show,attend and tell(image caption论文复现总结)
论文中的核心思想
GitHub上的Image-Caption项目https://github.com/sgrvinod/a-PyTorch-Tutorial-to-Image-Captioning
研究的问题—Image Caption
为图片自动生成caption的任务类似于场景理解,这是cv领域的一个核心问题。要想解决这个问题,不仅要求你的模型能够识别出图片中有什么物体,还得能够将图片中出现的场景与自然语言相联系。问题的核心是模仿人类将大量重要的视觉信息压缩成一句抽象的描述性语言。
解决问题的思路
2014年左右由于AlexNet,VGGNet等深度卷积神经网络的出现,使得Image Caption成为了一项研究的热点。一种新的解决问题的范式是,利用CNN当作提取图像特征向量的Encoder,RNN通过传递过来的特征向量decode出自然语言序列。本篇论文这种解决问题的思路之上增加了attention机制,对feature map每个像素点进行概率的估计,再进行加权求和。这种思想来自于,人们在观察图像中倾向于关注那些有用的信息,而忽略掉大量无用的信息。
至此我们确定复现该论文的基本思想是CNN + LSTM (RNN的变体)+ Attention.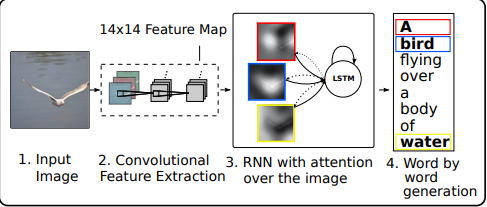
本篇文章的主要贡献
- 提出了两种基于attention的Image Caption生成器,本篇博文介绍的是能够利用BP算法训练的确定性的attention机制
- 可视化了attention在每个time step上focus的点
- 量化了加入attention机制以后网络在Flickr8k,Flickr30k,MS COCO的性能
模型细节
Encoder
使用CNN来提取出L个的特征向量 a \bold a a,每个向量都代表了一个feature map:
a = { a 1 , a 2 , . . . , a L } , a i ∈ R D \bold a = \{a_1,a_2,…,a_L\},a_i ∈R^D a={ a1,a2,…,aL},ai∈RD
这一部分很容易实现,我们可以利用VGGNet,Inception等已经在ImageNet上预训练好的CNN,将最后的flatten操作和全连接层去掉,直接得到一个feature map set。
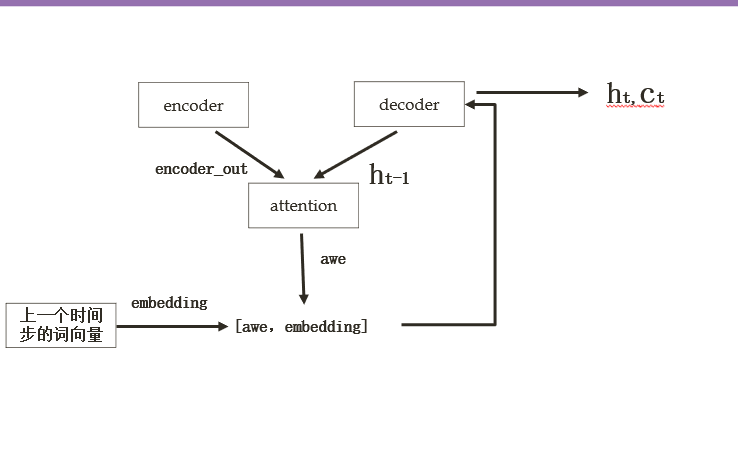
Decoder
使用了LSTM来在每个time step上生成一个word,LSTM的输入是被上一个time step的hidden state和cell state以及当前的context向量,而LSTM的输出是这一时刻的hidden_state和cell_state。
Attention
attention在这个模型中的作用就是生成Decoder每一个time step的context向量。利用CNN提取出来的L个特征向量 a \bold a a以及LSTM输出的 h t − 1 \bold h_{t-1} ht−1通过三个线性层以及一个softmax操作算出每一个像素点成为预测这个time step word的概率,再利用这个概率值对 a \bold a a加权求和输出。输出的向量与上一个time step的词向量进行拼接操作,作为这一时刻的context向量
模型代码的复现
Encoder的实现
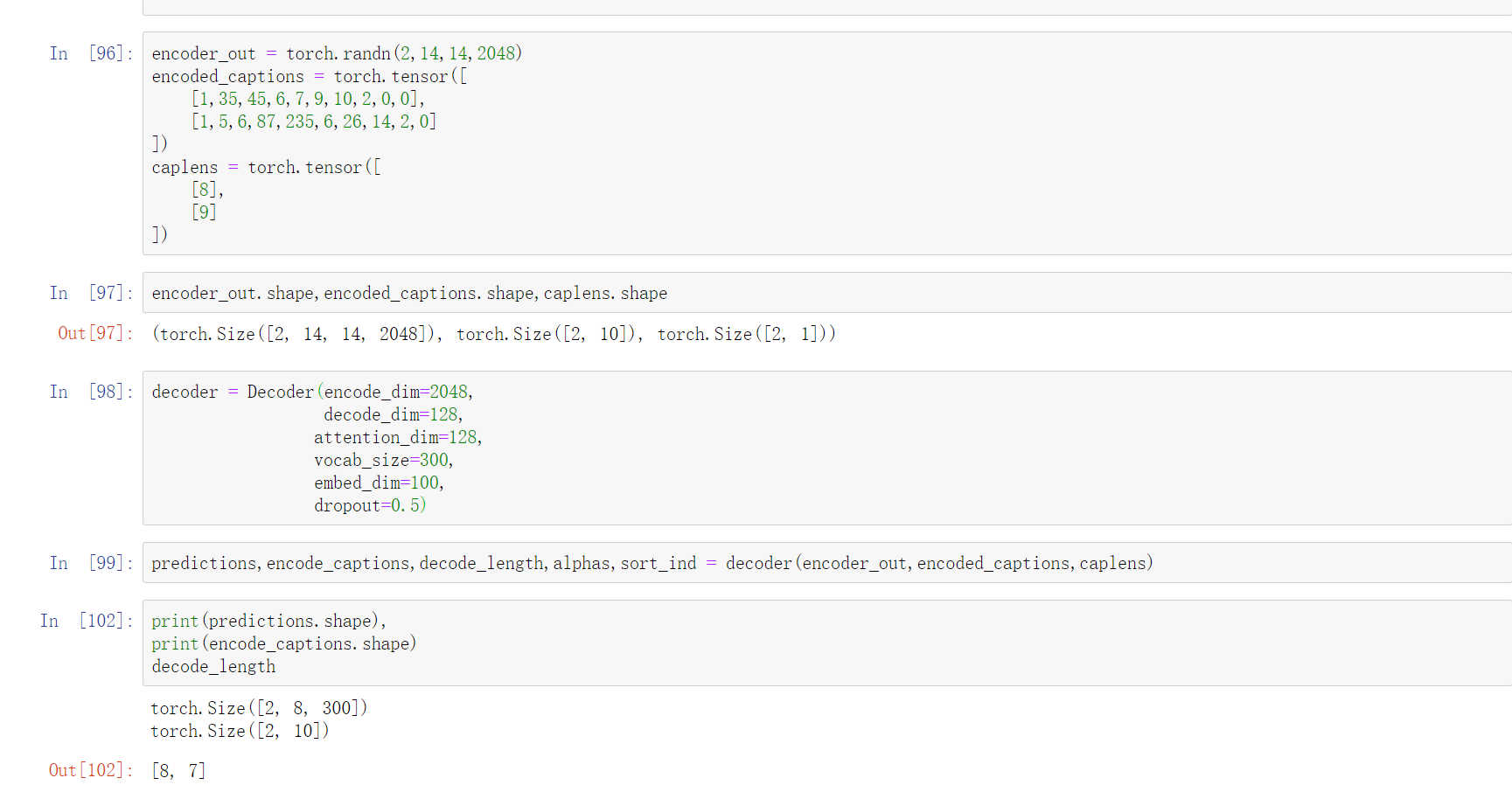
这里的Encoder中使用的是预训练好的resnet101,去除了最后两层的flatten,fully_connected_network,最后得到了2048个特征图
# models.pyimport torchfrom torch import nnimport torchvisionclass Encoder(nn.Module):def __init__(self,img_size=14):#img_size决定了最后feature map的宽高是多少,这里默认是 14 * 14super().