spring-cloud-eureka (三) 注册中心源码分析
Eureka是一个开源的服务治理框架,它提供了完成的Service Registry和Service Discovery实现,并且和Spring Cloud无缝集成,使用Spring Boot + Spring Cloud可以轻松的将注册中心搭建起来。
Eureka架构
基础架构
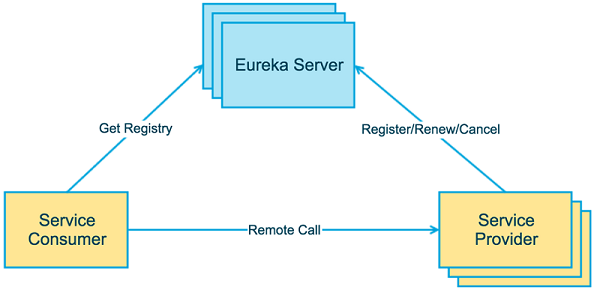
上图简单的描述了Eureka的基本结构,由3个角色组成:
- Eureka Server: 维护服务信息,包括实例信息,提供服务治理基础功能的功能,如服务注册和服务发现。
- Service Provider: 服务提供者,将自身提供的服务注册到Eureka Server,使服务消费者能够从Eureka Server中获取到。
- Service Consumer: 服务消费者,从Eureka Server中获取注册服务列表,从而调用相关的服务。
上述三个角色都是抽象的逻辑角色,在实际运行中,这几个角色可以是同一个实例。
高可用架构
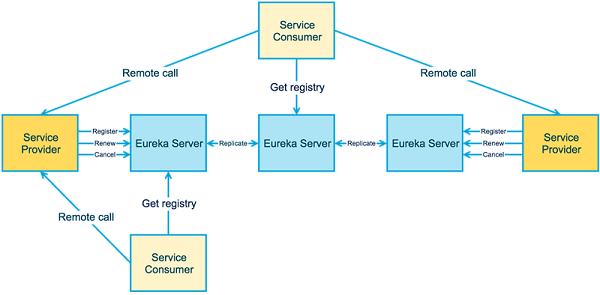
上图更进一步的展示了3个角色之间的交互。
- 服务提供者向Eureka Server发送服务注册、服务续约、服务下线等操作。
- Eureka Server 之间会进行注册服务的同步, 从而保证服务状态一致。
- 服务消费者向Eureka Server获取注册服务列表,并调用服务。
源码分析
服务注册
Eureka Server会维护一个服务清单列表,这个列表是一个双层结构的Map对象,其中第一层的key是服务名,第二层的key是服务实例名。
我们从Eureka Server 的配置类org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EurekaServerAutoConfiguration中可以找到, 发布的服务实例注册表是org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.InstanceRegistry。
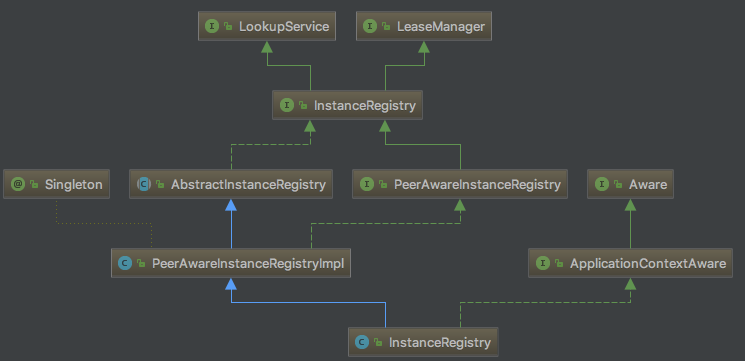
InstanceRegistry类继承了PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl类,所以它支持集群。
还有一个InstanceRegistry接口,它的完成路径是com.netflix.eureka.registry.InstanceRegistry。org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.InstanceRegistry类是它的实现类。该接口从字面意思可以理解为实例注册表,它继承了LeaseManager接口和LookupService接口。
- LookupService接口主要是查找正常运行的服务实例。
- LeaseManager接口主要是维护可用服务清单的,它将服务的可能期限抽象为租约期限,该接口负责为一个实例的租约的创建、续约、和下线。
发布事件
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.InstanceRegistry类会帮服务注册、服务续约、服务下线操作发布一个相应的事件,然后调用父类的方法。
...public class InstanceRegistry extends PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl implements ApplicationContextAware {...//服务注册@Overridepublic void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) {handleRegistration(info, resolveInstanceLeaseDuration(info), isReplication);super.register(info, isReplication);}//服务下线@Overridepublic boolean cancel(String appName, String serverId, boolean isReplication) {handleCancelation(appName, serverId, isReplication);return super.cancel(appName, serverId, isReplication);}//服务续约@Overridepublic boolean renew(final String appName, final String serverId,boolean isReplication) {log("renew " + appName + " serverId " + serverId + ", isReplication {}"+ isReplication);List<Application> applications = getSortedApplications();for (Application input : applications) {if (input.getName().equals(appName)) {InstanceInfo instance = null;for (InstanceInfo info : input.getInstances()) {if (info.getId().equals(serverId)) {instance = info;break;}}publishEvent(new EurekaInstanceRenewedEvent(this, appName, serverId,instance, isReplication));break;}}return super.renew(appName, serverId, isReplication);}...}
| 操作 | 事件 |
|---|---|
| 服务注册 | EurekaInstanceRegisteredEvent |
| 服务续约 | EurekaInstanceRenewedEvent |
| 服务下线 | EurekaInstanceCanceledEvent |
Eureka Server 集群同步
InstanceRegistry类继承了 PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl类,所以服务注册、续约、下线等操作完成后,会去调用PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl的相关逻辑。而PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl中主要是添加了一个广播的功能,拥有了将服务实例的注册、续约、下线等操作同步到其它Eureka Server的能力。
com.netflix.eureka.registry.PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl
