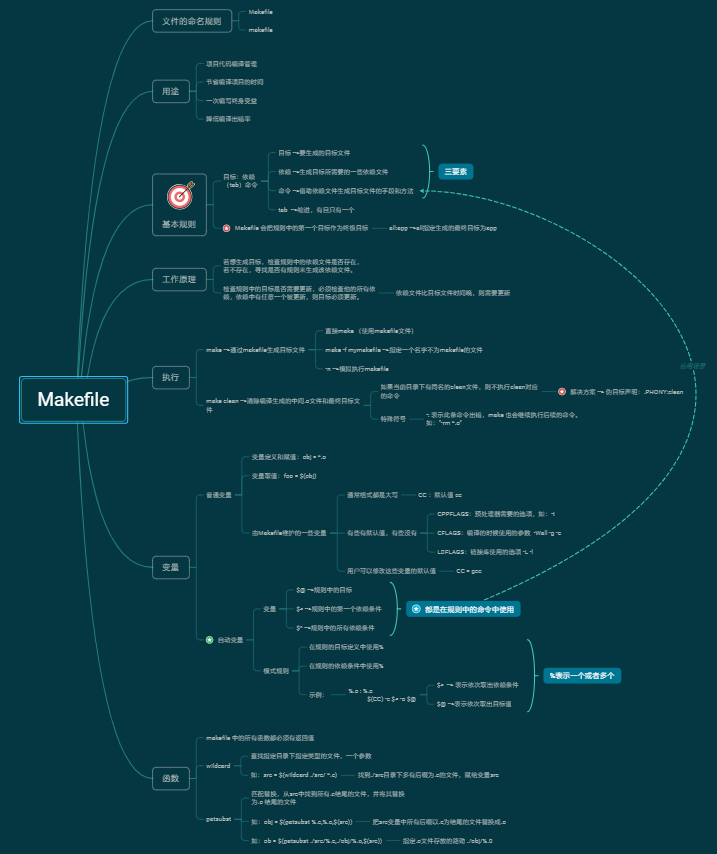
Js-this指向问题、call()、apply()、bind()改变this指向
0-零 - this几种指向
- 在全局中this:指向window。
- 对象方法中this:this指向该对象本身。
- 回调函数中this:指向window。
- 事件回调中this:指向e.currentTarget,给谁添加的事件监听就指向那个元素。
- 箭头函数中this:指向箭头函数外层的this。
- 类中this:指向实例化对象,哪个对象调用这个方法、this就指向哪个对象;静态方法和静态属性中:this指向这个类。
- call()、apply()、bind()中:将函数中this的指向 改变为这三个方法的第一个参数、当第一个参数为空或者为null时,表示将函数中的this指定到window。
Ⅰ- 壹 - 全局中this
全局对象的 this 是window
console.log(this);//windowfunction abc(){console.log(this);//window,严格模式下undefined}abc();
Ⅱ - 贰 - 对象方法中this
- 对象属性中使用 this,this 指向外层的 this 指向
- 对象方法中使用 this,this 指向该对象本身
可以理解为,属性描述 this 时,这个时候对象还没有生成,所以属性中的 this 指向外层的 this 指向;当调用对象的方法时,对象已经生成,所以方法中的 this 指向该对象本身。
对象属性中使用 this,this 指向外层的 this 指向
var a = 10;var obj1 = {a: 100,c: this.a, //属性中的this指向该对象的this,即windowinit: function () {console.log(this.a);//100 方法中的this指向该对象,即obj1console.log(this.c);//10}}obj1.init();
对象方法中使用 this,this 指向该对象本身
var a = 10;var obj1 = {a: 100,c: this.a, //属性中的this指向上一层的this,即windowinit: function () {console.log(this.a);//100,方法中的this指向该对象,即obj1var obj = {a: 1,c: this.a, //属性中的this指向上一层的this,即obj1b: function () {console.log(this.a);//1,方法中的this指向该对象,即objconsole.log(this.c);//100,方法中的this指向该对象,即obj}}obj.b();}}obj1.init();console.log(obj1.c);//10
Ⅲ - 叁 - 回调函数中this
将函数作为参数传入,无法确定该函数的原来的this指向。所以统一将回调函数中的this都指向window。
下面的案例中,如果函数abc()的this指向是window;函数obj.c()的this指向obj;将他们分别作为参数代入obj.b() 中,obj.b() 无法判读出他们原来的this指向。所以统一将this指向window。
function abc() {console.log(this);}var obj = {a: function () {this.b(this.c);// this.b(abc);},b: function (fn) {fn();console.log(this); //方法中的this指向该对象,即obj},c: function () {console.log(this); //回调函数中的 this 指向 window}}obj.a();
同理,forEach()、filter()、map()、some()、every()、promise…中函数都是回调函数,它们的 this 也都指向 window。
var arr=[1,2,3];arr.forEach(function(){console.log(this);//window})
Ⅳ - 肆 - 事件回调中this
事件侦听中的 this 指向 e.currentTarget,即给谁添加的事件侦听,this 就指向谁。
事件函数中的this,会覆盖普通对象中函数的this的指向;
// 事件侦听document.addEventListener("click",clickHandler);// 事件回调函数function clickHandler(e){// this--->e.currentTargetconsole.log(this);//document}var obj = {d: () => {console.log(this);//windowdocument.addEventListener("click", this.obj.loadHander);},loadHander(e) {console.log(this)//document}}obj.d();var obj = {d: () => {console.log(this); //windowdocument.addEventListener("click", e => this.obj.loadHander(e));},loadHander(e) {console.log(this) //obj}}obj.d();
Ⅴ - 伍 - 箭头函数中this
箭头函数改变了this指向,将指向箭头函数外层的this
var obj={a:function(){var arr=[1,2,3];arr.forEach(function(){console.log(this);//window 遵从于回调函数的this指向});arr.forEach(item=>{console.log(this);//obj 因为使用了箭头函数,就会忽略了回调函数的this指向})document.addEventListener("click",this.clickHandler);//objdocument.addEventListener("click",e=>{console.log(this);//obj 因为使用箭头函数,就会忽略了事件函数中this指向})},clickHandler:function(e){console.log(this)//document 遵从于事件函数中this---e.currentTarget}}obj.a();var obj = {d: () => {console.log(this);//windowdocument.addEventListener("click", this.obj.loadHander);},loadHander(e) {console.log(this, e.currentTarget)//this=>document e.currentTarget指向document}}obj.d();var obj = {d: () => {console.log(this); //windowdocument.addEventListener("click", e => this.obj.loadHander(e));},loadHander(e) {console.log(this, e.currentTarget) //this=>obj e.currentTarget指向document}}obj.d();
