【PyTorch学习笔记】6.循环神经网络
文章目录
- 40.时间序列表示
- 41.循环神经网络
- 42.RNN Layer使用
- 42.1 nn.RNN
- 42.2 nn.RNNCell
- 时间序列预测
- 44.RNN训练难题
- 45.LSTM Layer使用
- 45.1 nn.LSTM
- 45.2 nn.LSTMCell
- 46.情感分类实战
根据龙良曲Pytorch学习视频整理,视频链接:
【计算机-AI】PyTorch学这个就够了!
(好课推荐)深度学习与PyTorch入门实战——主讲人龙良曲
40.时间序列表示
Sequence representation
- [seq_len, feature_len]
- [word, word_vec]
one-hot - [words, word vec]
sparse
high-dim
semantic similarity
word2vec vs Glove
import torchimport torch.nn as nnfrom torchnlp.word_to_vector import GloVeword_to_idx = { 'hello': 0, 'world': 1}lookup_tensor = torch.tensor([word_to_idx['hello']], dtype=torch.long)embeds = nn.Embedding(2, 5) # 2 words in vocab, 5 dimensional embeddingshello_embed = embeds(lookup_tensor)print(hello_embed)""" tensor([[ 0.2565, -0.2827, -0.0259, -1.9533, 0.8330]], grad_fn=<EmbeddingBackward>) """vectors = GloVe()print(vectors['hello']) # 2GB文件
torchnlp包安装 pip install pytorch-nlp
41.循环神经网络
Weight sharing
Consistent memory
42.RNN Layer使用
input dim, hidden dim
rnn = nn.RNN(100, 10) # word_dim, memory/hprint(rnn._parameters.keys()) # odict_keys(['weight_ih_l0', 'weight_hh_l0', 'bias_ih_l0', 'bias_hh_l0'])print(rnn.weight_hh_l0.shape, rnn.weight_ih_l0.shape) # torch.Size([10, 10]) torch.Size([10, 100])print(rnn.bias_hh_l0.shape, rnn.bias_ih_l0.shape) # torch.Size([10]) torch.Size([10])
42.1 nn.RNN
- .__init__
(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers) - out, ht = forward(x, h0)
x: [seq_len, b, word_vec]
ho/ht: [num_layers, b, h_dim]
out: [seq_len, b, h_dim]
Single layer RNN
rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=100, hidden_size=20, num_layers=1)print(rnn) # RNN(100, 20)x = torch.randn(10, 3, 100)out, h = rnn(x, torch.zeros(1, 3, 20))print(out.shape, h.shape) # torch.Size([10, 3, 20]) torch.Size([1, 3, 20])
h是最后一个时间序列所有的memory状态;out是所有时间序列的最后一个memory状态
2 layer RNN
rnn = nn.RNN(100, 10, num_layers=2) # word_dim, memory/hprint(rnn._parameters.keys()) # odict_keys(['weight_ih_l0', 'weight_hh_l0', 'bias_ih_l0', 'bias_hh_l0', 'weight_ih_l1', 'weight_hh_l1', 'bias_ih_l1', 'bias_hh_l1'])print(rnn.weight_hh_l0.shape, rnn.weight_ih_l0.shape) # torch.Size([10, 10]) torch.Size([10, 100])print(rnn.bias_hh_l0.shape, rnn.bias_ih_l0.shape) # torch.Size([10]) torch.Size([10])
[T, b, h_dim], [layers, b, h_dim]
rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=100, hidden_size=20, num_layers=4)print(rnn) # RNN(100, 20, num_layers=4)x = torch.randn(10, 3, 100)out, h = rnn(x)print(out.shape, h.shape) # torch.Size([10, 3, 20]) torch.Size([4, 3, 20])
42.2 nn.RNNCell
- __init__
(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers) - ht = rnncell(xt, ht_1)
x: [b, word_vec]
ht_1/ht: [num_layers, b, h_dim]
out = torch.stack([h1, h2,…ht])
Functional
cell1 = nn.RNNCell(100, 30)cell2 = nn.RNNCell(30, 20)h1 = torch.zeros(3, 30)h2 = torch.zeros(3, 20)for xt in x:h1 = cell1(xt, h1)h2 = cell2(h1, h2)print(h1.shape) # torch.Size([3, 30])print(h2.shape) # torch.Size([3, 20])
43. 时间序列预测
