C++ 11 多线程学习笔记1 --线程创建
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av39161756?p=1
并发编程
包括多进程编程和多线程编程
进程之间相互通讯的方法
文件管道消息队列
多线程的优点
线程启动速度快轻量级开销低
多线程的缺点
管理较难不能在分布式系统下运行
运行环境
VS2013 + 控制台应用程序
1.HelloWord
#include <iostream>#include <thread>#include <future>using namespace std;void helloworld(){cout << "hello world \n";}int main(){//开启一个线程thread t(helloworld);cout << "hello world main thread\n";t.join();//主线程会等待t结束运行system("pause");return 0;}
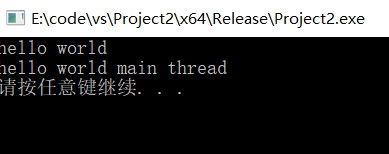
2.使用detach,主线程将不等子线程运行完就结束
#include <iostream>#include <thread>#include <future>using namespace std;void helloworld(){cout << "hello world" << endl;}int main(){//开启一个线程thread t(helloworld);t.detach();return 0;}
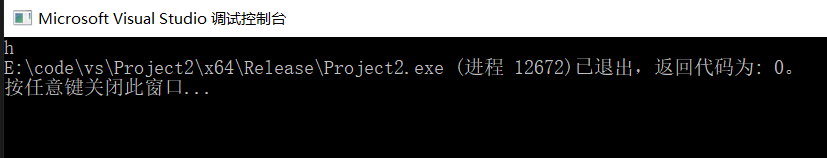
会只输出一个h就结束了
3.一个线程先使用了detach之后就不能join否则会报错。所以join之前先进行判断
#include <iostream>#include <thread>#include <future>using namespace std;void helloworld(){cout << "hello world" << endl;}int main(){//开启一个线程thread t(helloworld);t.detach();if (t.joinable()) {t.join();}return 0;}
4.异常处理
#include <iostream>#include <thread>#include <future>using namespace std;void helloworld(){cout << "hello world" << endl;}int main(){thread t(helloworld);for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {cout << "this is main thread" << endl;}//如果上面的代码抛出异常,t在join之前就会被销毁,这个时候代码就报错了t.join();return 0;}
修改为
#include <iostream>#include <thread>#include <future>using namespace std;void helloworld(){cout << "hello world" << endl;}int main(){thread t(helloworld);try {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {cout << "this is main thread" << endl;}}catch (...) {t.join();throw;}t.join();return 0;}
不管主线程是否抛出异常,t都可以正常join
5.通过类创建线程
#include <iostream>#include <thread>#include <future>using namespace std;void helloworld(){cout << "hello world" << endl;}class Fctor {public:void operator()() {for (int i = 0; i > -10; i--) {cout << "from t1: " << i << endl;}}};int main(){Fctor fct;thread t1(fct);for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {cout << "from main: " << i << endl;}//如果上面的代码抛出异常,t在join之前就会被销毁,这个时候代码就报错了t1.join();return 0;}

6.通过仿函数创建
#include <iostream>#include <thread>#include <future>using namespace std;class Fctor {public:void operator()() {for (int i = 0; i > -10; i--) {cout << "from t1: " << i << endl;}}};int main(){Fctor fct;//thread t1(fct);//也可以thread t1((Fctor()));for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {cout << "from main: " << i << endl;}//如果上面的代码抛出异常,t在join之前就会被销毁,这个时候代码就报错了t1.join();return 0;}
7.添加参数进行构造
#include <iostream>#include <thread>#include <future>#include <string>using namespace std;class Fctor {public:void operator()(std::string msg) {for (int i = 0; i > -10; i--) {cout << "from t1: " << msg << endl;}}};int main(){Fctor fct;string s = "hello world";thread t1((Fctor()),s);for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {cout << "from main: " << i << endl;}//如果上面的代码抛出异常,t在join之前就会被销毁,这个时候代码就报错了t1.join();return 0;}
8.通过引用传递参数std::ref
#include <iostream>#include <thread>#include <future>#include <string>using namespace std;class Fctor {public:void operator()(std::string& msg) {cout << "from t1: " << msg << endl;msg = "xiugai";}};int main(){Fctor fct;string s = "hello world";thread t1((Fctor()),std::ref(s));t1.join();cout << "from main: " << s << endl;return 0;}

9.不通过引用,(可能导致数据竞争),通过move创建
#include <iostream>#include <thread>#include <future>#include <string>using namespace std;class Fctor {public:void operator()(std::string msg) {cout << "from t1: " << msg << endl;msg = "xiugai";}};int main(){Fctor fct;string s = "hello world";cout << this_thread::get_id() << endl;thread t1((Fctor()),std::move(s));thread t2 = std::move(t1);t2.join();cout << "from main: " << s << endl;cout << "from main: " << t2.get_id()<< endl;return 0;}
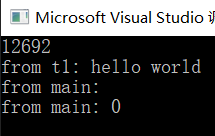
move把s移走了
10. hardware_concurrency输出可以并发编程的线程数量
#include <iostream>#include <thread>#include <future>#include <string>using namespace std;class Fctor {public:void operator()(std::string msg) {cout << "from t1: " << msg << endl;msg = "xiugai";}};int main(){Fctor fct;string s = "hello world";cout << this_thread::get_id() << endl;thread t1((Fctor()),std::move(s));t1.join();cout<<std::thread::hardware_concurrency()<<endl;return 0;}




































还没有评论,来说两句吧...