package com.netflix.eureka.registry;...public class PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl extends AbstractInstanceRegistry implements PeerAwareInstanceRegistry {...@Overridepublic boolean cancel(final String appName, final String id,final boolean isReplication) {//调用父类方法if (super.cancel(appName, id, isReplication)) {//发送广播replicateToPeers(Action.Cancel, appName, id, null, null, isReplication);...return true;}return false;}...@Overridepublic void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) {int leaseDuration = Lease.DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS;if (info.getLeaseInfo() != null && info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs() > 0) {leaseDuration = info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs();}//调用父类方法super.register(info, leaseDuration, isReplication);//发送广播replicateToPeers(Action.Register, info.getAppName(), info.getId(), info, null, isReplication);}...public boolean renew(final String appName, final String id, final boolean isReplication) {//调用父类方法if (super.renew(appName, id, isReplication)) {//发送广播replicateToPeers(Action.Heartbeat, appName, id, null, null, isReplication);return true;}return false;}...//发送同步消息的逻辑,如果是其它Eureka Server同步过来的,就返回不再发送同步消息。private void replicateToPeers(Action action, String appName, String id,InstanceInfo info /* optional */,InstanceStatus newStatus /* optional */, boolean isReplication) {Stopwatch tracer = action.getTimer().start();try {if (isReplication) {numberOfReplicationsLastMin.increment();}// If it is a replication already, do not replicate again as this will create a poison replicationif (peerEurekaNodes == Collections.EMPTY_LIST || isReplication) {return;}for (final PeerEurekaNode node : peerEurekaNodes.getPeerEurekaNodes()) {// If the url represents this host, do not replicate to yourself.if (peerEurekaNodes.isThisMyUrl(node.getServiceUrl())) {continue;}replicateInstanceActionsToPeers(action, appName, id, info, newStatus, node);}} finally {tracer.stop();}}//发送同步消息的操作, PeerEurekaNode.replicationClient最终调用的是JerseyReplicationClientprivate void replicateInstanceActionsToPeers(Action action, String appName,String id, InstanceInfo info, InstanceStatus newStatus,PeerEurekaNode node) {try {InstanceInfo infoFromRegistry = null;CurrentRequestVersion.set(Version.V2);switch (action) {case Cancel:node.cancel(appName, id);break;case Heartbeat:InstanceStatus overriddenStatus = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.get(id);infoFromRegistry = getInstanceByAppAndId(appName, id, false);node.heartbeat(appName, id, infoFromRegistry, overriddenStatus, false);break;case Register:node.register(info);break;case StatusUpdate:infoFromRegistry = getInstanceByAppAndId(appName, id, false);node.statusUpdate(appName, id, newStatus, infoFromRegistry);break;case DeleteStatusOverride:infoFromRegistry = getInstanceByAppAndId(appName, id, false);node.deleteStatusOverride(appName, id, infoFromRegistry);break;}} catch (Throwable t) {logger.error("Cannot replicate information to {} for action {}", node.getServiceUrl(), action.name(), t);}}...}
在同步过程中,会通过PeerEurekaNode对象中的replicationClient字段发送消息,该字段是com.netflix.eureka.cluster.HttpReplicationClient接口的实现类,默认是com.netflix.eureka.transport.JerseyReplicationClient。
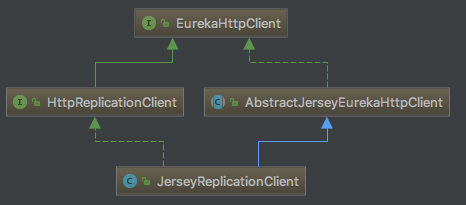
从上图中可以看到,该类是AbstractJerseyEurekaHttpClient类的子类,在上一章中我们分析过AbstractJerseyEurekaHttpClient类,这里就只分析JerseyReplicationClient类了。
JerseyReplicationClient类除了对服务续约、服务状态变更进行了扩展外,就是在http请求头中设置x-netflix-discovery-replication=true。
com.netflix.eureka.transport.JerseyReplicationClient