__init__()resnet = torchvision.models.resnet101(pretrained=True)#加载预训练的模型modules = list(resnet.children())[:-2] #children本身对应的是个generator,转换成list之后丢弃最后的两项self.resnet = nn.Sequential(*modules) #利用自带的序列容器将modules逐个装入self.adaptive_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((img_size,img_size))#因为不确定输入图片的大小,使用自适应的池化层将特征图转化成固定的大小def forward(self,images):#images:shape[batch_size,3,height,width]out = self.resnet(images)out = self.adaptive_pool(out) #[batch_size,2048,img_size,img_size]out = out.permute(0,2,3,1)#将轴的顺序做下调整,方便后面的计算#[batch_size,img_size,img_size,2048]return out

这里随机生成了一个batch的数据,输出的数据的shape与一开始的推测是一致的
Attention的实现
# models.pyclass Attention(nn.Module):def __init__(self,encode_dim,decode_dim,attention_dim):super().__init__()#对象属性的初始化self.encode_dim = encode_dimself.decode_dim = decode_dimself.attention_dim = attention_dimself.e_att = nn.Linear(encode_dim,attention_dim)#将cnn输出的feature转换成特定维度的线性层self.d_att = nn.Linear(decode_dim,attention_dim) #将decode输出的hidden_state转换成特定维度的线性层self.ful_att = nn.Linear(attention_dim,1)self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)self.relu = nn.ReLU()def forward(self,encoder_out,hidden_state):#encoder_out [batch_size,196,encoder_dim],196代表特征图上的196个像素点att1 = self.e_att(encoder_out) #[batch_size 196,attention_dim]att2 = self.d_att(hidden_state)#[batch_size,attention_dim]att = self.ful_att(self.relu(att1 + att2.unsqueeze(1)))#[batch_size,196,1]att = att.squeeze(2)alpha = self.softmax(att)#[batch_size,196] #每个像素的概率被计算出来了awe = (encoder_out * alpha.unsqueeze(2)).sum(dim=1)#每个像素点加权求和return awe,alpha
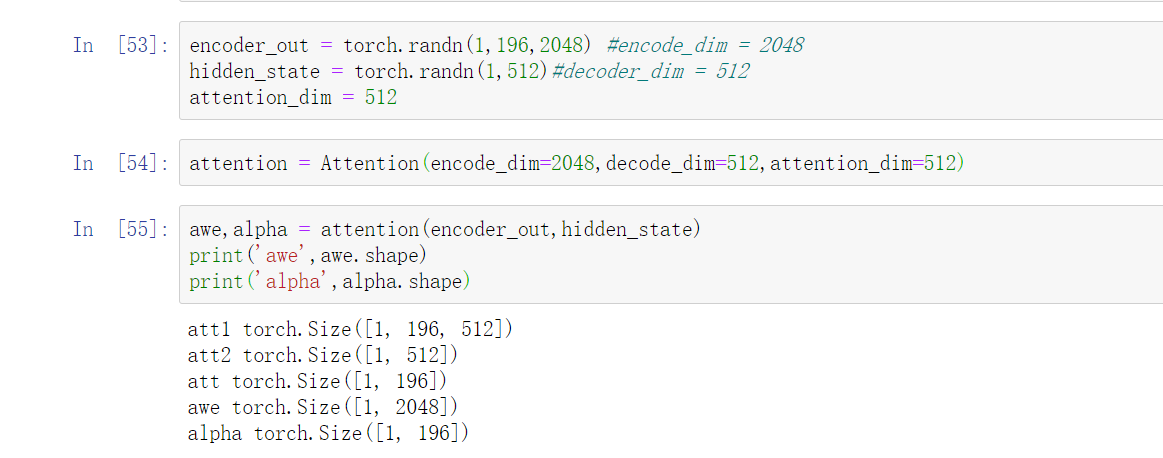
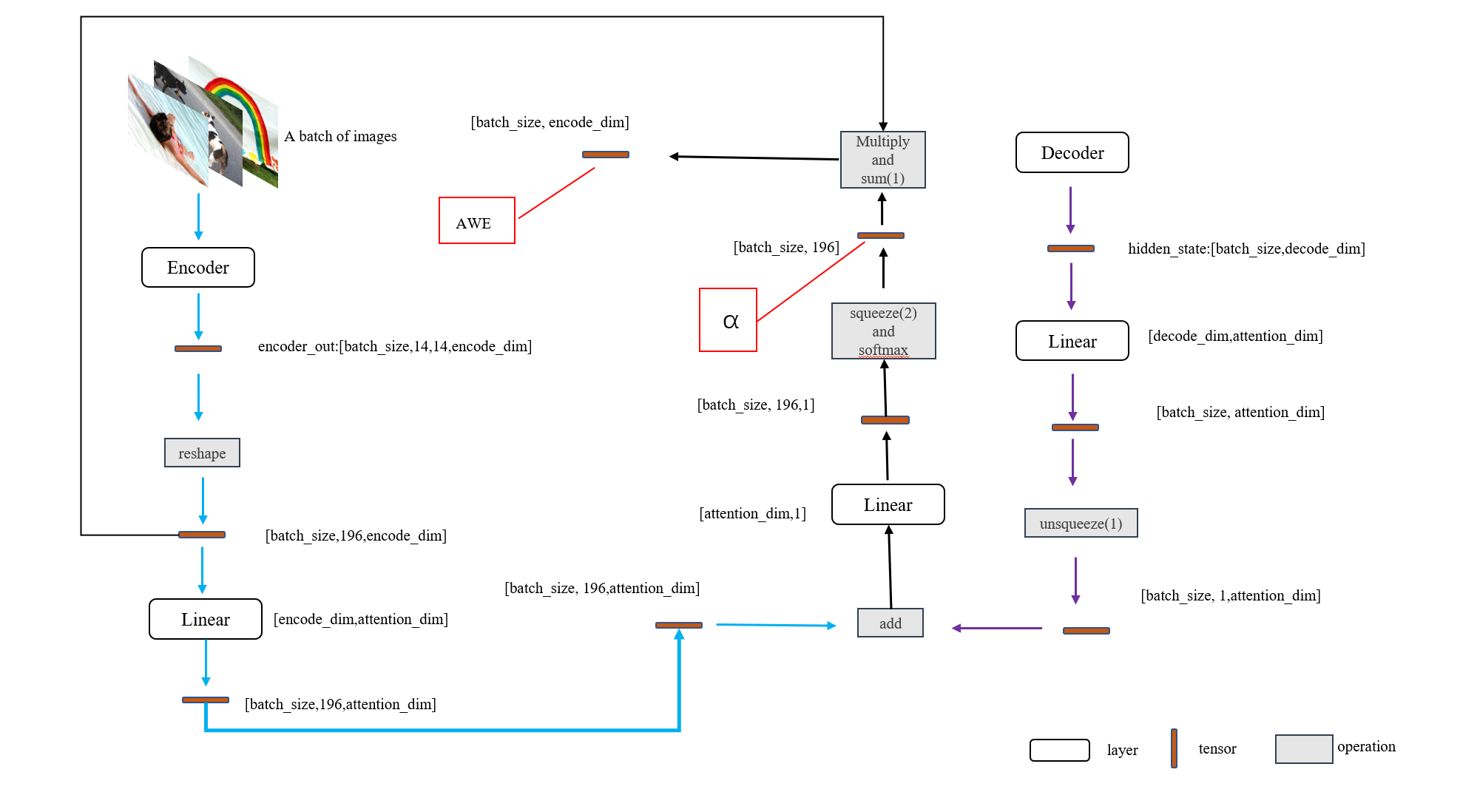
Decoder的实现
# models.pyclass Decoder(nn.Module):def __init__(self,encode_dim,decode_dim,attention_dim,embed_dim,vocab_size,dropout):super().__init__()self.encode_dim = encode_dim #feature map的个数self.decode_dim = decode_dim #decoder的向量维数self.attention_dim = attention_dim #设计的神经网络神经元的个数self.vocab_size = vocab_size #词典的大小self.embed_dim = embed_dim #每个词向量的维度大小self.attention = Attention(encode_dim,decode_dim,attention_dim)self.embeddings = nn.Embedding(vocab_size,embed_dim)self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()self.fc = nn.Linear(decode_dim,vocab_size)self.f_beta = nn.Linear(decode_dim,encode_dim)self.init_h = nn.Linear(encode_dim,decode_dim)self.init_c = nn.Linear(encode_dim,decode_dim)self.lstm = nn.LSTMCell((encode_dim + embed_dim),decode_dim)self.init_weight() #对一些参数进行初始化passdef init_weight(self):self.embeddings.weight.data.uniform_(-0.1, 0.1)self.fc.bias.data.fill_(0)self.fc.weight.data.uniform_(-0.1, 0.1)def init_hidden(self,encoder_out):#encoder_out[batch_size,num_pixels,encode_dim]mean_encoder_out = encoder_out.sum(dim=1)#shape [batch_size,encode_dim]h = self.init_h(mean_encoder_out)c = self.init_c(mean_encoder_out)return h, cdef forward(self,encoder_out,encode_captions,caplens):""" encoder_out:shape[batch_size,img_size,img_size,encoder_dim] encoder_captions是被序列化的caption[batch_size,max_len] max_len表示所有caption被填充到统一长度 caplens [batch_size,1]每个caption对应的长度 """#将高和宽的轴展开,看作height * width个像素点batch_size = encoder_out.size(0)encoder_out = encoder_out.reshape(batch_size,-1,self.encode_dim) #[batch_size,num_pixels,encoder_dim]num_pixels = encoder_out.size(1)#将输入数据进行降序排序,这里排序的目的是为了后面在每个时间步进行decode时方便,具体作用在后面代码解释caplens,sort_ind = caplens.view(-1).sort(dim = 0,descending=True)encoder_out = encoder_out[sort_ind]encode_captions = encode_captions[sort_ind]embeddings = self.embeddings(encode_captions)#shape[batch_size,max_len,embed_dim]#hidden_state和cell_state的初始状态由encoder_out通过两个全连接神经网络来获得h,c = self.init_hidden(encoder_out)#这里经过编码的caption是 《start》 + 原先序列长度 + 《end》,而我们decode的时候start不需要,所以需要的时间步减1decode_length = (caplens - 1).tolist()predictions = torch.ones(batch_size,max(decode_length),self.vocab_size)alphas = torch.ones(batch_size,max(decode_length),num_pixels)for t in range(max(decode_length)):""" 这里说明一下前面进行降序排列的原因,因为每个caption的实际长度不一样(caplens中进行了记录),所以decode的长度也不一样, 显然,caption越长,decode的长度就越长,下面的batch_size_t就是统计本次时间步还有多少需要decode,而需要decode都在序列的 前面 """batch_size_t = sum([l > t for l in decode_length])#统计本次时间步前多少需要decodeawe,alpha = self.attention(encoder_out[:batch_size_t],h[:batch_size_t])gate = self.sigmoid(self.f_beta(h[:batch_size_t]))#[batch_size,encode_dim] 门单元,决定awe那些像素点本次被需要awe = awe * gatecontext = torch.cat([awe,embeddings[:batch_size_t,t,:]],dim=1)#[batch_size,encode_dim + embed_dim]h,c = self.lstm(context,(h[:batch_size_t],c[:batch_size_t]))preds = self.fc(self.dropout(h)) #[batch_size,vocab_size]本次预测的结果,词表中的每一个单词都有一个对应的概率predictions[:batch_size_t,t,:] = predsalphas[:batch_size_t,t,:] = alphareturn predictions,encode_captions,decode_length,alphas,sort_indpass
所用数据集的介绍
论文中提到了三个标准数据集Flickr8k,Flickr30k,MS COCO,为了方便起见,我使用的是较小的Flickr8k数据集
Flickr8k的图片文件名和所对应的caption用一个json文件保存了起来,json文件大概格式如下
”“”json文件中除了images以外的字段这个项目用不到就没有列出,images中sentences和split以及filename字段比较重要split表示的是数据集划分{ 'train','val','test'}{"images":[{"sentids":[0,1,2,3,4],"imgid":0,"sentences":[{"tokens":["a","black","dog"],"raw":...,"imgid":0,"sentid":0}],"split":"train","filename":"...."},],}“”“
接下来我们处理文件需要完成下面几个目标:
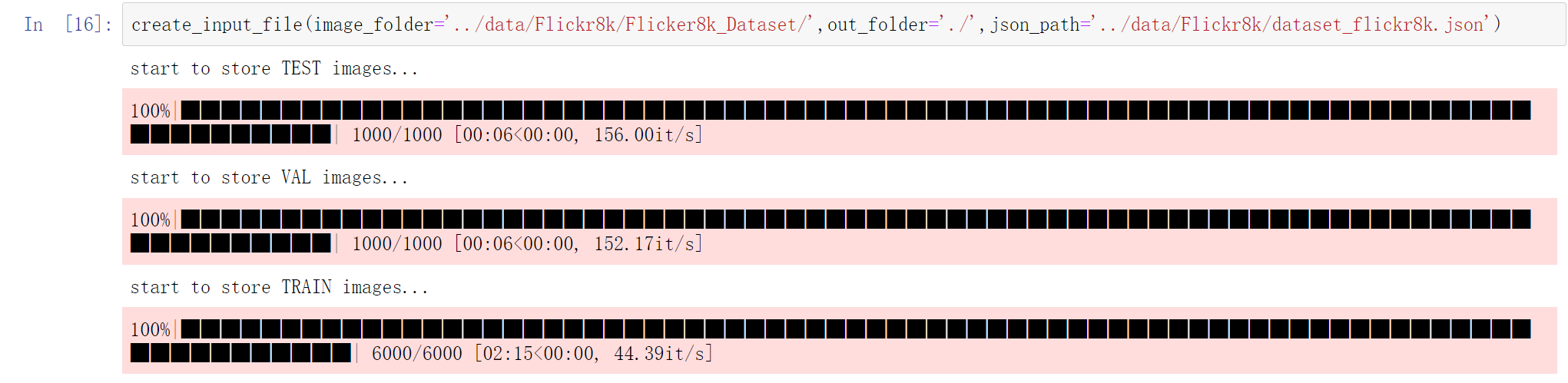
1.将所有图片通过文件名读入并保存成一个hdf5文件,这么做的原因是从磁盘中读入一个整体的文件效率更高,而一张张从文件夹中读取图片效率太低了。
2.遍历每张图片对应的sentences数组,其中的token是已经做了分词的caption,如果caption的长度小于最大长度(如我们不能让caption的长度超过100),我们将其保存到该图片对应的caption数组中。最后保证每个image都有对应的5个caption,如果不够就随机重复,如果超过就sample来随机抽取5个。
3.在读入caption构建一个词频表,最后将词频低于最小阈值的单词删除,并建立一张word_map的字典
4.将caption数组,word_map,caplens用json格式进行保存
# utils.pyfrom imageio import imreadfrom PIL import Imagedef create_input_file(image_folder,json_path,out_folder,cap_per_image = 5,min_word_freq = 5,max_len = 48):""" image_folder:image文件夹所在的路径 json_path json文件的完整路径 out_folder输出的文件保存在哪儿 cap_per_image 每张图片应该有多少caption min_word_freq最小词频 max_len caption中token最多数 """#把所需要的json格式文件加载进来with open(json_path,'r') as j:data = json.load(j)images = data['images']train_images_list = []train_captions_list = []val_images_list = []val_captions_list = []test_images_list = []test_captions_list = []word_freq = Counter() #counter是一个字典,不过有个方便更新词频的方法updatefor img in images:captions = [] #用于保存每个对应image的captionfor sentence in img['sentences']:word_freq.update(sentence['tokens'])if len(sentence['tokens'])<= max_len:captions.append(sentence['tokens'])#如果这个caption比最大长度短就增加if len(captions) == 0:continueif