ByteBuf在Netty占据着中重要的位置,上篇《[Netty——ByteBuf功能之说][Netty_ByteBuf]》讲了ByteBuf的工作原理和重要功能介绍。这篇从源码的角度来看ByteBuf。首先,来看一下主要的类继承结构图:
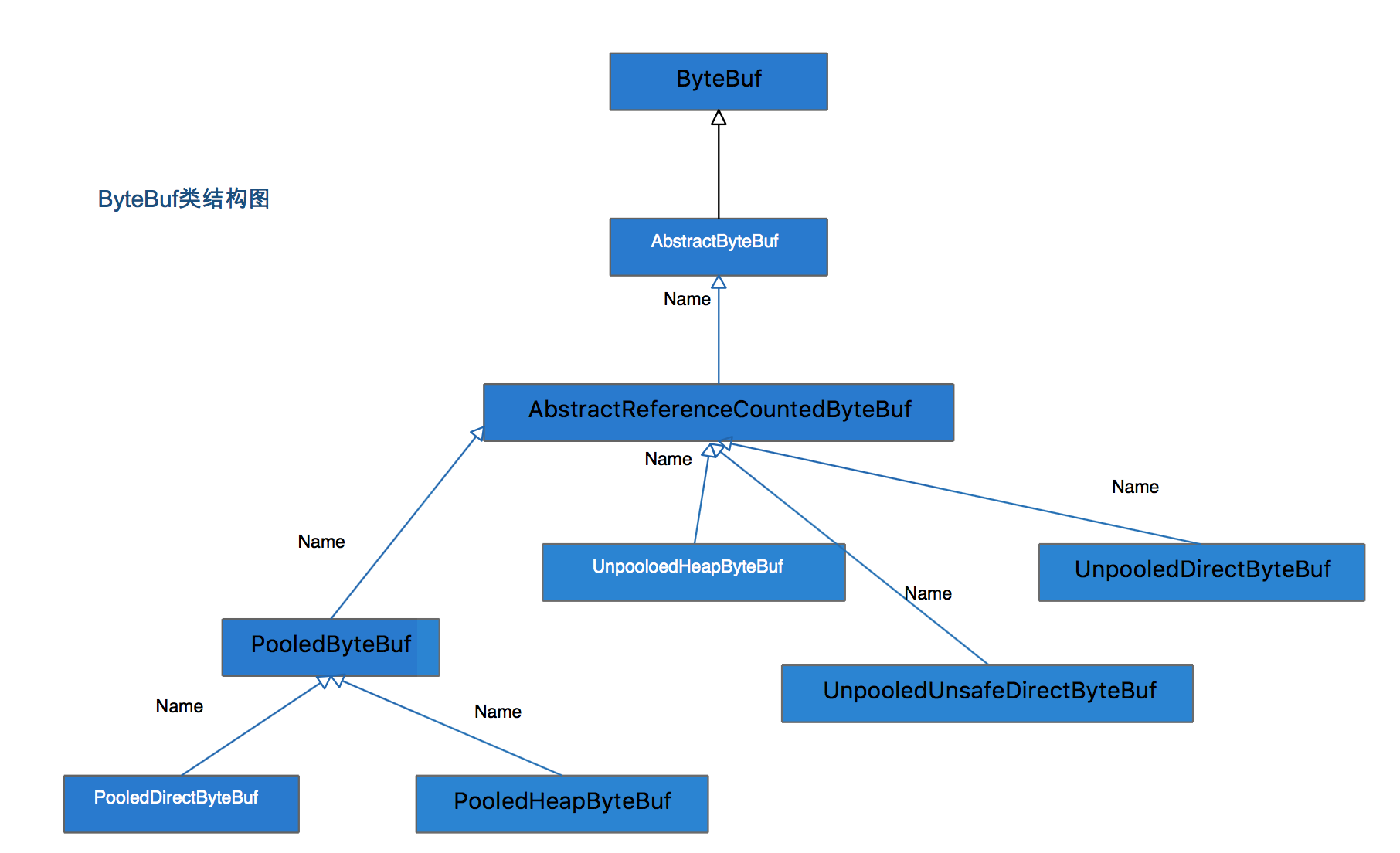
我们从两个角度看下上图: 从内容分配角度上分为:1,堆内存(HeapByteBuf)字节缓冲区,特点是内存的分配和回收速度快,可被JVM自动回收;缺点是如果进行Socket的I/O读写,需要额外做一次内存复制,将堆内存对应的缓冲区复制到内核Channel中,性能会有一定程度的下降。2,直接内存(DirectByteBuf)字节缓冲区:在堆外进行内存分配,相比于堆内存分配和回收速度会慢一些,但是将它写入或者从Socket Channel中读取会很快。经验表明:ByteBuf的最佳实践是在I/O通信线程的读写缓冲区使用DirectByteBuf,后端业务消息处理使用HeapByteBuf。 从内存回收角度看分为:1,对象池的ByteBuf和普通的ByteBuf。主要区别就是对象池的ByteBuf维护了一个内存池,可以循环利用创建的ByteBuf,提高内存的使用率,降低由于高负载导致的频繁GC。 好,下边,我来看下各个类的源码分析,由于我这里用思维导图进行的源码分析总结,将涉及到源码的部分放到了注释中,就不一一展示了,这里先看下总结的导图吧:
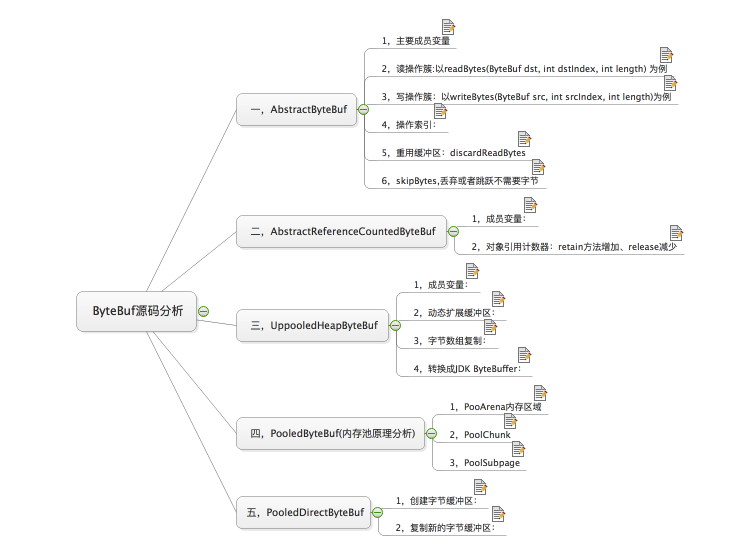
这里看下第一个吧,其它可以自己跟着思维导图查看,或者下载思维导图——[ByteBuf源码之析][ByteBuf]。AbstractByteBuf继承自ByteBuf,一些公共属性和功能会体现这个类中,源码分析:一,主要成员变量:说明:1,读索引、写索引、mark、最大容量等公共属性; 2,leakDetector 为static,用于检测对象的是否泄漏; 3,将缓存区实现放到子类实现,让子类决定是基于堆内存还是直接内存。static final ResourceLeakDetector<ByteBuf> leakDetector = new ResourceLeakDetector<ByteBuf>(ByteBuf.class);int readerIndex;int writerIndex;private int markedReaderIndex;private int markedWriterIndex;private int maxCapacity;/**************************************************/二,读操作簇:以readBytes(ByteBuf dst, int dstIndex, int length) 为例1,方法:@Overridepublic ByteBuf readBytes(ByteBuf dst, int dstIndex, int length) { checkReadableBytes(length); getBytes(readerIndex, dst, dstIndex, length); readerIndex += length; return this;}2,对缓冲区可用空间的校验:/** * Throws an {@link IndexOutOfBoundsException} if the current * {@linkplain #readableBytes() readable bytes} of this buffer is less * than the specified value. */protected final void checkReadableBytes(int minimumReadableBytes) { ensureAccessible(); if (minimumReadableBytes < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("minimumReadableBytes: " + minimumReadableBytes + " (expected: >= 0)"); } if (readerIndex > writerIndex - minimumReadableBytes) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(String.format( "readerIndex(%d) + length(%d) exceeds writerIndex(%d): %s", readerIndex, minimumReadableBytes, writerIndex, this)); }}3,校验通过后,调用getBytes方法,从当前读索引开始,复制length个字节到目标byte数组中。