spring与springmvc父子容器
1、spring和springmvc父子容器概念介绍
在spring和springmvc进行整合的时候,一般情况下我们会使用不同的配置文件来配置spring和springmvc,因此我们的应用中会存在至少2个ApplicationContext实例,由于是在web应用中,因此最终实例化的是ApplicationContext的子接口WebApplicationContext。如下图所示:
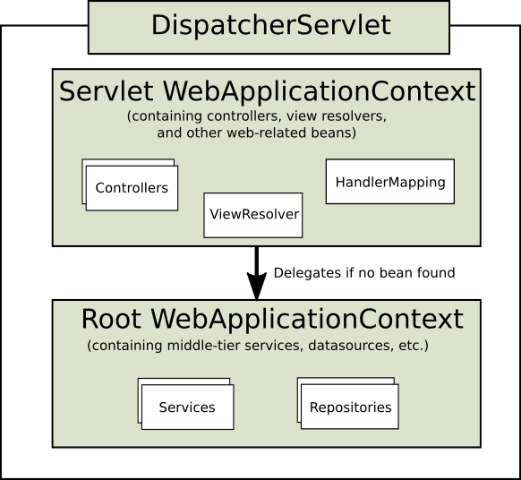
上图中显示了2个WebApplicationContext实例,为了进行区分,分别称之为:Servlet WebApplicationContext、Root WebApplicationContext。 其中:
Servlet WebApplicationContext:这是对J2EE三层架构中的web层进行配置,如控制器(controller)、视图解析器(view resolvers)等相关的bean。通过spring mvc中提供的DispatchServlet来加载配置,通常情况下,配置文件的名称为spring-servlet.xml。
Root WebApplicationContext:这是对J2EE三层架构中的service层、dao层进行配置,如业务bean,数据源(DataSource)等。通常情况下,配置文件的名称为applicationContext.xml。在web应用中,其一般通过ContextLoaderListener来加载。
以下是一个web.xml配置案例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app version="3.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaeehttp://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"><!—创建Root WebApplicationContext--><context-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/applicationContext.xml</param-value></context-param><listener><listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class></listener><!—创建Servlet WebApplicationContext--><servlet><servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/spring-servlet.xml</param-value></init-param><load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name><url-pattern>/*</url-pattern></servlet-mapping></web-app>
在上面的配置中:
1、 ContextLoaderListener会被优先初始化时,其会根据
2、DispatcherServlet在初始化时,会根据
父子容器的作用在于,当我们尝试从child context(即:Servlet WebApplicationContext)中获取一个bean时,如果找不到,则会委派给parent context (即Root WebApplicationContext)来查找。
如果我们没有通过ContextLoaderListener来创建Root WebApplicationContext,那么Servlet WebApplicationContext的parent就是null,也就是没有parent context。
2、为什么要有父子容器
笔者理解,父子容器的作用主要是划分框架边界。
在J2EE三层架构中,在service层我们一般使用spring框架, 而在web层则有多种选择,如spring mvc、struts等。因此,通常对于web层我们会使用单独的配置文件。例如在上面的案例中,一开始我们使用spring-servlet.xml来配置web层,使用applicationContext.xml来配置service、dao层。如果现在我们想把web层从spring mvc替换成struts,那么只需要将spring-servlet.xml替换成Struts的配置文件struts.xml即可,而applicationContext.xml不需要改变。
事实上,如果你的项目确定了只使用spring和spring mvc的话,你甚至可以将service 、dao、web层的bean都放到spring-servlet.xml中进行配置,并不是一定要将service、dao层的配置单独放到applicationContext.xml中,然后使用ContextLoaderListener来加载。在这种情况下,就没有了Root WebApplicationContext,只有Servlet WebApplicationContext。
3、**Root WebApplicationContext创建过程**源码分析
ContextLoaderListener用于创建ROOT WebApplicationContext,其实现了ServletContextListener接口的contextInitialized和contextDestroyed方法,在web应用启动和停止时,web容器(如tomcat)会负责回调这两个方法。而创建Root WebApplicationContext就是在contextInitialized中完成的,相关源码片段如下所示:
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {//...@Overridepublic void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());}//...}
可以看到ContextLoaderListener继承了ContextLoader类,真正的创建在操作,是在ContextLoader的initWebApplicationContext方法中完成。
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader#initWebApplicationContext
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {//1、保证只能有一个ROOT WebApplicationContext//尝试以”org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext.ROOT”为key从ServletContext中查找WebApplicationContext实例//如果已经存在,则抛出异常。//一个典型的异常场景是在web.xml中配置了多个ContextLoaderListener,那么后初始化的ContextLoaderListener就会抛出异常if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");}//2、打印日志,注意日志中的提示内容:"Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext”//这验证了我们之前的说法,ContextLoaderListener创建的是root WebApplicationContextLog logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");}long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();try {if (this.context == null) {// 3 创建WebApplicationContext实现类实例。其内部首先会确定WebApplicationContext实例类型。// 首先判断有没有<context-param>元素的<param-name>值为contextClass,如果有,则对应的<param-value>值,就是要创建的WebApplicationContext实例类型// 如果没有指定,则默认的实现类为XmlWebApplicationContext。这是在spring-web-xxx.jar包中的ContextLoader.properties指定的// 注意这个时候,只是创建了WebApplicationContext对象实例,还没有加载对应的spring配置文件this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);}//4 XmlWebApplicationContext实现了ConfigurableWebApplicationContext接口,因此会进入if代码块if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;// 4.1 由于WebApplicationContext对象实例还没有加载对应配置文件,spring上下文还没有被刷新,因此isActive返回false,进入if代码块if (!cwac.isActive()) {//4.2 当前ROOT WebApplicationContext的父context为null,则尝试通过loadParentContext方法获取父ApplicationContext,并设置到其中//由于loadParentContext方法目前写死返回null,因此可以忽略4.2这个步骤。if (cwac.getParent() == null) {ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);cwac.setParent(parent);}//4.3 加载配置spring文件。根据<context-param>指定的contextConfigLocation,确定配置文件的位置。configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);}}// 5、将创建的WebApplicationContext实例以”org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext.ROOT”为key设置到ServletContext中servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {currentContext = this.context;}else if (ccl != null) {currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);}if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");}if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");}return this.context;}catch (RuntimeException ex) {logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);throw ex;}catch (Error err) {logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);throw err;}}
