基于leaflet.js实现的轨迹回放
先看下效果图: (注意,这里是GIF图片,看起来会有些卡顿,但真实情况是很流畅的)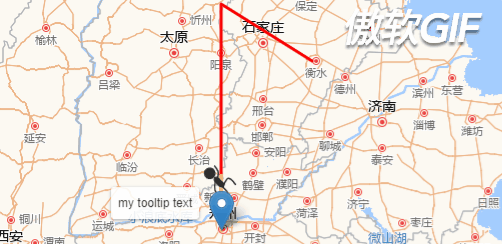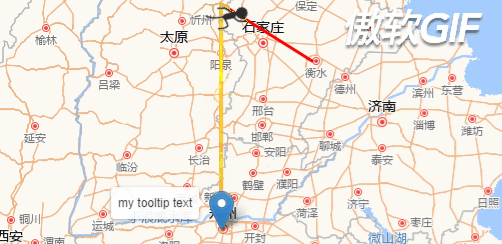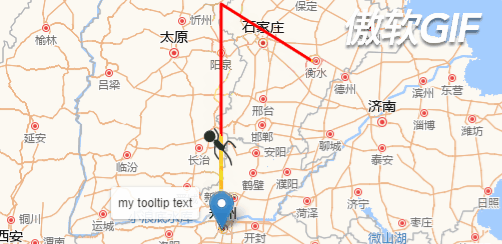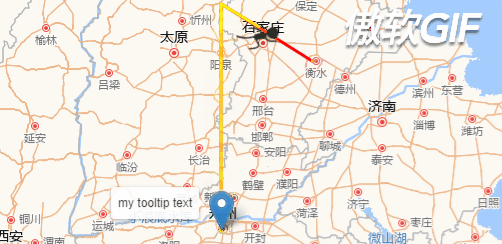
js文件们:(自己创建一个js文件,复制进去)
markerTrack.js:
L.Marker.addInitHook(function () {this.moveOptions = {origin: null,timer: null,done: 0,path: null,length: 0};this.setSpeed = function (speed) {this.moveOptions.speed = isNaN(parseFloat(speed)) || parseFloat(speed) <= 0 ? 200 : parseFloat(speed);};this.getSpeed = function () {return this.moveOptions.speed;};this.moveAlong = function (path, speed) {path = path instanceof L.Polyline ? path : new L.Polyline(path);this.moveOptions.path = path;this.moveOptions.length = L.GeometryUtil.length(path);this.moveOptions.speed = isNaN(parseFloat(speed)) || parseFloat(speed <= 0) ? 200 : parseFloat(speed);this._move();};this.pauseMove = function () {clearInterval(this.moveOptions.timer);this.moveOptions.timer = null;};this.resumeMove = function () {this._move();};this.stopMove = function () {this.pauseMove();this.moveOptions.done = 0;};this._move = function () {if (this.moveOptions.timer) return;let _t = this;this.moveOptions.timer = setInterval(function () {let done = _t.moveOptions.done;done += _t.moveOptions.speed / 1000 * 20;let radio = done / _t.moveOptions.length;radio >= 1 ? (radio = 0, done = 0) : true;_t.moveOptions.done = done;let p = L.GeometryUtil.interpolateOnLine(_t._map, _t.moveOptions.path, radio);_t.setLatLng(p.latLng);let pre_p = _t.moveOptions.path.getLatLngs()[p.predecessor];if (pre_p) {let passed = _t.moveOptions.path.getLatLngs().slice(0, p.predecessor + 1);passed.push(p.latLng);_t.fire('update_position', { path: passed});let deg = L.GeometryUtil.computeAngle(_t._map.project(pre_p), _t._map.project(p.latLng))_t._icon.style.transformOrigin = '50% 50%';_t._icon.style.transform += ' rotateZ(' + deg + 'deg)';}}, 20);}});
em.geometryutil.js:
// Packaging/modules magic dance.(function (factory) {factory(window.L)}(function (L) {"use strict";L.Polyline._flat = L.LineUtil.isFlat || L.Polyline._flat || function (latlngs) {// true if it's a flat array of latlngs; false if nestedreturn !L.Util.isArray(latlngs[0]) || (typeof latlngs[0][0] !== 'object' && typeof latlngs[0][0] !== 'undefined');};/** * @fileOverview Geometry utilities for distances and linear referencing. * @name L.GeometryUtil */L.GeometryUtil = L.extend(L.GeometryUtil || { }, {/** Shortcut function for planar distance between two {L.LatLng} at current zoom. @tutorial distance-length @param {L.Map} map map to be used for this method @param {L.LatLng} latlngA geographical point A @param {L.LatLng} latlngB geographical point B @returns {Number} planar distance */distance: function (map, latlngA, latlngB) {return map.latLngToLayerPoint(latlngA).distanceTo(map.latLngToLayerPoint(latlngB));},/** Shortcut function for planar distance between a {L.LatLng} and a segment (A-B). @param {L.Map} map map to be used for this method @param {L.LatLng} latlng - The position to search @param {L.LatLng} latlngA geographical point A of the segment @param {L.LatLng} latlngB geographical point B of the segment @returns {Number} planar distance */distanceSegment: function (map, latlng, latlngA, latlngB) {var p = map.latLngToLayerPoint(latlng),p1 = map.latLngToLayerPoint(latlngA),p2 = map.latLngToLayerPoint(latlngB);return L.LineUtil.pointToSegmentDistance(p, p1, p2);},/** Shortcut function for converting distance to readable distance. @param {Number} distance distance to be converted @param {String} unit 'metric' or 'imperial' @returns {String} in yard or miles */readableDistance: function (distance, unit) {var isMetric = (unit !