LeetCode - Medium - 173. Binary Search Tree Iterator
Topic
- Stack
- Tree
- Design
Description
https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-search-tree-iterator/
Implement the BSTIterator class that represents an iterator over the in-order traversal of a binary search tree (BST):
BSTIterator(TreeNode root)Initializes an object of theBSTIteratorclass. Therootof the BST is given as part of the constructor. The pointer should be initialized to a non-existent number smaller than any element in the BST.boolean hasNext()Returnstrueif there exists a number in the traversal to the right of the pointer, otherwise returnsfalse.int next()Moves the pointer to the right, then returns the number at the pointer.
Notice that by initializing the pointer to a non-existent smallest number, the first call to next() will return the smallest element in the BST.
You may assume that next() calls will always be valid. That is, there will be at least a next number in the in-order traversal when next() is called.
Example 1:
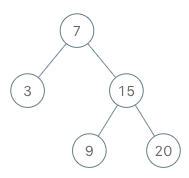
Input["BSTIterator", "next", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext"][[[7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []]Output[null, 3, 7, true, 9, true, 15, true, 20, false]ExplanationBSTIterator bSTIterator = new BSTIterator([7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]);bSTIterator.next(); // return 3bSTIterator.next(); // return 7bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return TruebSTIterator.next(); // return 9bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return TruebSTIterator.next(); // return 15bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return TruebSTIterator.next(); // return 20bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return False
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [ 1 , 1 0 5 ] [1, 10^5] [1,105].
- 0 < = N o d e . v a l < = 1 0 6 0 <= Node.val <= 10^6 0<=Node.val<=106
- At most 1 0 5 10^5 105 calls will be made to
hasNext, andnext.
Follow up:
- Could you implement
next()andhasNext()to run in average O(1) time and use O(h) memory, where h is the height of the tree?
Analysis
主要考察BST的中序遍历的非递归法。
方法一:我写的
方法二:别人写的
方法三:别人写的2
Submission
import java.util.LinkedList;import com.lun.util.BinaryTree.TreeNode;public class BinarySearchTreeIterator {//方法一:我写的public static class BSTIterator {private LinkedList<Object[]> stack;public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {stack = new LinkedList<>();stack.push(new Object[] { root, 0});}public int next() {while(!stack.isEmpty()) {Object[] arr = stack.peek();TreeNode node = (TreeNode)arr[0];int state = (int)arr[1];if(state == 0) {if(node.left != null)stack.push(new Object[] { node.left, 0});arr[1] = 1;}else{stack.pop();if(node.right != null)stack.push(new Object[] { node.right, 0});return node.val;}}return -1;}public boolean hasNext() {return !stack.isEmpty();}}//方法二:别人写的public static class BSTIterator2 {private LinkedList<TreeNode> stack;private TreeNode pointer;public BSTIterator2(TreeNode root) {stack = new LinkedList<>();pointer = root;}public int next() {while(hasNext()) {if(pointer != null) {stack.push(pointer);pointer = pointer.left;}else{TreeNode node = stack.pop();pointer = node.right;return node.val;}}return -1;//或抛异常}public boolean hasNext() {return !stack.isEmpty() || pointer != null;}}//方法三:别人写的2public static class BSTIterator3 {private LinkedList<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();public BSTIterator3(TreeNode root) {pushAll(root);}/** @return whether we have a next smallest number */public boolean hasNext() {return !stack.isEmpty();}/** @return the next smallest number */public int next() {TreeNode tmpNode = stack.pop();pushAll(tmpNode.right);return tmpNode.val;}private void pushAll(TreeNode node) {for (; node != null; stack.push(node), node = node.left);}}}
Test
import static org.junit.Assert.*;import org.junit.Test;import com.lun.medium.BinarySearchTreeIterator.BSTIterator;import com.lun.medium.BinarySearchTreeIterator.BSTIterator2;import com.lun.medium.BinarySearchTreeIterator.BSTIterator3;import com.lun.util.BinaryTree;import com.lun.util.BinaryTree.TreeNode;public class BinarySearchTreeIteratorTest {@Testpublic void test() {TreeNode root = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20);BSTIterator bSTIterator = new BSTIterator(root);assertEquals(3, bSTIterator.next());assertEquals(7, bSTIterator.next());assertTrue(bSTIterator.hasNext());assertEquals(9, bSTIterator.next());assertTrue(bSTIterator.hasNext());assertEquals(15, bSTIterator.next());assertTrue(bSTIterator.hasNext());assertEquals(20, bSTIterator.next());assertFalse(bSTIterator.hasNext());}@Testpublic void test2() {TreeNode root = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20);BSTIterator2 bSTIterator = new BSTIterator2(root);assertEquals(3, bSTIterator.next());assertEquals(7, bSTIterator.next());assertTrue(bSTIterator.hasNext());assertEquals(9, bSTIterator.next());assertTrue(bSTIterator.hasNext());assertEquals(15, bSTIterator.next());assertTrue(bSTIterator.hasNext());assertEquals(20, bSTIterator.next());assertFalse(bSTIterator.hasNext());}@Testpublic void test3() {TreeNode root = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20);BSTIterator3 bSTIterator = new BSTIterator3(root);assertEquals(3, bSTIterator.next());assertEquals(7, bSTIterator.next());assertTrue(bSTIterator.hasNext());assertEquals(9, bSTIterator.next());assertTrue(bSTIterator.hasNext());assertEquals(15, bSTIterator.next());assertTrue(bSTIterator.hasNext());assertEquals(20, bSTIterator.next());assertFalse(bSTIterator.hasNext());}}


























![vue 报错 [Vue warn]: Duplicate keys detected: 'a'. This may cause an update error. vue 报错 [Vue warn]: Duplicate keys detected: 'a'. This may cause an update error.](https://image.dandelioncloud.cn/images/20230531/2d80bd18d31e4608a6dee1e2add77ba8.png)




还没有评论,来说两句吧...