Sentence2Vec理解
论文原文:A simple but tough-to-beat baseline for sentence embedding
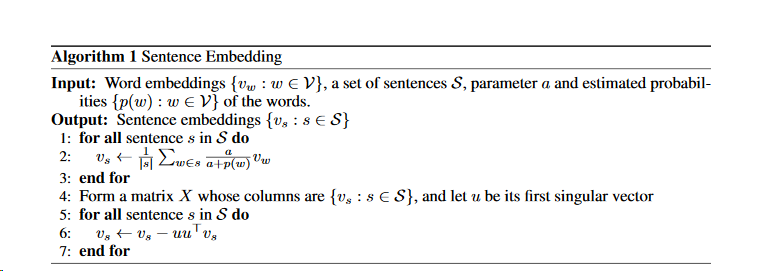
算法介绍
- 先对一个句子 v s v_s vs中所有词的词向量进行加权平均,其中每个词向量的权重可以表示为 a a + p ( w i ) \frac{a}{a+p(w_i)} a+p(wi)a,其中a为超参数,p(w)为词w的频率, ∣ s ∣ |s| ∣s∣为句长, v w i v_{w_i} vwi为词向量。
v s = 1 ∣ s ∣ ∑ i ∣ s ∣ a a + p ( w i ) v w i v_s = \frac{1}{|s| }\sum_{i}^{|s|} \frac{a}{a+p(w_i)} v_{w_i} vs=∣s∣1∑i∣s∣a+p(wi)avwi 使用PCA/SVD对向量值进行修改。
- 去除公共部分(也就是每个成分在主成分上的投影为 u T V s u^TV_s uTVs, 再乘以主成分u,得到 u T V s u u^TV_su uTVsu即为common部分,再用 V s V_s Vs减去公共部分得到最终的句向量),注意u是单位向量。
注:pca算法推导和基础知识
代码
import numpy as npfrom typing import Iterable, Listfrom gensim.models.keyedvectors import BaseKeyedVectorsfrom sklearn.decomposition import PCASentence = List[str]def word_vec(wv: BaseKeyedVectors, s: str):try:return wv.get_vector(s)except KeyError:return np.zeros(wv.vector_size)class SentenceVec:wv: BaseKeyedVectorsu: np.arraya: floatdef __init__(self, sentences: Iterable[Sentence], wv: BaseKeyedVectors, a: float = 1e-3):self.wv = wvself.a = aembedding_size = wv.vector_sizesentence_set = []for sentence in sentences:vs = self.weighted_average(sentence)sentence_set.append(vs) # add to our existing re-calculated set of sentences# calculate PCA of this sentence setpca = PCA(n_components=embedding_size)pca.fit(np.array(sentence_set))u = pca.components_[0] # the PCA vectoru = np.multiply(u, np.transpose(u)) # u x uT# pad the vector? (occurs if we have less sentences than embeddings_size)if len(u) < embedding_size:for i in range(embedding_size - len(u)):u = np.append(u, 0) # add needed extension for multiplication below# resulting sentence vectors, vs = vs -u x uT x vssentence_vecs = []for vs in sentence_set:sub = np.multiply(u, vs)sentence_vecs.append(np.subtract(vs, sub))self.u = uself.vec = sentence_vecsdef feature(self, sentence: Sentence):vs = self.weighted_average(sentence)return vs - vs * self.udef get_word_frequency(self, s) -> float:vocab = self.wv.vocab.get(s)return vocab.count / 10000000 if vocab else 0def weighted_average(self, sentence: Sentence):dim = self.wv.vector_sizea = self.avs = np.zeros(dim) # add all word2vec values into one vector for the sentencefor word in sentence:a_value = a / (a + self.get_word_frequency(word)) # smooth inverse frequency, SIFvs = np.add(vs, np.multiply(a_value, word_vec(self.wv, word))) # vs += sif * word_vectorvs = np.divide(vs, len(sentence)) # weighted averagereturn vs































还没有评论,来说两句吧...