二叉树实现(构造,遍历)-jav
构造函数-节点
public class TreeNode {public int val=0;public TreeNode left = null;public TreeNode right = null;public int getVal() {return val;}public TreeNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}//主函数import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.List;import java.util.Queue;import java.util.Stack;/****//*** @author Home**/public class BinTreeMain {/*** @param args*/private int[] array = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };private static List<TreeNode> nodeList = null;public static void main(String[] args) {new BinTreeMain().createBinTree();TreeNode root = nodeList.get(0);System.out.println("递归先序:");preOrder(root);System.out.println("非递归先序:");PreOrder(root);System.out.println("递归中序:");inOrder(root);System.out.println("非递归中序:");InOrder(root);System.out.println();postOrder(root);System.out.println();levelOrder(root);System.out.println();System.out.println(Height(root));new BinTreeMain().Mirror(root);levelOrder(root);System.out.println(isSymmetrical(root));}// 建树public void createBinTree() {nodeList = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)nodeList.add(new TreeNode(array[i]));for (int parentIndex = 0; parentIndex < array.length / 2 - 1; parentIndex++) {// 左孩子nodeList.get(parentIndex).left = nodeList.get(parentIndex * 2 + 1);nodeList.get(parentIndex).right = nodeList.get(parentIndex * 2 + 2);}int lastparentIndex = array.length / 2 - 1;nodeList.get(lastparentIndex).left = nodeList.get(lastparentIndex * 2 + 1);if (array.length % 2 == 