== 'imperial'),distanceStr;if (isMetric) {// show metres when distance is < 1km, then show kmif (distance > 1000) {distanceStr = (distance / 1000).toFixed(2) + ' km';}else {distanceStr = Math.ceil(distance) + ' m';}}else {distance *= 1.09361;if (distance > 1760) {distanceStr = (distance / 1760).toFixed(2) + ' miles';}else {distanceStr = Math.ceil(distance) + ' yd';}}return distanceStr;},/** Returns true if the latlng belongs to segment A-B @param {L.LatLng} latlng - The position to search @param {L.LatLng} latlngA geographical point A of the segment @param {L.LatLng} latlngB geographical point B of the segment @param {?Number} [tolerance=0.2] tolerance to accept if latlng belongs really @returns {boolean} */belongsSegment: function(latlng, latlngA, latlngB, tolerance) {tolerance = tolerance === undefined ? 0.2 : tolerance;var hypotenuse = latlngA.distanceTo(latlngB),delta = latlngA.distanceTo(latlng) + latlng.distanceTo(latlngB) - hypotenuse;return delta/hypotenuse < tolerance;},/** * Returns total length of line * @tutorial distance-length * * @param {L.Polyline|Array<L.Point>|Array<L.LatLng>} coords Set of coordinates * @returns {Number} Total length (pixels for Point, meters for LatLng) */length: function (coords) {var accumulated = L.GeometryUtil.accumulatedLengths(coords);return accumulated.length > 0 ? accumulated[accumulated.length-1] : 0;},/** * Returns a list of accumulated length along a line. * @param {L.Polyline|Array<L.Point>|Array<L.LatLng>} coords Set of coordinates * @returns {Array<Number>} Array of accumulated lengths (pixels for Point, meters for LatLng) */accumulatedLengths: function (coords) {if (typeof coords.getLatLngs == 'function') {coords = coords.getLatLngs();}if (coords.length === 0)return [];var total = 0,lengths = [0];for (var i = 0, n = coords.length - 1; i< n; i++) {total += coords[i].distanceTo(coords[i+1]);lengths.push(total);}return lengths;},/** Returns the closest point of a {L.LatLng} on the segment (A-B) @tutorial closest @param {L.Map} map map to be used for this method @param {L.LatLng} latlng - The position to search @param {L.LatLng} latlngA geographical point A of the segment @param {L.LatLng} latlngB geographical point B of the segment @returns {L.LatLng} Closest geographical point */closestOnSegment: function (map, latlng, latlngA, latlngB) {var maxzoom = map.getMaxZoom();if (maxzoom === Infinity)maxzoom = map.getZoom();var p = map.project(latlng, maxzoom),p1 = map.project(latlngA, maxzoom),p2 = map.project(latlngB, maxzoom),closest = L.LineUtil.closestPointOnSegment(p, p1, p2);return map.unproject(closest, maxzoom);},/** Returns the closest latlng on layer. Accept nested arrays @tutorial closest @param {L.Map} map map to be used for this method @param {Array<L.LatLng>|Array<Array<L.LatLng>>|L.PolyLine|L.Polygon} layer - Layer that contains the result @param {L.LatLng} latlng - The position to search @param {?boolean} [vertices=false] - Whether to restrict to path vertices. @returns {L.LatLng} Closest geographical point or null if layer param is incorrect */closest: function (map, layer, latlng, vertices) {var latlngs,mindist = Infinity,result = null,i, n, distance, subResult;if (layer instanceof Array) {// if layer is Array<Array<T>>if (layer[0] instanceof Array && typeof layer[0][0] !== 'number') {// if we have nested arrays, we calc the closest for each array// recursivefor (i = 0; i < layer.length; i++) {subResult = L.GeometryUtil.closest(map, layer[i], latlng, vertices);if (subResult.distance < mindist) {mindist = subResult.distance;result = subResult;}}return result;} else if (layer[0] instanceof L.LatLng|| typeof layer[0][0] === 'number'|| typeof layer[0].lat === 'number') { // we could have a latlng as [x,y] with x & y numbers or {lat, lng}layer = L.polyline(layer);} else {return result;}}// if we don't have here a Polyline, that means layer is incorrect// see