由子类实现,不同子类实现细节不同。4,读索引增加/**************************************************/三,写操作簇:以writeBytes(ByteBuf src, int srcIndex, int length)为例1,方法:@Overridepublic ByteBuf writeBytes(ByteBuf src, int srcIndex, int length) { ensureAccessible(); ensureWritable(length); setBytes(writerIndex, src, srcIndex, length); writerIndex += length; return this;}1.1,写入字节数组的长度校验:@Overridepublic ByteBuf ensureWritable(int minWritableBytes) { if (minWritableBytes < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format( "minWritableBytes: %d (expected: >= 0)", minWritableBytes)); } if (minWritableBytes <= writableBytes()) { return this; } if (minWritableBytes > maxCapacity - writerIndex) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(String.format( "writerIndex(%d) + minWritableBytes(%d) exceeds maxCapacity(%d): %s", writerIndex, minWritableBytes, maxCapacity, this)); } // Normalize the current capacity to the power of 2. int newCapacity = alloc().calculateNewCapacity(writerIndex + minWritableBytes, maxCapacity); // Adjust to the new capacity. capacity(newCapacity); return this;}1.1.1,如果当前写入数组长度大于可写字节数,则通过自身的动态扩展进行满足写需求。扩容方式:首先设置门限阈值threshold 4MB,如果=threshold直接返回,如果<threshold则以64进行倍增;如果>threshold则每次采用4MB扩张。@Overridepublic int calculateNewCapacity(int minNewCapacity, int maxCapacity) { if (minNewCapacity < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("minNewCapacity: " + minNewCapacity + " (expectd: 0+)"); } if (minNewCapacity > maxCapacity) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format( "minNewCapacity: %d (expected: not greater than maxCapacity(%d)", minNewCapacity, maxCapacity)); } final int threshold = 1048576 * 4; // 4 MiB page if (minNewCapacity == threshold) { return threshold; } // If over threshold, do not double but just increase by threshold. if (minNewCapacity > threshold) { int newCapacity = minNewCapacity / threshold * threshold; if (newCapacity > maxCapacity - threshold) { newCapacity = maxCapacity; } else { newCapacity += threshold; } return newCapacity; } // Not over