1)nodeList.get(lastparentIndex).right = nodeList.get(lastparentIndex * 2 + 2);}// 先序遍历输出-递归public static void preOrder(TreeNode node) {if (node != null) {System.out.print(node.val + "\t");preOrder(node.left);preOrder(node.right);}}// 先序遍历输出-非递归public static void PreOrder(TreeNode node) {Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();if (node != null) {TreeNode p = node;while (p != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {if (p != null) {System.out.print(p.val + "\t");stack.push(p);p = p.left;} else {//在刚才那个p的左子树为空,或者p为叶子节点时执行。p = stack.pop();p = p.right;}}}}// 中序遍历输出public static void inOrder(TreeNode node) {if (node != null) {inOrder(node.left);System.out.print(node.val + "\t");inOrder(node.right);}}//中序遍历-非递归public static void InOrder(TreeNode node){Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();if(node!=null){TreeNode p = node;while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){if(p!=null){stack.push(p);p = p.left;}else{p = stack.pop();System.out.print(p.val+"\t");p = p.right;}}}}// 后序递归遍历输出public static void postOrder(TreeNode node) {if (node != null) {postOrder(node.left);postOrder(node.right);System.out.print(node.val + "\t");}}//根据先序序列和中序序列唯一建造一棵二叉树,返回二叉树的根public TreeNode preAndinCreateTree(char[] pre,char[] in,int i,int j,int m,int n){//数组pre存储先序序列,i,j分别表示pre的上标和下标//in:中序序列,m,n分别表示in的上标和下标//函数返回先序序列和中序序列构成的树的根int k;TreeNode p=null;if(n<0)return null;p = new TreeNode(pre[i]);k = m;//在中序中找根while((k<=n)&&in[k]!