len(captions) < cap_per_image:captions = captions + [choice(captions) for _ in range(cap_per_image - len(captions))] #choice是从caption中随机取一个元素elif len(captions) > cap_per_image:captions = sample(captions,k=cap_per_image) #超过了就进行随机取样assert len(captions) == cap_per_imageif img['split'] in { 'train','restval'}:train_images_list.append(img['filename'])train_captions_list.append(captions)elif img['split'] == 'val':val_images_list.append(img['filename'])val_captions_list.append(captions)elif img['split'] == 'test':test_images_list.append(img['filename'])test_captions_list.append(captions)assert len(train_images_list) == len(train_captions_list)assert len(val_images_list) == len(val_captions_list)assert len(test_images_list) == len(test_captions_list)word = [w for w in word_freq if word_freq[w] > min_word_freq] #根据词频来筛掉单词#构建一个word_map出来word_map = { w:i+1 for i,w in enumerate(word)}word_map['<start>'] = len(word_map) + 1word_map['<end>'] = len(word_map) + 1word_map['<unk>'] = len(word_map) + 1word_map['<pad>'] = 0base_name = str(cap_per_image) + '_cap_per_image_' + str(min_word_freq) + '_min_word_freq' #这里的base文件名可以自己随便定义seed(223)#下面开始保存image,captions和caplensfor img_paths,img_caps,split in [(test_images_list,test_captions_list,'TEST'),(val_images_list,val_captions_list,'VAL'),(train_images_list,train_captions_list,'TRAIN')]:with h5py.File(os.path.join(out_folder,split + '_IMAGES_' + base_name + '.hdf5'),'a') as h:h.attrs['captions_per_image'] = cap_per_imageimages = h.create_dataset('images',(len(img_paths),3,256,256),dtype='uint8')enc_captions = list()caplens = list()print("start to store {0} images..." .format(split))for i,path in enumerate(tqdm(img_paths)):captions = img_caps[i] #注意这里要把第i个图片对应的caption取出来path = os.path.join(image_folder,path)img = imread(path) #拿到了第i个图片的数据,下面进行一些变形img = numpy.array(Image.fromarray(img).resize((256,256)))if len(img.shape) == 2:img = img[:,:,numpy.newaxis]img = numpy.concatenate([img,img,img],dim=2)img = img.transpose(2,0,1)#这几步的目的是将img转换成(3,256,256)images[i] = img #保存第i个图片for