https://github.com/makinacorpus/.GeometryUtil/issues/23if (! ( layer instanceof L.Polyline ) )return result;// deep copy of latlngslatlngs = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(layer.getLatLngs().slice(0)));// add the last segment for L.Polygonif (layer instanceof L.Polygon) {// add the last segment for each child that is a nested arrayvar addLastSegment = function(latlngs) {if (L.Polyline._flat(latlngs)) {latlngs.push(latlngs[0]);} else {for (var i = 0; i < latlngs.length; i++) {addLastSegment(latlngs[i]);}}};addLastSegment(latlngs);}// we have a multi polygon / multi polyline / polygon with holes// use recursive to explore and return the good resultif ( ! L.Polyline._flat(latlngs) ) {for (i = 0; i < latlngs.length; i++) {// if we are at the lower level, and if we have a L.Polygon, we add the last segmentsubResult = L.GeometryUtil.closest(map, latlngs[i], latlng, vertices);if (subResult.distance < mindist) {mindist = subResult.distance;result = subResult;}}return result;} else {// Lookup verticesif (vertices) {for(i = 0, n = latlngs.length; i < n; i++) {var ll = latlngs[i];distance = L.GeometryUtil.distance(map, latlng, ll);if (distance < mindist) {mindist = distance;result = ll;result.distance = distance;}}return result;}// Keep the closest point of all segmentsfor (i = 0, n = latlngs.length; i < n-1; i++) {var latlngA = latlngs[i],latlngB = latlngs[i+1];distance = L.GeometryUtil.distanceSegment(map, latlng, latlngA, latlngB);if (distance <= mindist) {mindist = distance;result = L.GeometryUtil.closestOnSegment(map, latlng, latlngA, latlngB);result.distance = distance;}}return result;}},/** Returns the closest layer to latlng among a list of layers. @tutorial closest @param {L.Map} map map to be used for this method @param {Array<L.ILayer>} layers Set of layers @param {L.LatLng} latlng - The position to search @returns {object} ``{layer, latlng, distance}`` or ``null`` if list is empty; */closestLayer: function (map, layers, latlng) {var mindist = Infinity,result = null,ll = null,distance = Infinity;for (var i = 0, n = layers.length; i < n; i++) {var layer = layers[i];if (layer instanceof L.LayerGroup) {// recursivevar subResult = L.GeometryUtil.closestLayer(map, layer.getLayers(), latlng);if (subResult.distance < mindist) {mindist = subResult.distance;result = subResult;}} else {// Single dimension, snap on points, else snap on closestif (typeof layer.getLatLng == 'function') {ll = layer.getLatLng();distance = L.GeometryUtil.distance(map, latlng, ll);}else {ll = L.GeometryUtil.closest(map, layer, latlng);if (ll) distance = ll.distance; // Can return null if layer has no points.}if (distance < mindist) {mindist = distance;result = { layer: layer, latlng: ll, distance: distance};}}}return result;},/** Returns the n closest layers to latlng among a list of input layers. @param {L.Map} map - map to be used for this method @param {Array<L.ILayer>} layers - Set of layers @param {L.LatLng} latlng - The position to search @param {?Number} [n=layers.length] - the expected number of output layers. @returns {Array<object>} an array of objects ``{layer, latlng, distance}`` or ``null`` if the input is invalid (empty list or negative n) */nClosestLayers: function (map, layers, latlng, n) {n = typeof n === 'number' ? n : layers.length;if (n < 1 || layers.length < 1) {return null;}var results = [];var distance, ll;for (var i = 0, m = layers.length; i < m; i++) {var layer = layers[i];if (layer instanceof L.LayerGroup) {// recursivevar subResult = L.GeometryUtil.closestLayer(map, layer.getLayers(), latlng);results.push(subResult);} else {// Single dimension, snap on points, else snap on closestif (typeof layer.getLatLng == 'function') {ll = layer.getLatLng();distance = L.GeometryUtil.distance(map, latlng, ll);}else {ll = L.GeometryUtil.closest(map, layer, latlng);if (ll) distance = ll.distance; // Can return null if layer has no points.