使用P6Spy格式化SQL语句
公司最近在做一个项目,开发过程中遇到点小问题,查询结果出不来,查看自带日志打印,有点不爽,特别是想复制sql语句到数据库navicat中去调试时,还要手动复制参数值,很是麻烦,那如果想打印出格式化的详细sql语句,我们该如何做呢?
一、pom.xml文件中添加依赖:
<dependency><groupId>p6spy</groupId><artifactId>p6spy</artifactId></dependency>
二、在profiles下的local和dev中加入spy.properties文件,配置自定义输出格式:
主要是指定数据库驱动(日期格式化、使用单行还是多行),指定输出方式控制台、log文件等)
#### #%L# P6Spy# %%# Copyright (C) 2013 P6Spy# %%# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.# You may obtain a copy of the License at## http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0## Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and# limitations under the License.# #L%##################################################################### P6Spy Options File ## See documentation for detailed instructions ## http://p6spy.github.io/p6spy/2.0/configandusage.html #################################################################################################################################### MODULES ## ## Module list adapts the modular functionality of P6Spy. ## Only modules listed are active. ## (default is com.p6spy.engine.logging.P6LogFactory and ## com.p6spy.engine.spy.P6SpyFactory) ## Please note that the core module (P6SpyFactory) can't be ## deactivated. ## Unlike the other properties, activation of the changes on ## this one requires reload. ###################################################################modulelist=com.p6spy.engine.spy.P6SpyFactory,com.p6spy.engine.logging.P6LogFactory,com.p6spy.engine.outage.P6OutageFactory################################################################# CORE (P6SPY) PROPERTIES ################################################################## A comma separated list of JDBC drivers to load and register.# (default is empty)## Note: This is normally only needed when using P6Spy in an# application server environment with a JNDI data source or when# using a JDBC driver that does not implement the JDBC 4.0 API# (specifically automatic registration).#driverlist=driverlist=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver# for flushing per statement# (default is false)#autoflush = false# sets the date format using Java's SimpleDateFormat routine.# In case property is not set, miliseconds since 1.1.1970 (unix time) is used (default is empty)#dateformat=# prints a stack trace for every statement logged#stacktrace=false# if stacktrace=true, specifies the stack trace to print#stacktraceclass=# determines if property file should be reloaded# Please note: reload means forgetting all the previously set# settings (even those set during runtime - via JMX)# and starting with the clean table# (default is false)#reloadproperties=falsereloadproperties=true# determines how often should be reloaded in seconds# (default is 60)#reloadpropertiesinterval=60# specifies the appender to use for logging# Please note: reload means forgetting all the previously set# settings (even those set during runtime - via JMX)# and starting with the clean table# (only the properties read from the configuration file)# (default is com.p6spy.engine.spy.appender.FileLogger)#appender=com.p6spy.engine.spy.appender.Slf4JLogger#appender=com.p6spy.engine.spy.appender.StdoutLogger#appender=com.p6spy.engine.spy.appender.FileLoggerappender=com.p6spy.engine.spy.appender.Slf4JLogger# name of logfile to use, note Windows users should make sure to use forward slashes in their pathname (e:/test/spy.log)# (used for com.p6spy.engine.spy.appender.FileLogger only)# (default is spy.log)#logfile = spy.log# append to the p6spy log file. if this is set to false the# log file is truncated every time. (file logger only)# (default is true)#append=true# class to use for formatting log messages (default is: com.p6spy.engine.spy.appender.SingleLineFormat)#logMessageFormat=com.p6spy.engine.spy.appender.SingleLineFormatlogMessageFormat=com.dmsdbj.itoo.tool.p6spy.P6SpyLogger# format that is used for logging of the date/time/... (has to be compatible with java.text.SimpleDateFormat)# (default is dd-MMM-yy)#databaseDialectDateFormat=dd-MMM-yydatabaseDialectDateFormat=yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss# whether to expose options via JMX or not# (default is true)#jmx=true# if exposing options via jmx (see option: jmx), what should be the prefix used?