j,caption in enumerate(captions):en_cap = [word_map['<start>']] + [word_map.get(w,word_map['<unk>']) for w in caption]\+ [word_map['<end>']] + [word_map['<pad>']] * (max_len - len(caption))enc_captions.append(en_cap)caplens.append(len(caption) + 2)assert images.shape[0] * cap_per_image == len(enc_captions) == len(caplens)with open(os.path.join(out_folder,split + '_CAPTIONS_' + base_name + '.json'),'w') as j:json.dump(enc_captions,j)with open(os.path.join(out_folder,split + '_CAPLENS_' + base_name + '.json'),'w') as j:json.dump(caplens,j)with open(os.path.join(out_folder,'WORDMAP_' + base_name +'.json'),'w') as j:json.dump(word_map,j)
创建我们实验所需要的dataset类
我们已经把所有图片文件保存在hdf5文件中,captions和caplens,word_map都保存在了对应json文件中,值得注意的一点是按照上面的代码逻辑,captions和caplens的长度是image数量的caption_per_image倍。
创建数据集的目标:
- 将所需要的三个文件加载进来
- 训练模式下每个getitem需要返回一张图片,一个caption和相对应的caplens
validate模式下需要将图像对应的所有caption全部返回
dataset.py
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
class CaptionDataset(Dataset):def __init__(self,data_folder,base_name,split,transform=None):self.split = splitself.transform = transformh = h5py.File(os.path.join(data_folder,split+ '_IMAGES_' + base_name + '.hdf5'),'r')self.images = h['images']self.cpi = h.attrs['captions_per_image']with open(os.path.join(data_folder,split + '_CAPLENS_' + base_name + '.json'),'r') as j:self.caplens = json.load(j)with open(os.path.join(data_folder,split + '_CAPTIONS_' + base_name + '.json'),'r') as j:self.captions = json.load(j)def __getitem__(self,i):img = torch.tensor(self.images[i // self.cpi]/255.)if self.transform:img = self.transform(img)caplen = torch.tensor([self.caplens[i]])caption = torch.tensor(self.captions[i])if self.split == 'TRAIN':return img,caption,caplenelse:all_captions = torch.tensor(self.captions[(i // self.cpi) * self.cpi: (i // self.cpi) * self.cpi + self.cpi])return img,caption,caplen,all_captionsdef __len__(self):return len(self.captions)


开始训练模型
截至目前为止,我们已经实现了需要的模型,将我们需要的数据集处理成了训练所需要的Dataset类型,在每个单元都进行了测试,保证在模型训练过程中不会发生意料之外的错误,下面开始设计训练评估模型所需要的一些函数.