}results.push({ layer: layer, latlng: ll, distance: distance});}}results.sort(function(a, b) {return a.distance - b.distance;});if (results.length > n) {return results.slice(0, n);} else {return results;}},/** * Returns all layers within a radius of the given position, in an ascending order of distance. @param {L.Map} map map to be used for this method @param {Array<ILayer>} layers - A list of layers. @param {L.LatLng} latlng - The position to search @param {?Number} [radius=Infinity] - Search radius in pixels @return {object[]} an array of objects including layer within the radius, closest latlng, and distance */layersWithin: function(map, layers, latlng, radius) {radius = typeof radius == 'number' ? radius : Infinity;var results = [];var ll = null;var distance = 0;for (var i = 0, n = layers.length; i < n; i++) {var layer = layers[i];if (typeof layer.getLatLng == 'function') {ll = layer.getLatLng();distance = L.GeometryUtil.distance(map, latlng, ll);}else {ll = L.GeometryUtil.closest(map, layer, latlng);if (ll) distance = ll.distance; // Can return null if layer has no points.}if (ll && distance < radius) {results.push({ layer: layer, latlng: ll, distance: distance});}}var sortedResults = results.sort(function(a, b) {return a.distance - b.distance;});return sortedResults;},/** Returns the closest position from specified {LatLng} among specified layers, with a maximum tolerance in pixels, providing snapping behaviour. @tutorial closest @param {L.Map} map map to be used for this method @param {Array<ILayer>} layers - A list of layers to snap on. @param {L.LatLng} latlng - The position to snap @param {?Number} [tolerance=Infinity] - Maximum number of pixels. @param {?boolean} [withVertices=true] - Snap to layers vertices or segment points (not only vertex) @returns {object} with snapped {LatLng} and snapped {Layer} or null if tolerance exceeded. */closestLayerSnap: function (map, layers, latlng, tolerance, withVertices) {tolerance = typeof tolerance == 'number' ? tolerance : Infinity;withVertices = typeof withVertices == 'boolean' ? withVertices : true;var result = L.GeometryUtil.closestLayer(map, layers, latlng);if (!result || result.distance > tolerance)return null;// If snapped layer is linear, try to snap on vertices (extremities and middle points)if (withVertices && typeof result.layer.getLatLngs == 'function') {var closest = L.GeometryUtil.closest(map, result.layer, result.latlng, true);if (closest.distance < tolerance) {result.latlng = closest;result.distance = L.GeometryUtil.distance(map, closest, latlng);}}return result;},/** Returns the Point located on a segment at the specified ratio of the segment length. @param {L.Point} pA coordinates of point A @param {L.Point} pB coordinates of point B @param {Number} the length ratio, expressed as a decimal between 0 and 1, inclusive. @returns {L.Point} the interpolated point. */interpolateOnPointSegment: function (pA, pB, ratio) {return L.point((pA.x * (1 - ratio)) + (ratio * pB.x),(pA.y * (1 - ratio)) + (ratio * pB.y));},/** Returns the coordinate of the point located on a line at the specified ratio of the line length. @param {L.Map} map map to be used for this method @param {Array<L.LatLng>|L.PolyLine} latlngs Set of geographical points @param {Number} ratio the length ratio, expressed as a decimal between 0 and 1, inclusive @returns {Object} an object with latLng ({LatLng}) and predecessor ({Number}), the index of the preceding vertex in the Polyline (-1 if the interpolated point is the first vertex) */interpolateOnLine: function (map, latLngs, ratio) {latLngs = (latLngs instanceof L.Polyline) ? latLngs.getLatLngs() : latLngs;var n = latLngs.length;if (n < 2) {return