4、Servlet WebApplicationContext创建过程源码分析
DispatcherServlet负责创建Servlet WebApplicationContext,并尝试将ContextLoaderListener创建的ROOT WebApplicationContext设置为自己的parent。其类图继承关系如下所示:
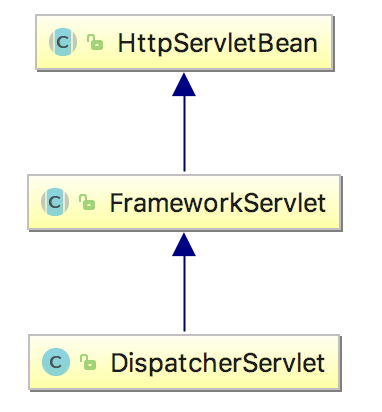
其中HttpServletBean继承了HttpServlet,因此在应用初始化时,其init方法会被调用,如下:
org.springframework.web.servlet.HttpServletBean#init
public final void init() throws ServletException {//...// 这个方法在HttpServletBean中是空实现initServletBean();if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");}}
HttpServletBean的init方法中,调用了initServletBean()方法,在HttpServletBean中,这个方法是空实现。FrameworkServlet覆盖了HttpServletBean中的initServletBean方法,如下:
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#initServletBean
@Overrideprotected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");}long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();try {// initWebApplicationContext方法中,创建了Servlet WebApplicationContext实例this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();initFrameworkServlet();}catch (ServletException ex) {this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);throw ex;}catch (RuntimeException ex) {this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);throw ex;}if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +elapsedTime + " ms");}}
上述代码片段中,我们可以看到通过调用FrameworkServlet的另一个方法initWebApplicationContext(),来真正创建WebApplicationContext实例,其源码如下:
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#initWebApplicationContext
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {//1 通过工具类WebApplicationContextUtils来获取Root WebApplicationContext// 其内部以”org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext.ROOT”为key从ServletContext中查找WebApplicationContext实例作为rootContextWebApplicationContext rootContext =WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());WebApplicationContext wac = null;//2、在我们的案例中是通过web.xml配置的DispatcherServlet,此时webApplicationContext为null,因此不会进入以下代码块if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use itwac = this.webApplicationContext;if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;if (!cwac.isActive()) {// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etcif (cwac.getParent() == null) {// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parentcwac.setParent(rootContext);}configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);}}}//3 经过第二步,wac依然为null,此时尝试根据FrameServlet的contextAttribute 字段的值,从ServletContext中获取Servlet WebApplicationContext实例,在我们的案例中,contextAttribute值为空,因此这一步过后,wac依然为nullif (wac == null) {// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context idwac = findWebApplicationContext();}//4 开始真正的创建Servlet WebApplicationContext,并将rootContext设置为parentif (wac == null) {// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local onewac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);}if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh// support or the context injected at construction time had already been// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.onRefresh(wac);}if (this.publishContext) {// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");}}return wac;}
5 java方式配置
最后,对于Root WebApplicationContext和Servlet WebApplicationContext的创建,我们也可以通过java代码的方式进行配置。spring通过以下几个类对此提供了支持:
AbstractContextLoaderInitializer:其用于动态的往ServletContext中注册一个ContextLoaderListener,从而创建Root WebApplicationContext
AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer:其用于动态的往ServletContext中注册一个DispatcherServlet,从而创建Servlet WebApplicationContext
对应的类图继承关系如下所示:
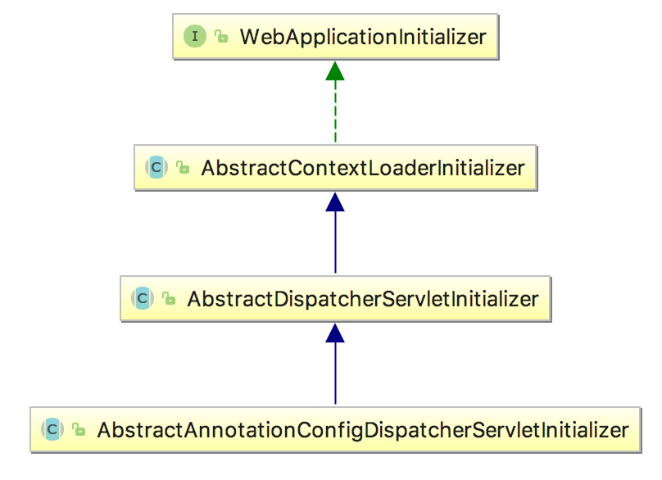
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer用于提供AbstractContextLoaderInitializer和AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer所需要的配置。
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer中有3个抽象方法需要实现:
public class MyWebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {//获得创建Root WebApplicationContext所需的配置类@Overrideprotected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {return new Class<?[] { RootConfig.class };}//获得创建Servlet WebApplicationContext所需的配置类@Overrideprotected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {return new Class<?[] { App1Config.class };}//获得DispatchServlet拦截的url@Overrideprotected String[] getServletMappings() {return new String[] { "/app1/*" };}}


































还没有评论,来说两句吧...