=pre[i])k++;p.left = preAndinCreateTree(pre,in,i+1,i+k-m,m,k-1);p.right = preAndinCreateTree(pre,in,i+k-m+1,j,k+1,n);return p;}// 层次遍历public static void levelOrder(TreeNode node) {Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();if (node != null) {queue.add(node);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode nnode = queue.poll();System.out.print(nnode.val + "\t");if (nnode.left != null)queue.add(nnode.left);if (nnode.right != null)queue.add(nnode.right);}}}// 求二叉树的高度public static int Height(TreeNode node) {int lh, rh;if (node == null)return 0;else {lh = Height(node.left);rh = Height(node.right);return 1 + (lh > rh ? lh : rh);}}// 操作给定的二叉树,将其变换为源二叉树的镜像。public void Mirror(TreeNode root) {if (root != null) {TreeNode temp = root.left;root.left = root.right;root.right = temp;Mirror(root.left);Mirror(root.right);}}/** 二叉树的下一个结点 给定一个二叉树和其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。* 注意,树中的结点不仅包含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的指针。*/// 对称的二叉树static boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode pRoot) {if (pRoot == null)return true;return lrSym(pRoot.left, pRoot.right);}static boolean lrSym(TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {if (left == null && right == null)return true;if (left != null && right != null)return left.val == right.val && lrSym(left.left, right.right)&& lrSym(left.right, right.left);return false;}}



























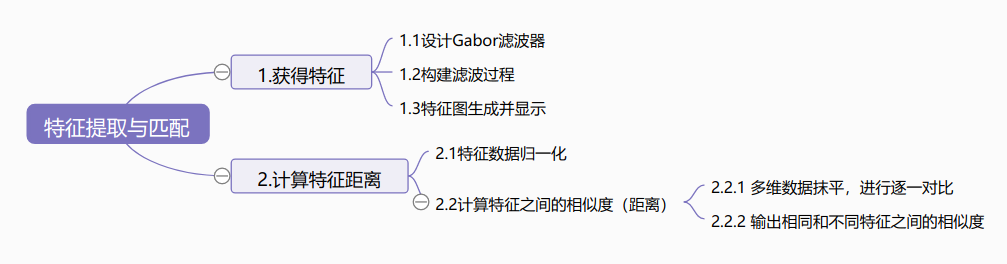
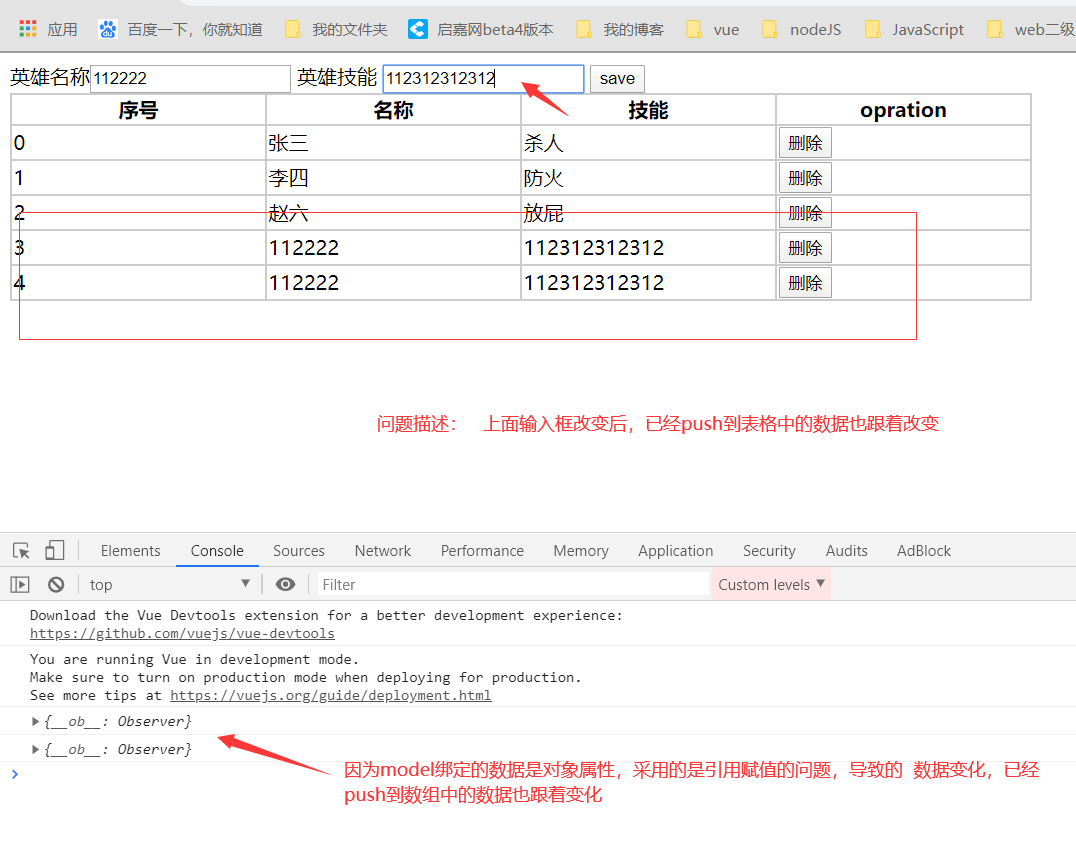
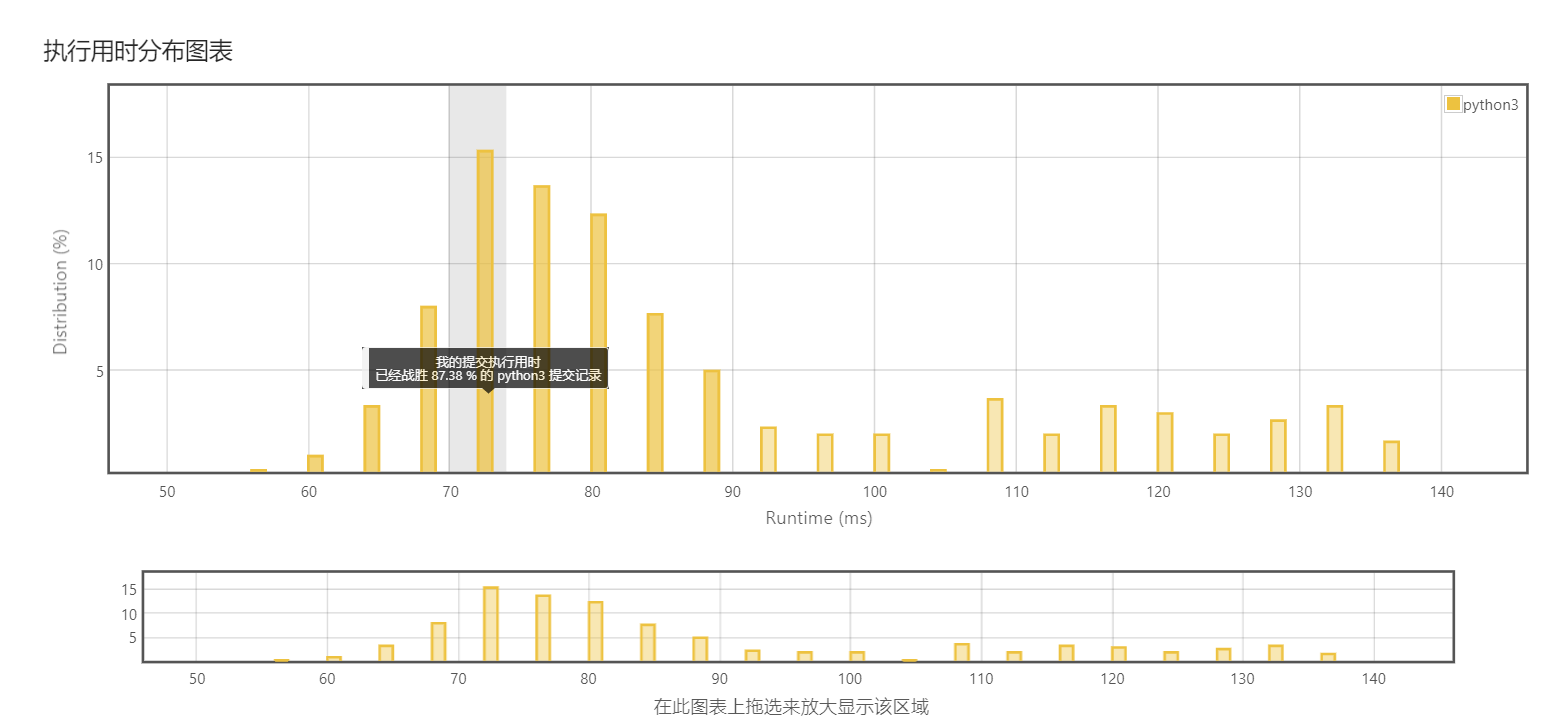



还没有评论,来说两句吧...