null;}// ensure the ratio is between 0 and 1;ratio = Math.max(Math.min(ratio, 1), 0);if (ratio === 0) {return {latLng: latLngs[0] instanceof L.LatLng ? latLngs[0] : L.latLng(latLngs[0]),predecessor: -1};}if (ratio == 1) {return {latLng: latLngs[latLngs.length -1] instanceof L.LatLng ? latLngs[latLngs.length -1] : L.latLng(latLngs[latLngs.length -1]),predecessor: latLngs.length - 2};}// project the LatLngs as Points,// and compute total planar length of the line at max precisionvar maxzoom = map.getMaxZoom();if (maxzoom === Infinity)maxzoom = map.getZoom();var pts = [];var lineLength = 0;for(var i = 0; i < n; i++) {pts[i] = map.project(latLngs[i], maxzoom);if(i > 0)lineLength += pts[i-1].distanceTo(pts[i]);}var ratioDist = lineLength * ratio;// follow the line segments [ab], adding lengths,// until we find the segment where the points should lie onvar cumulativeDistanceToA = 0, cumulativeDistanceToB = 0;for (var i = 0; cumulativeDistanceToB < ratioDist; i++) {var pointA = pts[i], pointB = pts[i+1];cumulativeDistanceToA = cumulativeDistanceToB;cumulativeDistanceToB += pointA.distanceTo(pointB);}if (pointA == undefined && pointB == undefined) { // Happens when line has no lengthvar pointA = pts[0], pointB = pts[1], i = 1;}// compute the ratio relative to the segment [ab]var segmentRatio = ((cumulativeDistanceToB - cumulativeDistanceToA) !== 0) ? ((ratioDist - cumulativeDistanceToA) / (cumulativeDistanceToB - cumulativeDistanceToA)) : 0;var interpolatedPoint = L.GeometryUtil.interpolateOnPointSegment(pointA, pointB, segmentRatio);return {latLng: map.unproject(interpolatedPoint, maxzoom),predecessor: i-1};},/** Returns a float between 0 and 1 representing the location of the closest point on polyline to the given latlng, as a fraction of total line length. (opposite of L.GeometryUtil.interpolateOnLine()) @param {L.Map} map map to be used for this method @param {L.PolyLine} polyline Polyline on which the latlng will be search @param {L.LatLng} latlng The position to search @returns {Number} Float between 0 and 1 */locateOnLine: function (map, polyline, latlng) {var latlngs = polyline.getLatLngs();if (latlng.equals(latlngs[0]))return 0.0;if (latlng.equals(latlngs[latlngs.length-1]))return 1.0;var point = L.GeometryUtil.closest(map, polyline, latlng, false),lengths = L.GeometryUtil.accumulatedLengths(latlngs),total_length = lengths[lengths.length-1],portion = 0,found = false;for (var i=0, n = latlngs.length-1; i < n; i++) {var l1 = latlngs[i],l2 = latlngs[i+1];portion = lengths[i];if (L.GeometryUtil.belongsSegment(point, l1, l2, 0.0001)) {portion += l1.distanceTo(point);found = true;break;}}if (!found) {throw "Could not interpolate " + latlng.toString() + " within " + polyline.toString();}return portion / total_length;},/** Returns a clone with reversed coordinates. @param {L.PolyLine} polyline polyline to reverse @returns {L.PolyLine} polyline reversed */reverse: function (polyline) {return L.polyline(polyline.getLatLngs().slice(0).reverse());},/** Returns a sub-part of the polyline, from start to end. If start is superior to end, returns extraction from inverted line. @param {L.Map} map map to be used for this method @param {L.PolyLine} polyline Polyline on which will be extracted the sub-part @param {Number} start ratio, expressed as a decimal between 0 and 1, inclusive @param {Number} end ratio, expressed as a decimal between 0 and 1, inclusive @returns {Array<L.LatLng>} new polyline */extract: function (map, polyline, start, end) {if (start > end) {return L.GeometryUtil.extract(map, L.GeometryUtil.reverse(polyline), 1.0-start, 1.0-end);}// Bound start and end to [0-1]start = Math.max(Math.min(start, 1), 0);end = Math.max(Math.min(end, 1), 0);var latlngs = polyline.getLatLngs(),startpoint = L.GeometryUtil.interpolateOnLine(map, polyline, start),endpoint = L.GeometryUtil.interpolateOnLine(map, polyline, end);// Return single point if start == endif (start == end) {var point = L.GeometryUtil.interpolateOnLine(map, polyline, end);return [point.latLng];}// Array.slice() works indexes at 0if (startpoint.predecessor == -1)startpoint.predecessor = 0;if (endpoint.predecessor == -1)endpoint.predecessor = 0;var result = latlngs.slice(startpoint.predecessor+1, endpoint.predecessor+1);result.unshift(startpoint.latLng);result.push(endpoint.latLng);return result;},/** Returns true if first polyline ends where other second starts. @param {L.PolyLine} polyline First polyline @param {L.PolyLine} other Second polyline @returns {bool} */isBefore: function (polyline, other) {if (!other) return false;var lla = polyline.getLatLngs(),llb = other.getLatLngs();return (lla[lla.length-1]).equals(llb[0]);},/** Returns true if first polyline starts where second ends. @param {L.PolyLine} polyline First polyline @param {L.PolyLine} other Second polyline @returns {bool} */isAfter: function (polyline, other) {if (!other) return false;var lla = polyline.getLatLngs(),llb = other.getLatLngs();return (lla[0]).equals(llb[llb.length-1]);},/** Returns true if first polyline starts where second ends or start. @param {L.PolyLine} polyline First polyline @param {L.PolyLine} other Second polyline @returns {bool} */startsAtExtremity: function (polyline, other) {if (!other) return false;var lla = polyline.getLatLngs(),llb = other.getLatLngs(),start = lla[0];return start.equals(llb[0]) || start.equals(llb[llb.length-1]);},/** Returns horizontal angle in degres between two points. @param {L.Point} a Coordinates of point A @param {L.Point} b Coordinates of point B @returns {Number} horizontal angle */computeAngle: function(a, b) {return (Math.atan2(b.y - a.y, b.x - a.x) * 180 / Math.PI);},/** Returns slope (Ax+B) between two points. @param {L.Point} a Coordinates of point A @param {L.Point} b Coordinates of point B @returns {Object} with ``a`` and ``b`` properties. */computeSlope: function(a, b) {var s = (b.y - a.y) / (b.x - a.x),o = a.y - (s * a.x);return { 'a': s, 'b': o};},/** Returns LatLng of rotated point around specified LatLng center. @param {L.LatLng} latlngPoint: point to rotate @param {double} angleDeg: angle to rotate in degrees @param {L.LatLng} latlngCenter: center of rotation @returns {L.LatLng} rotated point */rotatePoint: function(map, latlngPoint, angleDeg, latlngCenter) {var maxzoom = map.getMaxZoom();if (maxzoom === Infinity)maxzoom = map.getZoom();var angleRad = angleDeg*Math.PI/180,pPoint = map.project(latlngPoint, maxzoom),pCenter = map.project(latlngCenter, maxzoom),x2 = Math.cos(angleRad)*(pPoint.x-pCenter.x) - Math.sin(angleRad)*(pPoint.y-pCenter.y) + pCenter.x,y2 = Math.sin(angleRad)*(pPoint.x-pCenter.x) + Math.cos(angleRad)*(pPoint.y-pCenter.y) + pCenter.y;return map.unproject(new L.Point(x2,y2), maxzoom);},/** Returns the bearing in degrees clockwise from north (0 degrees) from the first L.LatLng to the second, at the first LatLng @param {L.LatLng} latlng1: origin point of the bearing @param {L.LatLng} latlng2: destination point of the bearing @returns {float} degrees clockwise from north. */bearing: function(latlng1, latlng2) {var rad = Math.PI / 180,lat1 = latlng1.lat * rad,lat2 = latlng2.lat * rad,lon1 = latlng1.lng * rad,lon2 = latlng2.lng * rad,y = Math.sin(lon2 - lon1) * Math.cos(lat2),x = Math.cos(lat1) * Math.sin(lat2) -Math.sin(lat1) * Math.cos(lat2) * Math.cos(lon2 - lon1);var bearing = ((Math.atan2(y, x) * 180 / Math.PI) + 360) % 360;return bearing >= 180 ? bearing-360 : bearing;},/** Returns the point that is a distance and heading away from the given origin point. @param {L.LatLng} latlng: origin point @param {float} heading: heading in degrees, clockwise from 0 