hdu 1165 递推
题目:
As is known, Ackermann function plays an important role in the sphere of theoretical computer science. However, in the other hand, the dramatic fast increasing pace of the function caused the value of Ackermann function hard to calcuate.
Ackermann function can be defined recursively as follows: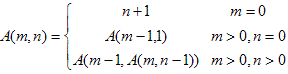
Now Eddy Gives you two numbers: m and n, your task is to compute the value of A(m,n) .This is so easy problem,If you slove this problem,you will receive a prize(Eddy will invite you to hdu restaurant to have supper).
其实就是给出这样一个表达式,给出m、n得到A(m,n)的值。
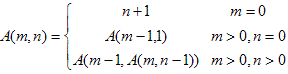
这个是数据范围:
Each line of the input will have two integers, namely m, n, where 0 < m < =3.
Note that when m<3, n can be any integer less than 1000000, while m=3, the value of n is restricted within 24.
一道递推问题,具体看代码。
/*m=0时:A(0,n) = n+1 ;m=1时:A(1,n) = A(1-1,A(1,n-1)) = A(0,A(1,n-1))= A(1,n-1)+1 = A(0,A(1,n-2) +1 = A(1,n-2)+ 2 = ...= A(1,n-n)+ n = A(1,0) + n = A(0,1)+n = n+2 ;m=2时:A(2,n) = A(1,A(2,n-1)) = A(2,n-1)+2 =A(1,A(2,n-2))+2 = A(2,n-2)+2*2 = ... =A(2,n-n)+2*n = A(2,0)+2*n =A(1,1)+2*n = 2*n +3 ;m=3时:直接递归求解就可以了也可以这样先递推一下再来,A(3,m) = A(2,A(3,n-1)) = 2*A(3,(n-1)) + 3 ;*/#include <map>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <cmath>#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>#include <iostream>#include <algorithm>using namespace std ;#define mem(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))#define inf 100000005int const maxn = 1000005 ;long long cal(int m,int n){if(m==0)return n+1;if(m==1)return n+2;if(m==2)return 2*n+3 ;if(m>0&&n==0)return cal(m-1,1);if(m>0&&n>0)return cal(m-1,cal(m,n-1));}int main(){int m,n;while(scanf("%d%d",&m,&n)!=EOF){if(m==3)printf("%I64d\n",cal(m,n));else if(m==1)printf("%d\n",n+2);else if(m==0)printf("%d\n",n+1);else if(m==2)printf("%d\n",2*n+3);}return 0 ;}


























![[C#版剑指offer]旋转数组的最小数字查询 [C#版剑指offer]旋转数组的最小数字查询](https://image.dandelioncloud.cn/dist/img/NoSlightly.png)


还没有评论,来说两句吧...