threshold. Double up to 4 MiB, starting from 64. int newCapacity = 64; while (newCapacity < minNewCapacity) { newCapacity <<= 1; } return Math.min(newCapacity, maxCapacity);}/**************************************************/四,操作索引:1,与索引相关主要涉及读写索引、mark、rest等,比较简单,看设置读索引方法:@Overridepublic ByteBuf readerIndex(int readerIndex) { if (readerIndex < 0 || readerIndex > writerIndex) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(String.format( "readerIndex: %d (expected: 0 <= readerIndex <= writerIndex(%d))", readerIndex, writerIndex)); } this.readerIndex = readerIndex; return this;}/**************************************************/五,重用缓冲区:discardReadBytes1,discardReadBytes方法:@Overridepublic ByteBuf discardReadBytes() { ensureAccessible(); if (readerIndex == 0) { return this; } if (readerIndex != writerIndex) { setBytes(0, this, readerIndex, writerIndex - readerIndex); writerIndex -= readerIndex; adjustMarkers(readerIndex); readerIndex = 0; } else { adjustMarkers(readerIndex); writerIndex = readerIndex = 0; } return this;}1.1,adjustMarkers(readerIndex)方法设置markedReaderIndex和markedWriteIndex:protected final void adjustMarkers(int decrement) { int markedReaderIndex = this.markedReaderIndex; if (markedReaderIndex <= decrement) { this.markedReaderIndex = 0; int markedWriterIndex = this.markedWriterIndex; if (markedWriterIndex <= decrement) { this.markedWriterIndex = 0; } else { this.markedWriterIndex = markedWriterIndex - decrement; } } else { this.markedReaderIndex = markedReaderIndex - decrement; markedWriterIndex -= decrement; }}/**************************************************/六,skipBytes,丢弃或者跳跃不需要字节1,看方法源码:@Overridepublic ByteBuf skipBytes(int length) { checkReadableBytes(length); readerIndex += length; return this;} 下边我们在来简单看下ButyBuf的几个重要的辅助类,其实都非常简单,为了更容易扩展,为了提供更多的基本功能,都是非常实用的,我们来看下简单说明:
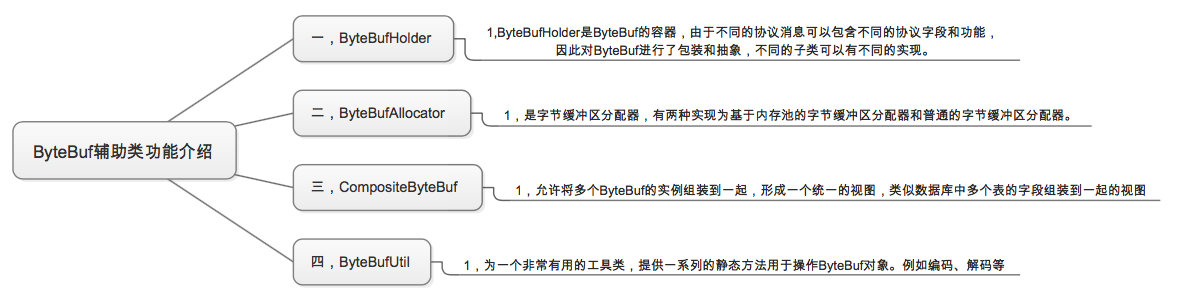
好,这样我么Netty的ByteBuf相关内容就学习完了,需要思考的是,作者对此的设计思路,实现方式,编码风格等,剩下就是我们多用多做多思考,来更进一步的理解了。接下来,Netty其它重要类源码的学习思考。。。欢迎大家多交流。 PS:思维导图下载地址:[ByteBuf源码分析][ByteBuf]。也可以到我的资源中进行下载。

































还没有评论,来说两句吧...