public class JerseyReplicationClient extends AbstractJerseyEurekaHttpClient implements HttpReplicationClient {...@Overrideprotected void addExtraHeaders(Builder webResource) {webResource.header(PeerEurekaNode.HEADER_REPLICATION, "true");}...}
com.netflix.eureka.cluster.PeerEurekaNode
public class PeerEurekaNode {...public static final String HEADER_REPLICATION = "x-netflix-discovery-replication";...}
Eureka Server之间的同步是在具体操作之后。
服务注册
比如服务注册,是在服务注册完成后,再执行服务同步。所以PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl会在同步之前调用父类AbstractInstanceRegistry的相关逻辑,比如服务注册,而我们在InstanceRegistry类和PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl类中都没有看到服务注册的逻辑,那么主要逻辑就肯定在它们的父类com.netflix.eureka.registry.AbstractInstanceRegistry类中了。
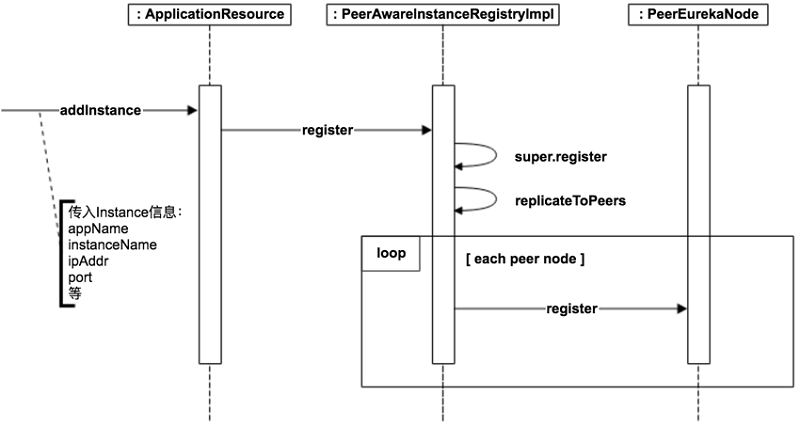
package com.netflix.eureka.registry;...public abstract class AbstractInstanceRegistry implements InstanceRegistry {...//服务清单private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> registry= new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>>();...public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) {try {read.lock();//获取服务的所有实例Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(registrant.getAppName());REGISTER.increment(isReplication);if (gMap == null) {final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gNewMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>();gMap = registry.putIfAbsent(registrant.getAppName(), gNewMap);if (gMap == null) {gMap = gNewMap;}}//获取实例的信息,如果以前没有注册过,就返回nullLease<InstanceInfo> existingLease = gMap.get(registrant.getId());// Retain the last dirty timestamp without overwriting it, if there is already a leaseif (existingLease != null && (existingLease.getHolder() != null)) {Long existingLastDirtyTimestamp = existingLease.getHolder().getLastDirtyTimestamp();Long registrationLastDirtyTimestamp = registrant.getLastDirtyTimestamp();logger.debug("Existing lease found (existing={}, provided={}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp);if (existingLastDirtyTimestamp > registrationLastDirtyTimestamp) {logger.warn("There is an existing lease and the existing lease's dirty timestamp {} is greater" +" than the one that is being registered {}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp);logger.warn("Using the existing instanceInfo instead of the new instanceInfo as the registrant");registrant = existingLease.getHolder();}} else {// The lease does not exist and hence it is a new registrationsynchronized (lock) {if (this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin > 0) {// Since the client wants to cancel it, reduce the threshold// (1// for 30 seconds, 2 for a minute)this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin = this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin + 2;this.numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold =(int) (this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());}}logger.debug("No previous lease information found; it is new registration");}//创建一个新的租约实例Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = new Lease<InstanceInfo>(registrant, leaseDuration);if (existingLease != null) {//如果以前注册过,就设置为以前的注册(启用)时间。