标准STL中list的各个接口的使用
list是标准STL的序列式容器,它里面的元素是有序的线性序列
STL中的list就是一个带头结点的循环双向链表,可以高效的删除和插入元素。
但是list是不支持随机访问的,因为它的存储空间是不连续的。
而且标准的STL的list我们是通过迭代器来遍历容器里的元素的,迭代器是一种检查容器内元素并遍历元素的数据类型。
标准STL中list的成员函数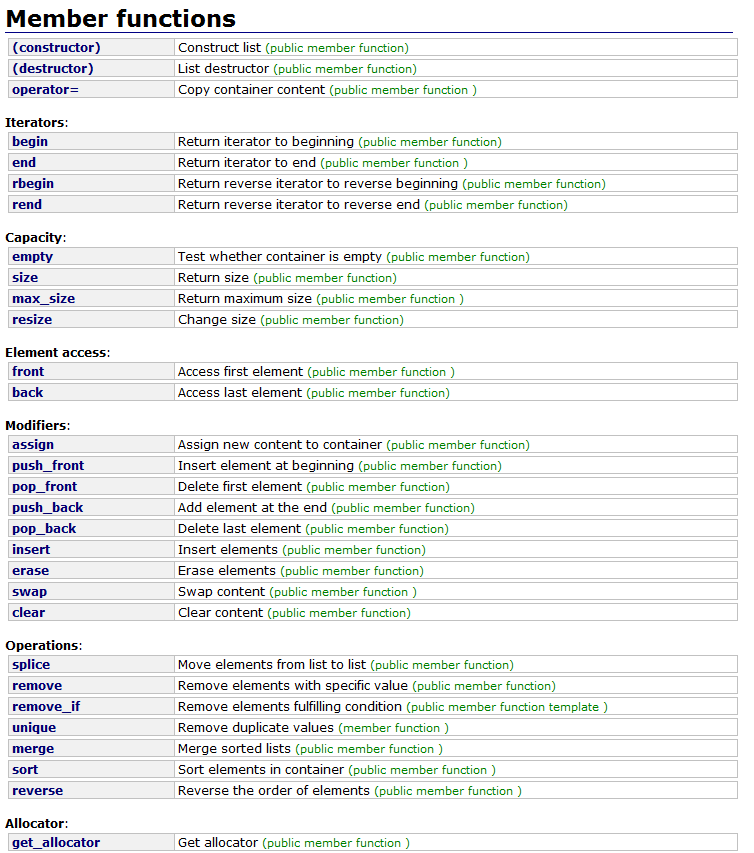
constructor:list的成员函数
1、explicit list ( const Allocator& = Allocator() );
默认的构造函数这个链表的是空的。
2、explicit list ( size_type n, const T& value = T(), const Allocator& = Allocator() );
带参数的构造函数,构造有n个值为value结点
3、template < class InputIterator >
list ( InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const Allocator& = Allocator() );
构造函数的参数类型为迭代器的类型
4、list ( const list
#include<iostream>#include<list>using namespace std;void FunTest(){list<int>first;//使用默认的构造函数创造first这个对象,但是这个对象里面的内容是空的list<int>second(4, 100);//使用带参数的构造函数去创建4个值为100的结点的对象list<int>third(second.begin(), second.end());//使用带迭代器参数的构造函数将一段区间的内容复制过来list<int>forth(third);//拷贝构造函数list<int>::iterator it1;//使用迭代器去遍历first对象里的元素list<int>::iterator it2;//使用迭代器去遍历second对象里的元素list<int>::iterator it3;//使用迭代器去遍历third对象里的元素list<int>::iterator it4;//使用迭代器去遍历forth对象里的元素it1 = first.begin();while (it1 != first.end()){cout << *it1 << " ";++it1;}cout << endl;it2 = second.begin();while (it2 != second.end()){cout << *it2 << " ";++it2;}cout << endl;it3 = third.begin();while (it3 != third.end()){cout << *it3 << " ";++it3;}cout << endl;it4 = forth.begin();while (it4 != forth.end()){cout << *it4 << " ";++it4;}cout << endl;}
2、destructor关于析构函数的使用:
~list ( );
它是用来回收我们之前分配的内存,当然STL中的内存分配是由它自己的空间配置器来分配内存的
3、operator=对运算符’=’的重载
void FunTest2(){list<int> first(5, 10);list<int> second(3, 1);list<int>::iterator it2;it2 = second.begin();while (it2 != second.end()){cout << *it2 << " ";++it2;}cout << endl;list<int>::iterator it1;second = first;it1= second.begin();while (it1 != second.end()){cout << *it1 << " ";++it1;}cout << endl;}
4、迭代器的使用
1>begin()
iterator begin ();
const_iterator begin () const;
2>end();
iterator end ();
const_iterator end () const;
void FunTest3(){list<int> l(10,100);list<int>::iterator it1=l.begin();//l.begin返回的是非const类型的迭代器是可以修改的while (it1 != l.end()){*it1=10;//迭代器里的解引用这个操作符是重载过的表示迭代器里结点里的data的值cout << *it1 << " ";++it1;}cout << endl;}void FunTest4(){list<int>l(10, 2);list<int>::const_iterator it = l.begin();while (it != l.end()){//*it = 10;//是不能赋值的因为const修饰的迭代器表示这里面的内容是不可以修改的cout << *it << " ";++it;}//以上的迭代器都是正向遍历容器里的元素的}
3>rbegin():
reverse_iterator rbegin();
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const;
3>rend():
reverse_iterator rend();
const_reverse_iterator rend() const;
void FunTest5(){list<int>l;l.push_back(1);l.push_back(2);l.push_back(3);l.push_back(4);list<int>::reverse_iterator it = l.rbegin();while (it != l.rend()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}}//打印出来的结果是4,3,2,1,因为这个迭代器是反向遍历的,它的头相当于正向迭代器的尾
5、Capacity:关于容量的一些方法
empty();
bool empty ( ) const;
size()
size_type size() const();
max_size():