#utils.py#为了记录一些评价指标的变化而创建的类class AverageMetric(object):def __init__(self):self.reset()passdef reset(self):self.val = 0self.count = 0self.avg = 0self.sum = 0def update(self,val,n = 1):self.val = valself.sum += val * nself.count += nself.avg = self.sum / self.count# utils.py#为了计算top5的准确率def accuracy(predict,targets,k):#predict:[num_words,vocab_size] 注意经过pack_padded_sequence处理后batch轴消失了,而是把decode的长度做了累和#targets:[num_words]num_words = predict.size(0)#看看一共需要比较多少个单词targets = targets.view(-1,1) #[num_words,1]_,ind = predict.topk(k,1,True,True) #这里的index就是对应word的索引 #[num_words,k]targets = targets.expand_as(ind) #[num_words,k]correct = targets.eq(ind).sum().item()return correct / num_words * 100.0
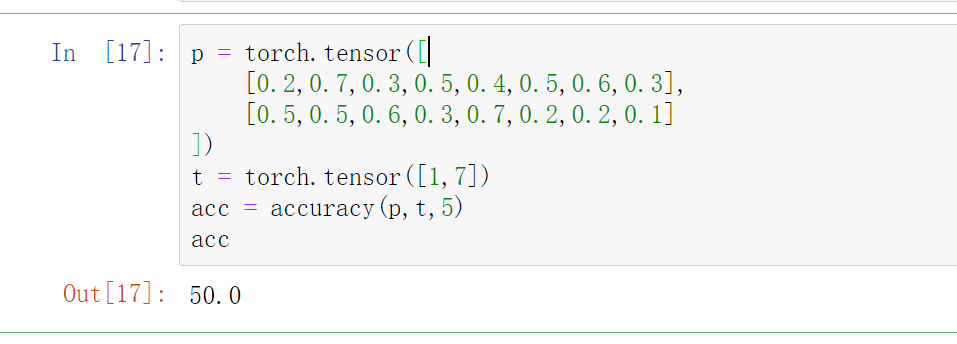
这里模拟了两个word的情况,第一个word中前5概率的索引是[1,6,3,5,4]包含了1,所以这个word被判定正确,第二个word中5概率的索引是
[4,2,0,1,3] 不包括7,所以被判定错误,最后的正确率是50%
from time import timedef train(train_loader,encoder,decoder,encoder_optimizer,decoder_optimizer,criterion,epoch):''' train_loader:在训练模式下,train_loader在每一次迭代过程中返回给我们的数据是: img:[batch_size,3,256,256] caption:[batch_size,max_len + 2]这里之所以加2是因为包含了<start>和<end> caplen:[batch_size,1] '''encoder.train()decoder.train()batch_time = AverageMetric() #为了记录一个batch的时间data_load = AverageMetric() #记录加载一次数据所用的时间losses = AverageMetric() #loss值top5acc = AverageMetric() #top5准确度,就是每次预测概率最高的五个词与正确答案比对,有一个对了就算正确start = time()for i, (img,caption,caplen) in enumerate(train_loader):data_load.updata(time() - start)img = img.to(device)caption = caption.to(device)caplen = caplen.to(device)encoder_out = encoder(img)predict,encode_captions,decode_length,alphas,sort_ind = decoder(encoder_out,caption,caplen)#predict [batch_size,max(decode_length),vocab_size]#encode_captions:[batch_size,max_len + 2]predict_copy = predict.clone() #后面用来计算top5accuracy的使用predict = predict.argmax(dim=2) #拿到每个序列每个位置概率最大的那个单词,用于后面做cross_entropytargets = encode_captions[:,1:] #每个caption的第一个<start>需要被去掉因为他不是被decode出来的predict = pack_padded_sequence(predict,decode_length,batch_first=True).data.to(device)targets = pack_padded_sequence(targets,decode_length,batch_first=True).data.to(device)loss = criterion(predict,targets)encoder_optimizer.zero_grad()decoder_optimizer.zero_grad()loss.backward()encoder_optimizer.step()decoder_optimizer.step()top5 = accuracy(predict_clone,targets)losses.update(loss.item(),sum(decode_length))top5acc.update(top5,sum(decode_length))batch_time.update(time() - start)start = time()if i % print_freq == 0 and i != 0:print('Epoch: [{0}][{1}/{2}]\t''Batch Time {batch_time.val:.3f} ({batch_time.avg:.3f})\t''Data Load Time {data_load.val:.3f} ({data_time.avg:.3f})\t''Loss {loss.val:.4f} ({loss.avg:.4f})\t''Top-5 Accuracy {top5.val:.3f} ({top5.avg:.3f})'.format(epoch, i, len(train_loader),batch_time=batch_time,data_load=data_load, loss=losses,top5=top5acc))""" 这里谈一下pack_padded_sequence的效果,对于rnn任务而言,一个batch中不同的序列,它们的实际长度可能并不相同,而是在序列的最后用<pad>(0) 将它们补齐到了一样的长度,而在decode的过程中我们利用了batch_size_t的小trick避免了补齐的0被拿去decode的情况。 现在的predict是我们的预测结果,targets是原始的标签,很显然它们的长度不一样,都存在着补0的情况,所以我们传入了一个decode_length,来表达 一个batch中每个序列的实际编码长度,这样就可以使得二者长度对齐了。 """def validate(val_loader,encoder,decoder,criterion):encoder.eval()decoder.eval()#进入评估模式以后dropout会失效#定义了3个标准量batch_time = AverageMeter()losses = AverageMeter()top5accs = AverageMeter()start = time.time()#references里面是正确的caption,一般一张图片有五个正确的caption,hypotheses是模型做出的推断references = list()hypotheses = list()with torch.no_grad():for i,(imgs,caps,caplens,allcaps) in enumerate(val_loader):imgs = imgs.to(device)caps = caps.to(device)caplens = caplens.to(device)imgs = encoder(imgs)scores, caps_sorted,decode_lengths, alphas,sort_ind = decoder(imgs,caps,caplens)scores_copy = scores.clone()targets = caps_sorted[:,1:]scores = pack_padded_sequence(scores,decode_lengths,batch_first=True).data.to(device)targets = pack_padded_sequence(targets,decode_lengths,batch_first=True).data.to(device)loss = criterion(scores,targets)losses.update(loss.item(),sum(decode_lengths))top5 = accuracy(scores,targets,5)top5accs.update(top5,sum(decode_lengths))batch_time.update(time.time() - start)start = time.time()if i % print_freq == 0:print('Validation: [{0}/{1}]\t''Batch Time {batch_time.val:.3f} ({batch_time.avg:.3f})\t''Loss {loss.val:.4f} ({loss.avg:.4f})\t''Top-5 Accuracy {top5.val:.3f} ({top5.avg:.3f})\t'.format(i, len(val_loader),batch_time=batch_time,loss=losses, top5=top5accs))allcaps = allcaps[sort_ind]#这一部分是为了将start和pad去掉for j in range(allcaps.shape[0]):img_caps = allcaps[j].tolist()img_captions = list(map(lambda c:[w for w in c if w not in { word_map['<start>'],word_map['<pad>']}],img_caps))references.append(img_captions)#这一部分拿到了一个batch所有推断出的句子_,preds = torch.max(scores_copy,dim=2)preds = preds.tolist()temp_preds = list()for j,p in enumerate(preds):temp = preds[j][:decode_lengths[j]]temp_preds.append(temp)preds = temp_predshypotheses.extend(preds)assert len(references) == len(hypotheses)#计算bleu-4的分数bleu4 = corpus_bleu(references,hypotheses)print('\n * LOSS - {loss.avg:.3f}, TOP-5 ACCURACY - {top5.avg:.3f}, BLEU-4 - {bleu}\n'.format(loss=losses,top5=top5accs,bleu=bleu4))return bleu4
开始模型的训练
这一部分我做了简洁化处理,主要是为了帮助理解训练过程,数据从loss采用的cross_entropy,看作一个多分类问题。每次训练一个epoch后,用validate函数计算一些bleu4的分数,最后得出最好的分数。
import timeimport torch.backends.cudnn as cudnnimport torch.optimimport torch.utils.dataimport torchvision.transforms as transformsfrom torch import nnfrom torch.nn.utils.rnn import pack_padded_sequencefrom models import Encoder,Decoderfrom datasets import *from utils import *from nltk.translate.bleu_score import corpus_bleudata_folder = '/mnt/hdd3/std2021/xiejun/datasets/flickr8k'base_name = '5_cap_per_img_5_min_word_freq'emb_dim = 512attention_dim = 512decode_dim = 512dropout = 0.5device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")cudnn.benchmark = Truestart_epoch = 0epochs = 10epochs_since_improvement = 0batch_size = 32encoder_lr = 1e-4decoder_lr = 4e-4alpha_c = 1.best_bleu4 = 0.print_freq = 100checkpoint = Nonedef main():global best_bleu4,checkpoint,start_epoch,base_name,word_map,epoch,epochs_since_improvement,reversed_mapwith open(os.path.join(data_folder,'WORDMAP_' + base_name + '.json')) as j:word_map = json.load(j)decoder = Decoder(attention_dim=attention_dim,decode_dim=decode_dim,embed_dim=emb_dim,vocab_size=len(word_map),dropout=dropout,encode_dim= 2048)decoder_optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(decoder.parameters(),lr=decoder_lr)encoder = Encoder()encoder_optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(params=encoder.parameters(),lr=encoder_lr)decoder = decoder.to(device)encoder = encoder.to(device)criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device)normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(CaptionDataset(data_folder,base_name,'TRAIN',transform=transforms.Compose([normalize])),batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=True,pin_memory=True)val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(CaptionDataset(data_folder,base_name,'VAL',transform=transforms.Compose([normalize])),batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=True,pin_memory=True)for epoch in range(start_epoch,epochs):train(train_loader=train_loader,decoder=decoder,criterion=criterion,encoder=encoder,encoder_optimizer=encoder_optimizer,decoder_optimizer=decoder_optimizer,epoch=epoch)recent_bleu4 = validate(val_loader=val_loader,encoder=encoder,decoder=decoder,criterion=criterion,)is_best = recent_bleu4 > best_bleu4best_bleu4 = max(recent_bleu4,best_bleu4)
































还没有评论,来说两句吧...