HDU 6155 Subsequence Count(矩阵 + DP + 线段树)题解
题意:01串,操作1:把l r区间的0变1,1变0;操作2:求出l r区间的子序列种数
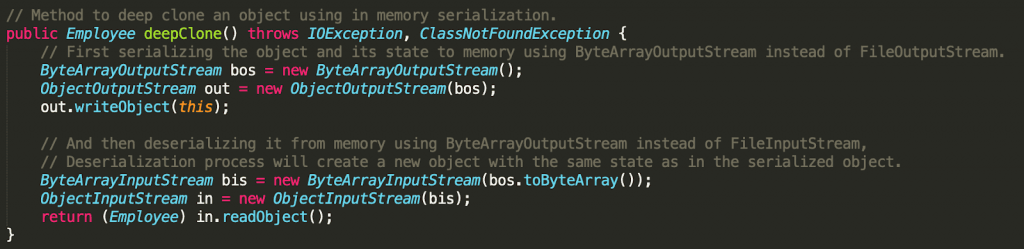
思路:设DP[i][j]为到i为止以j结尾的种数,假设j为0,那么dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][1] + dp[i -1][0] (0结尾新串) + dp[i - 1][0] (0结尾旧串) - dp[i - 1][0] (重复) + 1(0本身被重复时去除)。
那么可以得到转移时的矩阵
\left( \begin{matrix} dp[i - 1][0] & dp[i - 1][1] & 1 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end{matrix} \right) * \left( \begin{matrix} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 1 &1 & 0 \\ 1 & 0 & 1 \end{matrix} \right) = \left( \begin{matrix} dp[i][0] & dp[i][1] & 1 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end{matrix} \right)
那么我们只要用线段树维护连续的矩阵乘积就行了。
如果翻转,那么存在一个规律,可以打表找出,直接实现连续区间矩阵乘积的翻转。
代码:
#include<cmath>#include<set>#include<map>#include<queue>#include<cstdio>#include<vector>#include<cstring>#include <iostream>#include<algorithm>using namespace std;typedef long long ll;typedef unsigned long long ull;const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;const int M = 50 + 5;const ull seed = 131;const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;const ll MOD = 1000000007;char str[maxn];struct Mat{ll s[3][3];void init(){memset(s, 0, sizeof(s));}};Mat Mamul(Mat a, Mat b){Mat ret;ret.init();for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){for(int k = 0; k < 3; k++){ret.s[i][j] = (ret.s[i][j] + a.s[i][k] * b.s[k][j]) % MOD;}}}return ret;}Mat mul[maxn << 2];int lazy[maxn << 2];void is(Mat &a, char s){if(s == '0'){a.s[0][0] = 1, a.s[0][1] = 0, a.s[0][2] = 0;a.s[1][0] = 1, a.s[1][1] = 1, a.s[1][2] = 0;a.s[2][0] = 1, a.s[2][1] = 0, a.s[2][2] = 1;}else{a.s[0][0] = 1, a.s[0][1] = 1, a.s[0][2] = 0;a.s[1][0] = 0, a.s[1][1] = 1, a.s[1][2] = 0;a.s[2][0] = 0, a.s[2][1] = 1, a.s[2][2] = 1;}}void change(Mat &a){swap(a.s[0][0], a.s[1][1]);swap(a.s[1][0], a.s[0][1]);swap(a.s[2][0], a.s[2][1]);}void pushdown(int rt){if(lazy[rt]){lazy[rt << 1] ^= lazy[rt];lazy[rt << 1 | 1] ^= lazy[rt];change(mul[rt << 1]);change(mul[rt << 1 | 1]);lazy[rt] = 0;}}void pushup(int rt){mul[rt] = Mamul(mul[rt << 1], mul[rt << 1 | 1]);}void build(int l, int r, int rt){lazy[rt] = 0;if(l == r){is(mul[rt], str[l]);return;}int m = (l + r) >> 1;build(l, m, rt << 1);build(m + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1);pushup(rt);}void update(int L, int R, int l, int r, int rt){if(L <= l && R >= r){lazy[rt] ^= 1;change(mul[rt]);return;}pushdown(rt);int m = (l + r) >> 1;if(L <= m)update(L, R, l, m, rt << 1);if(R > m)update(L, R, m + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1);pushup(rt);}Mat query(int L, int R, int l, int r, int rt){if(L <= l && R >= r){return mul[rt];}pushdown(rt);int m = (l + r) >> 1;Mat ret;ret.init();for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++)ret.s[i][i] = 1;if(L <= m)ret = Mamul(ret, query(L, R, l, m, rt << 1));if(R > m)ret = Mamul(ret, query(L, R, m + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1));pushup(rt);return ret;}int main(){// Mat a, b;// is(a, '0'), is(b, '1');// a = Mamul(Mamul(Mamul(a, b), b), b);// for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){// for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){// printf("%d ", a.s[i][j]);// }// puts("");// }// printf("\n\n\n\n");//// is(a, '1'), is(b, '0');// a = Mamul(Mamul(Mamul(a, b), b), b);// for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){// for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){// printf("%d ", a.s[i][j]);// }// puts("");// }// printf("\n\n\n\n");int T;scanf("%d", &T);while(T--){int n, q;scanf("%d%d", &n, &q);scanf("%s", str + 1);build(1, n, 1);while(q--){int op, l, r;scanf("%d%d%d", &op, &l, &r);if(op == 1){update(l, r, 1, n, 1);}else{Mat a;a.init();a.s[0][2] = 1;a = Mamul(a, query(l, r, 1, n, 1));ll ans = (a.s[0][0] + a.s[0][1]) % MOD;printf("%lld\n", ans);}}}return 0;}
转载于 //www.cnblogs.com/KirinSB/p/11215317.html
//www.cnblogs.com/KirinSB/p/11215317.html





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...