size_type max_size () const;
resize()://具有增容和裁剪的作用
void resize ( size_type sz, T c = T() );
void FunTest6(){list<int>l(10);cout << l.empty()<<endl;//判断链表空不空cout << l.size()<<endl;//结点的个数cout << l.max_size()<<endl;l.resize(5);//相当于裁减让链表只剩下5个结点cout << l.size() << endl;l.resize(10, 8);//将链表变成10个值为8的结点cout << l.size() << endl;}
front():
reference front ( );
const_reference front ( ) const;
back();
reference back ( );
const_reference back ( ) const;
void FunTest7(){list<int>l(10, 2);l.push_back(8);cout << l.front()<<endl;cout << l.back();}//front和back是以引用值的方式返回的
5、Modifiers:关于修改链表的 内容
1>assign():
template
void assign ( InputIterator first, InputIterator last );//参数直接给成迭代器类型的,赋值的是一段区间
void assign ( size_type n, const T& u );//直接赋值给链表值为u的结点
void FunTest8(){list<int>first;list<int>second(10,20);first.assign(7, 10);cout << first.size()<<endl;list<int>::iterator it1;it1 = first.begin();while (it1 != first.end()){cout << *it1 << " ";++it1;}cout << endl;first.assign(second.begin(), second.end());list<int>::iterator it2;it2 = first.begin();while (it2 != first.end()){cout << *it2 << " ";++it2;}cout << endl;cout << first.size();}//list中assign的使用
2>push_front():
void push_front ( const T& x );
3>push_back():
void push_back ( const T& x );
4>pop_front():
void pop_front ( )
5>pop_back():
void pop_back ( );
void FunTest9(){list<int> l;l.push_back(1);l.push_back(2);l.push_back(3);l.push_back(4);l.push_back(5);l.pop_back();l.pop_back();l.push_front(7);l.push_front(8);l.push_front(9);l.pop_front();l.pop_front();list<int>::iterator it2;it2 = l.begin();while (it2 != l.end()){cout << *it2 << " ";++it2;}cout << endl;}//list中push_back的用法,pop_back,push_front,pop_front的用法
6>insert():
iterator insert ( iterator position, const T& x );
void insert ( iterator position, size_type n, const T& x );
template
void insert ( iterator position, InputIterator first, InputIterator last );
void FunTest10(){list<int>first;list<int>second;list<int>third;//iterator insert ( iterator position, const T& x );first.insert(first.begin(), 8);//void insert(iterator position, size_type n, const T& x);second.insert(second.begin(), 4, 9);//void insert ( iterator position, InputIterator first, InputIterator last );third.insert(third.begin(), second.begin(), second.end());list<int>::iterator it2;it2 = first.begin();while (it2 != first.end()){cout << *it2 << " ";++it2;}cout << endl;list<int>::iterator it3;it3 = second.begin();while (it3 != second.end()){cout << *it3 << " ";++it3;}cout << endl;list<int>::iterator it4;it4= second.begin();while (it4 != second.end()){cout << *it4 << " ";++it4;}cout << endl;}//list中insert的用法
7>erase():
iterator erase ( iterator position );
iterator erase ( iterator first, iterator last );
void FunTest11(){list<int>l(10, 2);//iterator erase(iterator position);l.erase(l.begin());cout << l.size()<<endl;//iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last);l.erase(l.begin(), l.end());cout << l.size()<<endl;}//erase的用法