degrees north. @param {float} distance: distance in meters @returns {L.latLng} the destination point. Many thanks to Chris Veness at http://www.movable-type.co.uk/scripts/latlong.html for a great reference and examples. */destination: function(latlng, heading, distance) {heading = (heading + 360) % 360;var rad = Math.PI / 180,radInv = 180 / Math.PI,R = 6378137, // approximation of Earth's radiuslon1 = latlng.lng * rad,lat1 = latlng.lat * rad,rheading = heading * rad,sinLat1 = Math.sin(lat1),cosLat1 = Math.cos(lat1),cosDistR = Math.cos(distance / R),sinDistR = Math.sin(distance / R),lat2 = Math.asin(sinLat1 * cosDistR + cosLat1 *sinDistR * Math.cos(rheading)),lon2 = lon1 + Math.atan2(Math.sin(rheading) * sinDistR *cosLat1, cosDistR - sinLat1 * Math.sin(lat2));lon2 = lon2 * radInv;lon2 = lon2 > 180 ? lon2 - 360 : lon2 < -180 ? lon2 + 360 : lon2;return L.latLng([lat2 * radInv, lon2]);},/** Returns the the angle of the given segment and the Equator in degrees, clockwise from 0 degrees north. @param {L.Map} map: map to be used for this method @param {L.LatLng} latlngA: geographical point A of the segment @param {L.LatLng} latlngB: geographical point B of the segment @returns {Float} the angle in degrees. */angle: function(map, latlngA, latlngB) {var pointA = map.latLngToContainerPoint(latlngA),pointB = map.latLngToContainerPoint(latlngB),angleDeg = Math.atan2(pointB.y - pointA.y, pointB.x - pointA.x) * 180 / Math.PI + 90;angleDeg += angleDeg < 0 ? 360 : 0;return angleDeg;},/** Returns a point snaps on the segment and heading away from the given origin point a distance. @param {L.Map} map: map to be used for this method @param {L.LatLng} latlngA: geographical point A of the segment @param {L.LatLng} latlngB: geographical point B of the segment @param {float} distance: distance in meters @returns {L.latLng} the destination point. */destinationOnSegment: function(map, latlngA, latlngB, distance) {var angleDeg = L.GeometryUtil.angle(map, latlngA, latlngB),latlng = L.GeometryUtil.destination(latlngA, angleDeg, distance);return L.GeometryUtil.closestOnSegment(map, latlng, latlngA, latlngB);},});return L.GeometryUtil;}));
一个简单的demo,需要适当修改:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>路径轨迹回放</title><meta charset="utf-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><!-- leaflet。js的基础依赖 --><link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="../leaflet/dist/leaflet.css"><script type="text/javascript" src="../leaflet/dist/leaflet.js"></script><!-- 轨迹回放的自定义插件(依赖于leaflet。js) --><script type="text/javascript" src="../customLib/markerTrack.js"></script><script type="text/javascript" src="../customLib/em.geometryutil.js"></script></head><style> body { margin: 0; padding: 0; } #map { position: absolute; top: 0; bottom: 0; width: 100%; } </style><body><div id='map'></div><script type="text/javascript"> /* 这块代码是引入地图的,根据自己的项目来就好(我的项目里面是离线地图) */ // --start引入地图-- var url = 'http://localhost:9090/img/{z}/{x}/{y}.png'; // var url = '"http://webrd0{s}.is.autonavi.com/appmaptile?x={x}&y={y}&z={z}&lang=zh_cn&size=1&scale=1&style=8'; var map = L.map('map',{ center: [34.694,113.587], zoom: 6, zoomControl: false }); //将图层加载到地图上,并设置最大的聚焦还有map样式 L.tileLayer(url, { maxZoom: 18, minZoom: 3 }).addTo(map); // --end引入地图-- /** * 开始轨迹回放的代码 */ // 运动的轨迹 var polyline = L.polyline([[34.694,113.587],[38.694,113.587],[37.694,115.587]],{ color: 'red'}).addTo(map); // 轨迹运动的图标 var m = L.marker([34.694,113.587],{ icon:L.icon({ iconUrl:'img/run.png', iconAnchor: [25, 15], })}).addTo(map); //添加一条线段也记录已经路过的点 var passed=L.polyline([[]],{ color:'yellow'}).addTo(map); m.on('update_position',function (e) { //每次坐标更新。然后也更新路径 passed.setLatLngs(e.path); }); // 开始运动 m.moveAlong(polyline,300000); </script></body></html>
别忘点赞!
































还没有评论,来说两句吧...