使用箭头函数侦听事件回调,因为箭头函数是匿名函数,所以没有办法清除,可以通过自定义箭头函数来进行清除。
//原始的document.documentElement.addEventListener("click", clickHandler);function clickHandler(e) {console.log(this);//html}//document.documentElement.removeEventListener("click", clickHandler);//普通的箭头匿名函数,因为是匿名函数,所以没有办法清除document.documentElement.addEventListener("click",e=>clickHandler())function clickHandler(e) {console.log(this);//window}//定义的箭头函数,可以removeEventListenervar handler = e => { clickHandler(e)};document.documentElement.addEventListener("click", handler);function clickHandler(e) {console.log(this);//window}//document.documentElement.removeEventListener("click", handler);
Ⅵ - 陆 - 类中this
- 类中的 this 指实例化的对象,谁调用方法,在类的函数中 this 就是那个实例对象
静态属性和静态方法中的 this 指的是这个类
//ES6中类的写法
class Rect{constructor(){this.elem=this.createElem();}createElem(){if(this.elem) return this.elem;let div=document.createElement("div");Object.assign(div.style,{width:"50px",height:"50px",backgroundColor:"red",position:"absolute",left:"0px"});div.addEventListener("click",e=>this.clickHandler(e))return div;}
}
//实例化对象
let rect=new Rect();
//上面代码中的this全都指向rect
ES6中类的写法和ES5中类的写法:
//ES6中类的写法class Box{static a=3;b=4;static c=this.a;//this指Box,static c=3;constructor(){}play(){//this 指实例化对象}static once(){//this 指Box}}// ES5中没有类,借用原型的概念实现类function Box(){//相当于ES6中constructor()}Box.a=3;//相当于ES6中的static a=3;Box.once=function(){//相当于ES6中的static once(){};}Box.prototype.b=4;//相当于上述中的b=4;Box.prototype.play=function(){//相当于上述中的play(){};}
Ⅶ - 柒 - call()、apply()、bind()方法改变this指向
| 方法名 | 参数 | 简述 |
|---|---|---|
| call() | 第一个参数为this指向的对象,第二个参数为函数的参数只能一个一个的添加 | 函数会立刻执行, |
| apply() | 第一个参数为this指向的对象,第二个参数为函数的参数可以是数组、列表或者扩展运算符 | 函数会立刻执行, |
| bind() | 第一个参数就是函数里面 的this就是的内容 | 函数不会立刻执行, |
一 call()
- 会立即执行函数;
- 如果有一个参数,且该参数为对象类型,则表示将函数中 this 的指向改变为这里带入的参数;
- 函数中如果没有this,call就没有任何意义了,和普通的执行函数概念一样;
- call() 在执行函数时,函数的参数从第二位开始依次写入;
- 如果使用call() 或者apply() ,第一个参数为空或者是null,就意味着将函数中this 重定向到 window;
语法: 方法名.call(对象);
function fn(_a,_b){this.a=_a;this.b=_b;}fn();//等同于fn.call();//立即执行函数,this指向windowlet obj={ };fn.call(obj);//立即执行函数,且this指向obj,将obj带入到函数替代函数中this的指向,原有的this会被指向objfn(3,4);//等同于fn.call(obj,3,4);
二 apply()
- apply() 和 call() 一样都是改变this的指向为第一个参数对象;
- apply() 的参数只有2个,第一个参数为函数中 this 的指向,第二个参数是函数所需的所有参数的数组,列表
如果使用call() 或者apply() ,第一个参数为空或者是null,就意味着将函数中this 重定向到 window;
function fn(_a,_b){
this.a=_a;
this.b=_b;
}
fn();//等同于
fn.call();//立即执行函数,this指向windowlet obj={ };
fn.apply(obj);//立即执行函数,且this指向objfn(3,4);//等同于
fn.apply(obj,[3,4]);
1 获取数组的最小值案例