8>swap():
void swap ( list
void FunTest12(){list<int>l1(10, 2);list<int>l2(10, 3);l2.swap(l1);list<int>::iterator it4;it4 = l1.begin();cout << "l1:";while (it4 !=l1.end()){cout << *it4 << " ";++it4;}cout << endl;cout << "12:";list<int>::iterator it5=l2.begin();while (it5 != l2.end()){cout << *it5 << " ";++it5;}}//list中swap的用法将两个链表的内容交换
9>clear():
void clear ( );list中clear的用法,清除所有元素
void FunTest13(){list<int>l(10,5);cout<<l.size()<<endl;l.clear();cout << l.size();}//list中clear的用法,清除所有元素
6、Operations:
1>splice():
void splice ( iterator position, list
void FunTest14(){//void splice(iterator position, list<T, Allocator>& x);list<int>l1(10, 12);list<int>l2(10, 13);l1.splice(l1.begin(), l2);//把l1的元素从头全部搬移到l2中list<int>::iterator it5 = l2.begin();while (it5 != l2.end()){cout << *it5 << " ";++it5;}cout << endl;list<int>::iterator it6 = l1.begin();while (it6 != l1.end()){cout << *it6 << " ";++it6;}cout << endl;//void splice(iterator position, list<T, Allocator>& x, iterator i);list<int>l3(10, 1);list<int>l4(10, 2);list<int>::iterator it7 = l4.begin();++it7;l3.splice(l3.begin(), l4,it7);list<int>::iterator it8 = l4.begin();while (it8 != l4.end()){cout << *it8 << " ";++it8;}cout << endl;list<int>::iterator it9 = l3.begin();while (it9 != l3.end()){cout << *it9 << " ";++it9;}cout << endl;//void splice(iterator position, list<T, Allocator>& x, iterator first, iterator last);list<int>l5(10, 100);list<int>l6(10, 200);l5.splice(l5.begin(), l6, ++l6.begin(), l6.end());//把l6从++l6.begin()到l6.end()个元素全部搬移到l5中list<int>::iterator it10 = l5.begin();while (it10 != l5.end()){cout << *it10<<" ";it10++;}cout << endl;}//list中splice的用法
2>remove():
void remove ( const T& value );
void FunTest15(){list<int>l1(10, 8);l1.remove(8);//移除l1中所有值为8的结点cout << l1.size();}//list中remove的用法
3>remove_if():
template
void remove_if ( Predicate pred );//对这个用法还不太了解
4>unique():
void unique ( );//删除重复的元素只保留一份
template
void unique ( BinaryPredicate binary_pred );
void FunTest16(){/*void unique(); template <class BinaryPredicate> void unique(BinaryPredicate binary_pred);*/list<int>l1(10, 100);l1.unique();//只保留一份,移除重复元素cout << l1.size();}
5>merge():
void merge ( list
void FunTest17(){//void merge(list<T, Allocator>& x);list<int>l1(10, 1);list<int>l2(10, 2);l1.merge(l2);//把l2中所有的元素都合并到l1中list<int>::iterator it10 = l1.begin();while (it10 != l1.end()){cout << *it10 << " ";it10++;}cout << endl;/*template <class Compare> void merge(list<T, Allocator>& x, Compare comp);*/}
6>sort()://对链表的的无序元素进行排序
void sort ( );
template
void sort ( Compare comp );//涉及到仿函数的使用决定是升序排列还是降序排列
void FunTest18(){list<int>l;l.push_back(3);l.push_back(1);l.push_back(4);l.sort();list<int>::iterator it1 = l.begin();while (it1 != l.end()){cout << *it1 << " ";++it1;}}





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...