(没有明白这个操作的目的)lease.setServiceUpTimestamp(existingLease.getServiceUpTimestamp());}//保存进到服务实例集合中gMap.put(registrant.getId(), lease);synchronized (recentRegisteredQueue) {recentRegisteredQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>(System.currentTimeMillis(),registrant.getAppName() + "(" + registrant.getId() + ")"));}// This is where the initial state transfer of overridden status happensif (!InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN.equals(registrant.getOverriddenStatus())) {logger.debug("Found overridden status {} for instance {}. Checking to see if needs to be add to the "+ "overrides", registrant.getOverriddenStatus(), registrant.getId());if (!overriddenInstanceStatusMap.containsKey(registrant.getId())) {logger.info("Not found overridden id {} and hence adding it", registrant.getId());overriddenInstanceStatusMap.put(registrant.getId(), registrant.getOverriddenStatus());}}InstanceStatus overriddenStatusFromMap = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.get(registrant.getId());if (overriddenStatusFromMap != null) {logger.info("Storing overridden status {} from map", overriddenStatusFromMap);registrant.setOverriddenStatus(overriddenStatusFromMap);}// Set the status based on the overridden status rulesInstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = getOverriddenInstanceStatus(registrant, existingLease, isReplication);registrant.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus);// If the lease is registered with UP status, set lease service up timestampif (InstanceStatus.UP.equals(registrant.getStatus())) {//重新记录当前时间为服务注册(启用)时间lease.serviceUp();}registrant.setActionType(ActionType.ADDED);//记录最近的操作记录。recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(lease));registrant.setLastUpdatedTimestamp();invalidateCache(registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getVIPAddress(), registrant.getSecureVipAddress());logger.info("Registered instance {}/{} with status {} (replication={})",registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getId(), registrant.getStatus(), isReplication);} finally {read.unlock();}}...}
上面就是Eureka Server服务注册的主要逻辑。
服务下线
在了解了服务注册的逻辑后, 服务下线的逻辑就简单很多了。主要是将服务实例从服务实例集合中删除,并留下删除时间和记录。
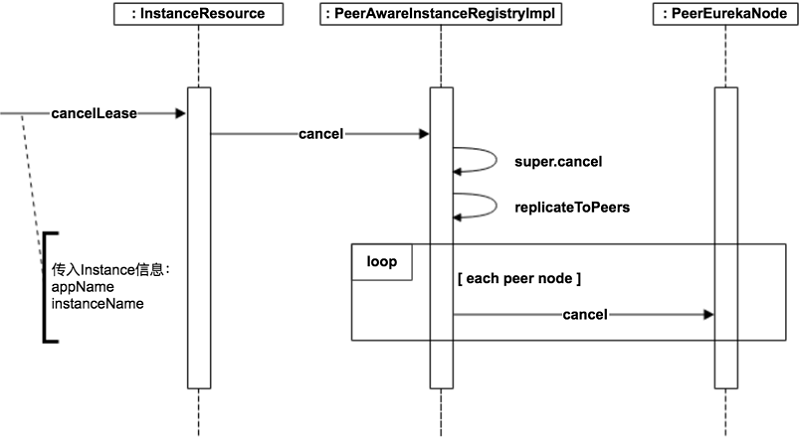
package com.netflix.eureka.registry;...public abstract class AbstractInstanceRegistry implements InstanceRegistry {...@Overridepublic boolean cancel(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication) {return internalCancel(appName, id, isReplication);}/** * {@link #cancel(String, String, boolean)} method is overridden by {@link PeerAwareInstanceRegistry}, so each * cancel request is replicated to the peers. This is however not desired for expires which would be counted * in the remote peers as valid cancellations, so self preservation mode would not kick-in. */protected boolean internalCancel(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication) {try {read.lock();//统计下线服务实例数CANCEL.increment(isReplication);Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(appName);Lease<InstanceInfo> leaseToCancel = null;if (gMap != null) {//删除下线的服务实例leaseToCancel = gMap.remove(id);}synchronized (recentCanceledQueue) {recentCanceledQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>(System.currentTimeMillis(), appName + "(" + id + ")"));}InstanceStatus instanceStatus = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.remove(id);if (instanceStatus != null) {logger.debug("Removed instance id {} from the overridden map which has value {}", id, instanceStatus.name());}if (leaseToCancel == null) {//统计没有找到的下线服务实例数CANCEL_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication);logger.warn("DS: Registry: cancel failed because Lease is not registered for: {}/{}", appName, id);return false;} else {//更新下线/剔除时间leaseToCancel.cancel();InstanceInfo instanceInfo = leaseToCancel.getHolder();String vip = null;String svip = null;if (instanceInfo != null) {instanceInfo.setActionType(ActionType.DELETED);//记录下线/剔除动作recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(leaseToCancel));instanceInfo.setLastUpdatedTimestamp();vip = instanceInfo.getVIPAddress();svip = instanceInfo.getSecureVipAddress();}invalidateCache(appName, vip, svip);logger.info("Cancelled instance {}/{} (replication={})", appName, id, isReplication);return true;}} finally {read.unlock();}}...}
服务续约
服务续约就是一个心跳机制,服务实例每过一段时间就要向Eureka Server报告, 我还正常, 这样才不会被服务剔除机制给删除掉。在代码逻辑里面,就是更新一个租约的最后修改时间,而这个最后修改时间一般会往后加一个租凭期限,这个期限默认是90秒;而在判断租约过期时,也会再加一次租凭期限,所以,默认情况下,一个服务实例如果180秒还没有续约的话,就会判定这个服务实例已不能正常提供服务。
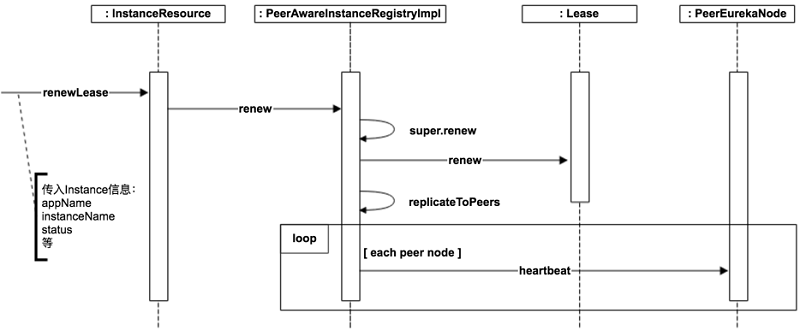
package com.netflix.eureka.registry;...public abstract class AbstractInstanceRegistry implements InstanceRegistry {...public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) {...//将租凭期限做为租约的实例属性,这个值是从子类PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl传递过来的Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = new Lease<InstanceInfo>(registrant, leaseDuration);...}...//服务续约的逻辑public boolean renew(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication) {RENEW.increment(isReplication);Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(appName);Lease<InstanceInfo> leaseToRenew = null;if (gMap != null) {leaseToRenew = gMap.get(id);}if (leaseToRenew == null) {RENEW_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication);logger.warn("DS: Registry: lease doesn't exist, registering resource: {} - {}", appName, id);return false;} else {InstanceInfo instanceInfo = leaseToRenew.getHolder();if (instanceInfo != null) {// touchASGCache(instanceInfo.getASGName());InstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = this.getOverriddenInstanceStatus(instanceInfo, leaseToRenew, isReplication);if (overriddenInstanceStatus == InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN) {logger.info("Instance status UNKNOWN possibly due to deleted override for instance {}"+ "; re-register required", instanceInfo.getId());RENEW_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication);return false;}if (!instanceInfo.getStatus().equals(overriddenInstanceStatus)) {Object[] args = {instanceInfo.getStatus().name(),instanceInfo.getOverriddenStatus().name(),instanceInfo.getId()};logger.info("The instance status {} is different from overridden instance status {} for instance {}. "+ "Hence setting the status to overridden status", args);instanceInfo.setStatus(overriddenInstanceStatus);}}renewsLastMin.increment();//更新续约时间/最后修改时间leaseToRenew.renew();return true;}}...}public class Lease<T> {...//默认的租凭期限public static final int DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS = 90;...private long duration;public Lease(T r, int durationInSecs) {holder = r;registrationTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();lastUpdateTimestamp = registrationTimestamp;duration = (durationInSecs * 1000);}//续约更新最后修改时间public void renew() {lastUpdateTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis() + duration;}...