# jmx naming pattern constructed is: com.p6spy(.<jmxPrefix>)?:name=<optionsClassName># please note, if there is already such a name in use it would be unregistered first (the last registered wins)# (default is none)#jmxPrefix=################################################################## DataSource replacement ## ## Replace the real DataSource class in your application server ## configuration with the name com.p6spy.engine.spy.P6DataSource ## (that provides also connection pooling and xa support). ## then add the JNDI name and class name of the real ## DataSource here ## ## Values set in this item cannot be reloaded using the ## reloadproperties variable. Once it is loaded, it remains ## in memory until the application is restarted. ## ###################################################################realdatasource=/RealMySqlDS#realdatasourceclass=com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource################################################################## DataSource properties ## ## If you are using the DataSource support to intercept calls ## to a DataSource that requires properties for proper setup, ## define those properties here. Use name value pairs, separate ## the name and value with a semicolon, and separate the ## pairs with commas. ## ## The example shown here is for mysql ## ###################################################################realdatasourceproperties=port;3306,serverName;myhost,databaseName;jbossdb,foo;bar################################################################## JNDI DataSource lookup ## ## If you are using the DataSource support outside of an app ## server, you will probably need to define the JNDI Context ## environment. ## ## If the P6Spy code will be executing inside an app server then ## do not use these properties, and the DataSource lookup will ## use the naming context defined by the app server. ## ## The two standard elements of the naming environment are ## jndicontextfactory and jndicontextproviderurl. If you need ## additional elements, use the jndicontextcustom property. ## You can define multiple properties in jndicontextcustom, ## in name value pairs. Separate the name and value with a ## semicolon, and separate the pairs with commas. ## ## The example shown here is for a standalone program running on ## a machine that is also running JBoss, so the JDNI context ## is configured for JBoss (3.0.4). ## ## (by default all these are empty) ###################################################################jndicontextfactory=org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory#jndicontextproviderurl=localhost:1099#jndicontextcustom=java.naming.factory.url.pkgs;org.jboss.nameing:org.jnp.interfaces#jndicontextfactory=com.ibm.websphere.naming.WsnInitialContextFactory#jndicontextproviderurl=iiop://localhost:900################################################################# P6 LOGGING SPECIFIC PROPERTIES ################################################################## filter what is logged# please note this is a precondition for usage of: include/exclude/sqlexpression# (default is false)#filter=false# comma separated list of strings to include# please note that special characters escaping (used in java) has to be done for the provided