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport torchimport torch.nn as nnimport torch.optim as optimnum_time_steps = 50input_size = 1hidden_size = 16output_size = 1lr = 0.01class Net(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(Net, self).__init__()self.rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=input_size,hidden_size=hidden_size,num_layers=1,batch_first=True)for p in self.rnn.parameters():nn.init.normal_(p, mean=0.0, std=0.001)self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)def forward(self, x, hidden_prev):out, hidden_prev = self.rnn(x, hidden_prev)# [b, seq, h] => [seq, h] b=1out = out.view(-1, hidden_size)# [seq, h] => [seq, 1]out = self.linear(out)# [seq, 1] => [1, seq, 1]out = out.unsqueeze(dim=0)return out, hidden_prevmodel = Net()criterion = nn.MSELoss()optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr)hidden_prev = torch.zeros(1, 1, hidden_size)for iter in range(6000):start = np.random.randint(3, size=1)[0]time_steps = np.linspace(start, start + 10, num_time_steps)data = np.sin(time_steps)data = data.reshape(num_time_steps, 1)x = torch.tensor(data[:-1]).float().view(1, num_time_steps - 1, 1)y = torch.tensor(data[1:]).float().view(1, num_time_steps - 1, 1)output, hidden_prev = model(x, hidden_prev)hidden_prev = hidden_prev.detach() # 改requirse_grad为false,切断反向传播loss = criterion(output, y)model.zero_grad()loss.backward()# 检查梯度信息# for p in model.parameters():# print(p.grad.norm())# torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(p, 10)optimizer.step()if iter % 100 == 0:print('Iteration: {} loss {}'.format(iter, loss.item()))start = np.random.randint(3, size=1)[0]time_steps = np.linspace(start, start + 10, num_time_steps)data = np.sin(time_steps)data = data.reshape(num_time_steps, 1)x = torch.tensor(data[:-1]).float().view(1, num_time_steps - 1, 1)y = torch.tensor(data[1:]).float().view(1, num_time_steps - 1, 1)predictions = []input = x[:, 0, :] # [b, seq, feature] => [b, feature]for _ in range(x.shape[1]):input = input.view(1, 1, 1)(pred, hidden_prev) = model(input, hidden_prev)input = pred # tensor([[[0.8720]]], grad_fn=<UnsqueezeBackward0>)predictions.append(pred.detach().numpy().ravel()[0])x = x.data.numpy().ravel()plt.scatter(time_steps[:-1], x.ravel(), s=90)plt.plot(time_steps[:-1], x.ravel())plt.scatter(time_steps[1:], predictions)plt.show()
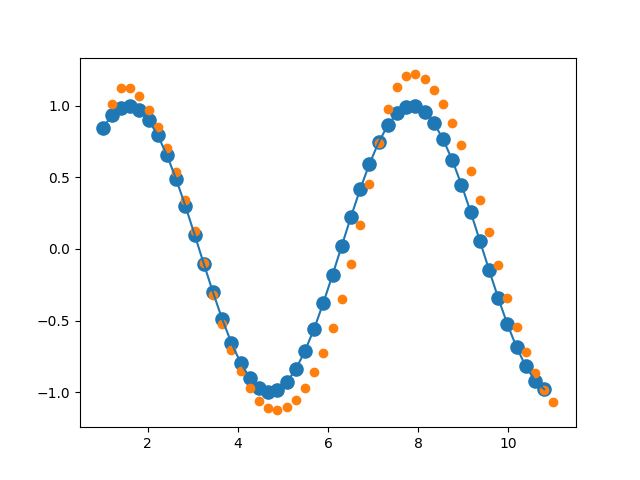
44.RNN训练难题
- Gradient Exploding
解决办法:Gradient Clipping - Gradient Vanishing
解决办法:LSTM
45.LSTM Layer使用
45.1 nn.LSTM
- __init__
(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers)
LSTM.forward()
out, (ht, ct) = lstm(x, [ht_0, ct_0])
x: [seq_len, b, word_vec]
h/c: [num_layers, b, h_dim]
out: [seq_len, b, h_dim]lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=100, hidden_size=20, num_layers=4)
print(lstm) # LSTM(100, 20, num_layers=4)
x = torch.rand(10, 3, 100)
out, (h, c) = lstm(x)
print(out.shape, h.shape, c.shape) # torch.Size([10, 3, 20]) torch.Size([4, 3, 20]) torch.Size([4, 3, 20])
45.2 nn.LSTMCell
- __init__
(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers)
LSTMCell.forward()
- ht, ct = lstmcell(xt, [ht_0, ct_0])
xt: [b, word_vec]
h/c: [ b, h_dim]
Single layer