}public class PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl extends AbstractInstanceRegistry implements PeerAwareInstanceRegistry {...@Overridepublic void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) {//设置默认租凭期限int leaseDuration = Lease.DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS;if (info.getLeaseInfo() != null && info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs() > 0) {//如果服务实例有设置租凭期限,就设置为服务实例的租凭期限。leaseDuration = info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs();}super.register(info, leaseDuration, isReplication);replicateToPeers(Action.Register, info.getAppName(), info.getId(), info, null, isReplication);}...}
服务剔除
上面分析中说到如果一个服务实例180秒还没有更新最后修改时间的话, 就将会被服务剔除机制删除。
在该机制中,还有一个保护机制,就是如果在一定时间段内,判断服务续约成功的实例数低于续约阈值(最大心跳总数的85%,相当于服务实例数*2,因为心跳消息默认30s发送一次),Eureka Server会将当前的实例信息保护起来,让这些实例不会过期。当然前提是要开启自我保护机制,默认是开启的,也可以配置eureka.server.enable-self-preservation=false来关闭保护机制。
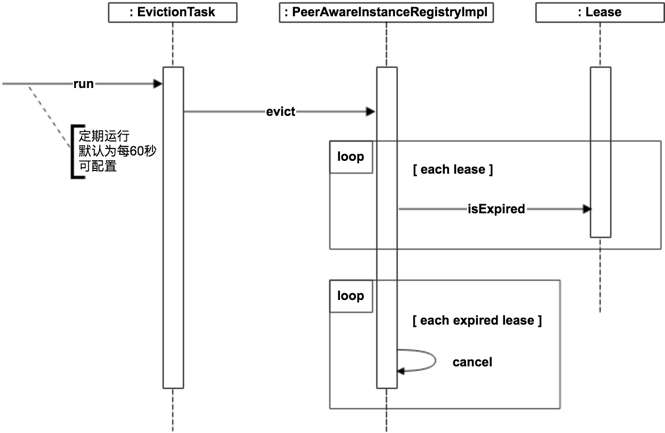
public abstract class AbstractInstanceRegistry implements InstanceRegistry {...@Overridepublic void evict() {evict(0l);}//服务剔除逻辑public void evict(long additionalLeaseMs) {logger.debug("Running the evict task");//保护机制,实现逻辑在PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl中。if (!isLeaseExpirationEnabled()) {logger.debug("DS: lease expiration is currently disabled.");return;}// We collect first all expired items, to evict them in random order. For large eviction sets,// if we do not that, we might wipe out whole apps before self preservation kicks in. By randomizing it,// the impact should be evenly distributed across all applications.List<Lease<InstanceInfo>> expiredLeases = new ArrayList<>();for (Entry<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> groupEntry : registry.entrySet()) {Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseMap = groupEntry.getValue();if (leaseMap != null) {for (Entry<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseEntry : leaseMap.entrySet()) {Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = leaseEntry.getValue();//判断是否过期if (lease.isExpired(additionalLeaseMs) && lease.getHolder() != null) {expiredLeases.add(lease);}}}}// To compensate for GC pauses or drifting local time, we need to use current registry size as a base for// triggering self-preservation. Without that we would wipe out full registry.int registrySize = (int) getLocalRegistrySize();int registrySizeThreshold = (int) (registrySize * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());int evictionLimit = registrySize - registrySizeThreshold;int toEvict = Math.min(expiredLeases.size(), evictionLimit);if (toEvict > 0) {logger.info("Evicting {} items (expired={}, evictionLimit={})", toEvict, expiredLeases.size(), evictionLimit);//传入当前时间为种子生成随机,避免 Java 的伪随机情况Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());for (int i = 0; i < toEvict; i++) {// Pick a random item (Knuth shuffle algorithm)int next = i + random.nextInt(expiredLeases.size() - i);//随机调换后面的元素到当前位置( i )Collections.swap(expiredLeases, i, next);Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = expiredLeases.get(i);String appName = lease.getHolder().getAppName();String id = lease.getHolder().getId();EXPIRED.increment();logger.warn("DS: Registry: expired lease for {}/{}", appName, id);//剔除服务internalCancel(appName, id, false);}}}...}public class Lease<T> {...