regular expression# (default is empty)#include =# comma separated list of strings to exclude# (default is empty)#exclude =# sql expression to evaluate if using regex# please note that special characters escaping (used in java) has to be done for the provided regular expression# (default is empty)#sqlexpression =#list of categories to exclude: error, info, batch, debug, statement,#commit, rollback and result are valid values# (default is info,debug,result,resultset,batch)#excludecategories=info,debug,result,resultset,batchexcludecategories=info,debug,result,resultset# Execution threshold applies to the standard logging of P6Spy.# While the standard logging logs out every statement# regardless of its execution time, this feature puts a time# condition on that logging. Only statements that have taken# longer than the time specified (in milliseconds) will be# logged. This way it is possible to see only statements that# have exceeded some high water mark.# This time is reloadable.## executionThreshold=integer time (milliseconds)# (default is 0)#executionThreshold=################################################################# P6 OUTAGE SPECIFIC PROPERTIES ################################################################## Outage Detection## This feature detects long-running statements that may be indicative of# a database outage problem. If this feature is turned on, it will log any# statement that surpasses the configurable time boundary during its execution.# When this feature is enabled, no other statements are logged except the long# running statements. The interval property is the boundary time set in seconds.# For example, if this is set to 2, then any statement requiring at least 2# seconds will be logged. Note that the same statement will continue to be logged# for as long as it executes. So if the interval is set to 2, and the query takes# 11 seconds, it will be logged 5 times (at the 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 second intervals).## outagedetection=true|false# outagedetectioninterval=integer time (seconds)## (default is false)#outagedetection=false# (default is 60)#outagedetectioninterval=30
三、数据库datasource.xml:
<!--数据库连接设置--><bean id="dataSource" class="com.p6spy.engine.spy.P6DataSource"><constructor-arg><ref bean="dataSourceDefault"/></constructor-arg></bean>
四、local下的log4j.properties文件添加代码(红框里的为新加代码):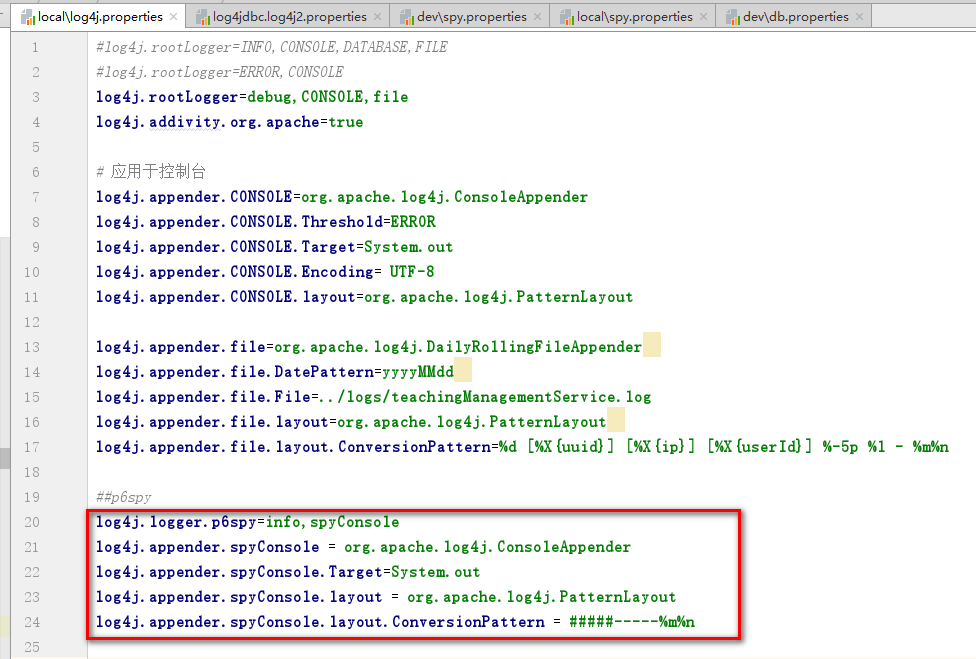
五、初次运行效果:
#####-----1504860808714|2|statement|connection 0|SELECT * FROM t_course c LEFT JOIN t_teacher_course tc ON tc.course_id =c.id LEFT JOIN t_training_programs tp ON tp.course_id=c.id WHERE tp.semester_id = ? AND tp.grade = ? AND tc.teacher_id = ? AND c.is_delete = 0 AND tc.is_delete = 0 AND tp.is_delete = 0|SELECT * FROM t_course c LEFT JOIN t_teacher_course tc ON tc.course_id =c.id LEFT JOIN t_training_programs tp ON tp.course_id=c.id WHERE tp.semester_id = 'YVMEMS37M5KWYDM7LXEX01' AND tp.grade = '2013级' AND tc.teacher_id = '06493cbbdf79f909d6ab0a' AND c.is_delete = 0 AND tc.is_delete = 0 AND tp.is_delete = 0
但是这样的结果,我们还是不太清晰,P6SpyLogger打印的不该是这样的格式,后来发现是tool里的jar包没有下载,于是:
1、在资源管理器中打开代码,按shift+鼠标右键,打开命令窗口: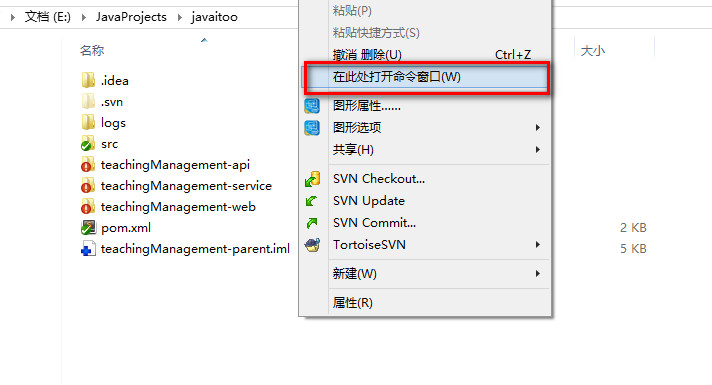
2、命令窗口中输入:mvn compile -U,强制下载tool里jar包: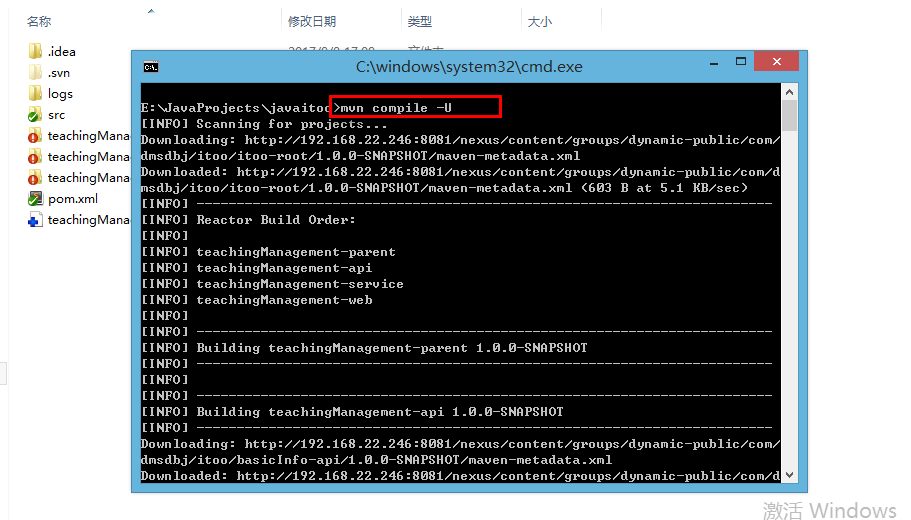
六、最终运行结果:
#####-----2017-09-08 16:59:16:358 | took 3ms | statement | connection 0SELECT * FROM t_course c LEFT JOIN t_teacher_course tc ON tc.course_id =c.id LEFT JOIN t_training_programs tp ON tp.course_id=c.id WHERE tp.semester_id = 'YVMEMS37M5KWYDM7LXEX01' AND tp.grade = '2013级' AND tc.teacher_id = '06493cbbdf79f909d6ab0a' AND c.is_delete = 0 AND tc.is_delete = 0 AND tp.is_delete = 0;
这样我们就可以直观看出sql语句,直接到navicat测试了,怎么样,这样是不是很方便,快来试试吧!
感谢您的阅读!






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...