var arr=[1,2,3,4,5];var min=Math.min.apply(null,arr);//Math方法使用//重构minvar Maths={min:function(){if(arguments.length===0) return;var min=arguments[0];if(arguments.length===1) return min;for(var i=1;i<arguments.length;i++){min=min.arguments[i]?arguments:min;}return min;}}//使用Maths.min.apply(null,arr);
2 将一个元素集合转为数组
<div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><script>var divs=document.getElementsByTagName("div");console.log(divs);//HTMLCollection(5) [div, div, div, div, div]var arr=Array.prototype.slice.call(divs);//var arr=[].slice.call(divs);//跟上面的写法意思一样console.log(arr);//[div, div, div, div, div]//重构转换数组Array.prototype.slice.call() 实现原理:class Arrays{constructor(){}slice(start,end){if(start===undefined) start=0;if(end===undefined) end=this.length;var arr=[];for(var i=start;i<end;i++){arr.push(this[i]);}return arr;}}//使用var arr=new Arrays();arr.slice.call(document.getElementsByTagName("div"));</script>
三 bind()
- 当需要在回调函数中重新执行回调函数中的this,就需要是用bind来指向对象
bind() 会返回一个对象,函数里面 的this就是绑定的内容。
//函数会延时执行
var obj={ a:1};setTimeout((function(){console.log(this);//打印{a:1}}).bind(obj),10000);//绑定到obj
//在事件中 绑定this的指向为objvar obj={a:1,b:function(){this.handler=this.clickHandler.bind(this);document.addEventListener("click",this.handler)},clickHandler:function(e){console.log(this);document.removeEventListener("click",this.handler)}}obj.b();
1 红绿黄灯切换
var id;function setLight() {arguments[0](arguments[1], arguments[2]);}function showLight(fn,fn2){clearTimeout(id);console.log(this.toString());id = setTimeout(fn, 2000, fn2, arguments.callee.bind(this));}setLight(showLight.bind("红"),showLight.bind("黄"),showLight.bind("绿"));
四 call()、apply()、bind()方法区别
- 定时器 延时器 事件绑定 都不可以用因为call apply会立刻执行函数
- call apply第一参数都一样为this的指向,call第二个参数只能一个一个的填写而apply可以是数组或者列表也可以使用扩展运算符 (…)
- 可以使用bind() 将一个函数绑定为某个对象但不会立刻执行
将函数中 this 的指向改变为这里带入的第一个参数,当第一个参数为空或者是null时,表示将函数中 this 重定向到 window;
//在延时器中使用会立即执行不会等待10秒执行
var obj={ a:1};setTimeout((function(){console.log(this);}).call(obj),10000);
//function fn(_a,_b){this.a=_a;this.b=_b;}fn.call();//this指向windowfn.apply();//this指向windowlet obj={ };fn.call(obj);//立即执行函数,且this指向objfn.apply(obj);//立即执行函数,且this指向objfn.bind(obj);//不执行,只是将this指向obj
0 - 0 - 知识点:
一 对象,事件 箭头函数 this
var obj = {d: () => {console.log(this);//windowdocument.addEventListener("click", this.obj.loadHander);},loadHander(e) {console.log(this, e.currentTarget)//this=>document e.currentTarget指向document}}obj.d();var obj = {d: () => {console.log(this); //windowdocument.addEventListener("click", e => this.obj.loadHander(e));},loadHander(e) {console.log(this, e.currentTarget) //this=>obj e.currentTarget指向document}}obj.d();
二 this总结
- 在全局中this:指向window。
- 对象方法中this:this指向该对象本身。
- 回调函数中this:指向window。
- 事件回调中this:指向e.currentTarget,给谁添加的事件监听就指向那个元素。
- 箭头函数中this:指向箭头函数外层的this。
- 类中this:指向实例化对象,哪个对象调用这个方法、this就指向哪个对象;静态方法和静态属性中:this指向这个类。
- call()、apply()、bind()中:将函数中this的指向 改变为这三个方法的第一个参数、当第一个参数为空或者为null时,表示将函数中的this指定到window。






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...