//默认的租凭期限public static final int DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS = 90;...private long duration;public Lease(T r, int durationInSecs) {holder = r;registrationTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();lastUpdateTimestamp = registrationTimestamp;duration = (durationInSecs * 1000);}//续约更新最后修改时间public void renew() {lastUpdateTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis() + duration;}//判断是否过期,当前时间>最后修改时间+租凭期限public boolean isExpired(long additionalLeaseMs) {return (evictionTimestamp > 0 || System.currentTimeMillis() > (lastUpdateTimestamp + duration + additionalLeaseMs));}...}
下面我们来看看自保护机制的逻辑
public class PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl extends AbstractInstanceRegistry implements PeerAwareInstanceRegistry {...//定时更新续约阈值,默认15分钟private void scheduleRenewalThresholdUpdateTask() {timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {@Overridepublic void run() {updateRenewalThreshold();}}, serverConfig.getRenewalThresholdUpdateIntervalMs(),serverConfig.getRenewalThresholdUpdateIntervalMs());}...//保护机制的判断逻辑@Overridepublic boolean isLeaseExpirationEnabled() {if (!isSelfPreservationModeEnabled()) {// The self preservation mode is disabled, hence allowing the instances to expire.return true;}//判断服务续约成功的实例数低于注册数的85%return numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold > 0 && getNumOfRenewsInLastMin() > numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold;}//判断是否打开保护机制@Overridepublic boolean isSelfPreservationModeEnabled() {return serverConfig.shouldEnableSelfPreservation();}...//更新续约阈值private void updateRenewalThreshold() {try {Applications apps = eurekaClient.getApplications();int count = 0;for (Application app : apps.getRegisteredApplications()) {for (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) {if (this.isRegisterable(instance)) {++count;}}}synchronized (lock) {// Update threshold only if the threshold is greater than the// current expected threshold of if the self preservation is disabled.// 更新续约阈值的判断(这里存在一定问题,会使保护机制一直存在),应用实例每分钟最大心跳数( count * 2 ) 小于期望最小每分钟续租次数( serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold() * numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold ),不重新计算if ((count * 2) > (serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold() * numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold)|| (!this.isSelfPreservationModeEnabled())) {this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin = count * 2;this.numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold = (int) ((count * 2) * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());}}logger.info("Current renewal threshold is : {}", numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold);} catch (Throwable e) {logger.error("Cannot update renewal threshold", e);}}...}
上面的代码中有两个逻辑
- 自我保护的判断逻辑
isLeaseExpirationEnabled()方法是其入口,首先判断是否打开保护机制,默认开启。然后再判断服务续约成功的实例数低于续约阈值,默认是注册数*2的85%,因为心跳是30秒发送一次,而剔除机制是1分钟执行一次。 - 更新自我保护
scheduleRenewalThresholdUpdateTask()方法是该逻辑的入口, 在这个方法中,创建了一个定时任务,默认是每15分钟更新一次续约阈值。
updateRenewalThreshold()方法封装了更新阈值的逻辑。但是如果应用实例每分钟最大心跳数( count * 2 ) 小于期望最小每分钟续租次数( serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold() * numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold ),不重新计算时,并且服务实例确实不可用了,那么自我保护状态会一直存在。
参考资料
《spring cloud 微服务实战》
Eureka 源码解析 —— 应用实例注册发现(四)之自我保护机制
深度剖析服务发现组件Netflix Eureka
































还没有评论,来说两句吧...