream>
包含头文件,将iostream文件的内容添加·到代码中
- 下面的语句是做什么用的? using namespace std;
using是预编译器指令,让其使用std命名空间
- 什么语句可以用来打印短语“Hello, world”,然后开始新的一行?
std::cout<<“Hello world” << std::endl;
- 什么语句可以用来创建名为cheeses的整数变量
int cheeses;
- 什么语句可以用来将值32赋给变量cheeses?
cheeses = 32
=运算符,将右侧赋值给左侧
- 什么语句可以用来将从键盘输入的值读入变量cheeses中?
std::cin>>cheeses;
- 什么语句可以用来打印“We have X varieties of cheese,”,其中X为变量cheeses的当前值。
std::cout << “We have “ << cheeses << “ varieties of cheese.” << std::endl;
“We have “ 是字符串
cheeses 是变量名
- 下面的函数原型指出了关于函数的哪些信息?
int froop(double t);
void rattle(int n);
int prune(void);
函数名叫froop(),带有一个参数t,参数类型是double类型,并且函数返回一个整值类型。
所以调用函数froop()时,要提供一个double类型的参数,该函数将返回一个int值
函数名叫rattle,带有一个参数n,参数类型是int类型,函数没有返回值
函数名prune,函数没有参数,不接受任何参数,返回一个int值
- 定义函数时,在什么情况下不必使用关键字return?
当函数没有返回值时,比如void函数,或者以后要讲的构造函数和析构函数等等。
- 假设你编写的main()函数包含如下代码: cout << “Please enter your PIN: “;
而编译器指出cout是一个未知标识符。导致这种问题的原因很可能是什么?指出3种修复这种问题的方法。
原因:在代码中没有声明命名空间,导致编译器不认识
解决办法:
1.using namespace std;
2.using std::cout
3.std::cout
编程题:
- 编写一个c++程序,显示姓名地址
1 #include<iostream>2 using namespace std;3 int main()4 {5 cout<<"xioajiejie"<<endl;6 cout<<"heibei"<<endl;7 return 0;8 }
结果:
[bsk@localhost one]$ ./a.outxioajiejieheibei
- 编写一个c++程序,要求用户输入一个以long为单位的距离,然后将它转换为码(long等于220码)
1 #include<iostream>2 using namespace std;3 int main()4 {5 double distance;6 cout<<"Enter the distance(in long)";7 cin >> distance;8 cout<<"The distance "<<distance<<" long equals " <<220*distance <<endl;9 return 0;10 }
结果:
Enter the distance(in long)2The distance 2 long equals 440
3.编写一个c++程序,他使用3个用户定义的函数(包括main(),并生成下面的输出:
Three blind mice
Three blind mice
See how they run
See how they run
其中一个函数要调用两次,该函数生成前两行;另外一个函数也调用两次,并生成其余的输出。
#include<iostream>using namespace std;void print_mice(void){cout<<"Three blind mice"<<endl; }void print_run(void){cout<<"See how they run"<<endl; }int main(){print_mice();print_mice();print_run();print_run();return 0;}
- 编写一个程序,让用户输入其年龄,然后显示该年龄包含多少个月:
Enter your age:29
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main(){int age;cout << "Enter your age:";cin >> age;cout << "your age include "<< age*12 <<" months"<< endl;return 0;}
- 编写一个程序,其中main()调用一个用户定义的的函数(以摄氏温度值为参数,并返回相应的华氏温度值)。
该程序按下面的格式要求用户输入摄氏温度值,并显示结果:
Please enter a Celsius value:20
20 degrees Celsius is 69 degrees Fahrenheit.
下面是转换公式:
华氏温度=1.8*摄氏温度+32.0
#include<iostream>using namespace std;double CtoF(double C){double F=1.8*C+32.0;return F;}int main(){double celsiusValue,fahrenheitValue;cout << "Please enter a Celsius value: ";cin >> celsiusValue;fahrenheitValue=CtoF(celsiusValue);cout << celsiusValue << " degrees Celsius is " << fahrenheitValue << " degress Fahrenheit" << endl;}
- 编写一个程序,其main()调用一个用户的函数(以光年为参数,并返回对应天文单位的值)。
该程序按下面的格式要求用户输入光年值,并显示结果:
Enter the number of light years: 4.2
4.2 light years =265608 astronomical units.
天文单位是从地球到太阳的平均距离(约150000000公里或93000000英里),光年是光一年走的距离(约10万亿公里或6万亿英里)(除太阳外,最近的恒星大约离地球4.2光年)。请使用double类型,转换公式为:1光年=63240天文单位。
#include<iostream>using namespace std;double LtoA(double lYears){double aUnits=lYears*63240;return aUnits;}int main(){double lYears;cout << "Enter the number of light years: ";cin >> lYears;double aYears=LtoA(lightYears);cout << lYears << " light Years =" << aYears << " astronomical units "<< endl;return 0;}


























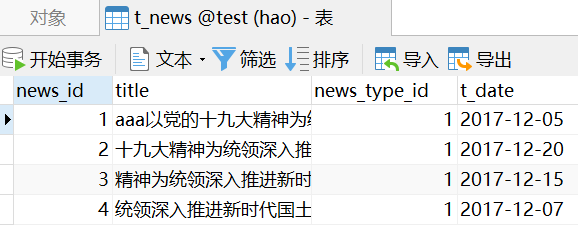
![vue 报错 [Vue warn]: Duplicate keys detected: 'a'. This may cause an update error. vue 报错 [Vue warn]: Duplicate keys detected: 'a'. This may cause an update error.](https://image.dandelioncloud.cn/images/20230531/2d80bd18d31e4608a6dee1e2add77ba8.png)




还没有评论,来说两句吧...