cell = nn.LSTMCell(input_size=100, hidden_size=20)print(cell) # LSTMCell(100, 20)h = torch.zeros(3, 20)c = torch.zeros(3, 20)for xt in x:h, c = cell(xt, [h, c])print(h.shape, c.shape) # torch.Size([3, 20]) torch.Size([3, 20])
Two layers
cell1 = nn.LSTMCell(input_size=100, hidden_size=30)cell2 = nn.LSTMCell(input_size=30, hidden_size=20)h1 = torch.zeros(3, 30)c1 = torch.zeros(3, 30)h2 = torch.zeros(3, 20)c2 = torch.zeros(3, 20)for xt in x:h1, c1 = cell1(xt, [h1, c1])h2, c2 = cell2(h1, [h2, c2])print(h2.shape, c2.shape) # torch.Size([3, 20]) torch.Size([3, 20])
46.情感分类实战
Google CoLab
- Continuous 12 hours
- free K80 for GPU
- no need to cross GFW
没有谷歌账号不能使用Colaboratory,码一下
import torchimport torch.nn as nnimport numpy as npfrom torchtext import data, datasets# load datasetTEXT = data.Field(tokenize='spacy')LABEL = data.LabelField(dtype=torch.float)train_data, test_data = datasets.IMDB.split(TEXT, LABEL)print('len of train data:', len(train_data))print('len of test data:', len(test_data))print(train_data.examples[15].text)print(train_data.examples[15].label)class RNN(nn.Module):def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, hidden_dim):super(RNN, self).__init__()# [0-10001] => [100]self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)# [100] => [256]self.rnn = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers=2, bidirectional=True, dropout=0.5)# [25*2] => [1]self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim*2, 1)self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5)def forward(self, x):# [seq, b, 1] => [seq, b, 100]embedding = self.dropout(self.embedding(x))# output: [seq, b, hid_dim*2]# hidden/h, [num_layer*2, b, hid_dim]# cell/c: [num_layer*2, b, hid_dim]output, (hidden, cell) = self.rnn(embedding)# [num_layer*2, b, hid_dim] => 2 of [b, hid_dim] => [b, hid_dim*2]hidden = torch.cat([hidden[-2], hidden[-1]], dim=1)# [b, hid_dim*2] => [b, 1]hidden = self.dropout(hidden)out = self.fc(hidden)return out# load word embeddingrnn = RNN(len(TEXT.vocab), 100, 256)pretrained_embedding = TEXT.vocab.vectorsprint('pretrained_embedding:', pretrained_embedding.shape)rnn.embedding.weight.data.copy_(pretrained_embedding)print('embedding layer inited.')def binary_acc(preds, y):preds = torch.round((torch.sigmoid(preds)))correct = torch.eq(preds, y).float()acc = correct.sum() / len(correct)return accdef eval(rnn, iterator, criteon):avg_acc = []rnn.eval()with torch.no_grad():for batch in iterator:# [b, 1] => [b]pred = rnn(batch.text).squeeze(1)loss = criteon(pred, batch.label)acc = binary_acc(pred, batch.label).item()avg_acc.append(acc)avg_acc = np.array(avg_acc).mean()print('>>>test:', avg_acc)def train(rnn, iterator, optimizer, criteon):avg_acc = []rnn.train()for i, batch in enumerate(iterator):# [seq, b] => [b, 1] => [b]pred = rnn(batch.text).squeeze(1)loss = criteon(pred, batch.label)acc = binary_acc(pred, batch.label).item()avg_acc.append(acc)optimizer.zero_grad()loss.backward()optimizer.step()def main():passif __name__ == '__main__':main()
只是抄了一下代码,并没有动脑子































还没有评论,来说两句吧...