Day 8: Dictionaries and Maps

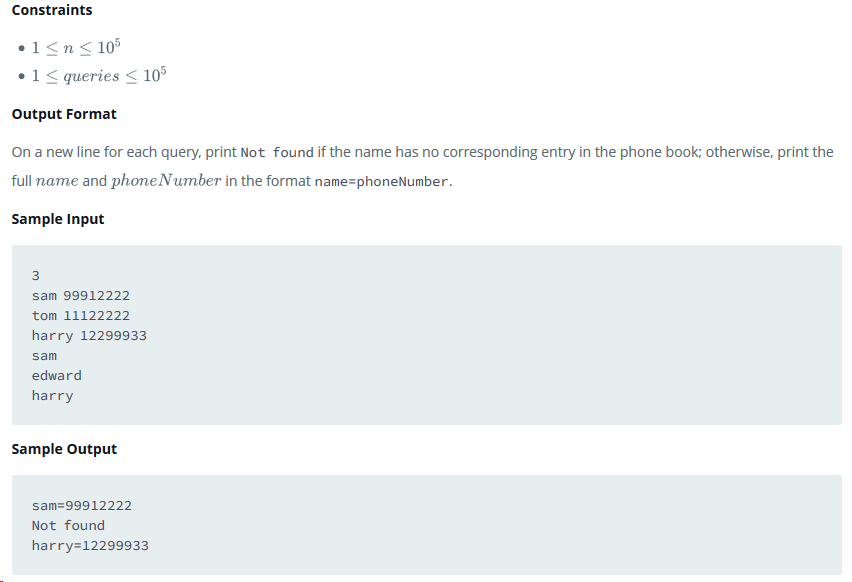

C++,方法一:
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<string>#include<vector>#include<algorithm>#include<map>#include<math.h>#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main(){int n;string name;long num;cin >> n;cin.ignore();map <string, long> pBook;/*以array的方式,向map中插入*/for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){cin >> name;cin >> num;pBook[name] = num;}/*对输入信息进行查找*/while (cin >> name){/*使用find()函数直接查找*/if (pBook.find(name) != pBook.end()){cout << name << "=" << pBook.find(name)->second << endl;}else{cout << "Not found" << endl;}}system("pause");return 0;}
C++,方法二:
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<string>#include<vector>#include<algorithm>#include<map>#include<math.h>#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main(){map<string, int> phoneBook;map<string, int>::iterator iter;int n;cin >> n;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {string name;int phoneNumber;cin >> name;cin >> phoneNumber;/* 以pair的方式,向map中插入 */phoneBook.insert(pair<string, int>(name, phoneNumber));}string objectName;while (cin >> objectName) {/* 使用迭代器进行查找 */iter = phoneBook.find(objectName);if (iter != phoneBook.end())cout << iter->first<< "=" << iter->second << endl;elsecout << "Not found" << endl;}system("pause");return 0;}
python3:
n = int(input())phoneBook = {}for num in range(0, n):#输入的是元组(sum,1111222)tup = tuple(input().split(' '))#将元组存入字典中 {sum:1111222}phoneBook[tup[0]] = tup[1]for num in range(0, n):name = input()if name in phoneBook:print("%s=%s" %(name,phoneBook[name]))else:print('Not found')
总结:
C++:
map数据结构:
1.插入元素:
// 定义一个map对象map<int, string> mapStudent;// 第一种 用insert函數插入pairmapStudent.insert(pair<int, string>(000, "student_zero"));// 第二种 用insert函数插入value_type数据mapStudent.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(001, "student_one"));// 第三种 用"array"方式插入mapStudent[123] = "student_first";mapStudent[456] = "student_second";
2.查找元素:
//使用迭代器map<int,string>::iterator iter;// find 返回迭代器指向当前查找元素的位置否则返回map::end()位置iter = mapStudent.find("123");if(iter != mapStudent.end())cout<<"Find, the value is"<<iter->second<<endl;elsecout<<"Do not Find"<<endl;
3.刪除与清空元素:
//迭代器刪除iter = mapStudent.find("123");mapStudent.erase(iter);//用关键字刪除int n = mapStudent.erase("123"); //如果刪除了會返回1,否則返回0//用迭代器范围刪除 : 把整个map清空mapStudent.erase(mapStudent.begin(), mapStudent.end());//等同于mapStudent.clear()
4.map的大小:
int nSize = mapStudent.size();
5.map的基本操作函数:
C++ maps是一种关联式容器,包含“关键字/值”对begin() 返回指向map头部的迭代器clear() 删除所有元素count() 返回指定元素出现的次数empty() 如果map为空则返回trueend() 返回指向map末尾的迭代器equal_range() 返回特殊条目的迭代器对erase() 删除一个元素find() 查找一个元素get_allocator() 返回map的配置器insert() 插入元素key_comp() 返回比较元素key的函数lower_bound() 返回键值>=给定元素的第一个位置max_size() 返回可以容纳的最大元素个数rbegin() 返回一个指向map尾部的逆向迭代器rend() 返回一个指向map头部的逆向迭代器size() 返回map中元素的个数swap() 交换两个mapupper_bound() 返回键值>给定元素的第一个位置value_comp() 返回比较元素value的函数
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/sevenjoin/article/details/81943864
python3:
将输入的数据作为一对,使用元组 tuple,元组 (sum,1111222) ,使用split(‘ ‘)去除输入的空格。
即:
tup = tuple(input().split(' '))
将元组存入字典中,得到字典 {sum:1111222}。
即:
phoneBook[tup[0]] = tup[1]
查找字典中是否包含 name:
for num in range(0, n):name = input()if name in phoneBook:print("%s=%s" %(name,phoneBook[name]))else:print('Not found')
所有代码如下:
n = int(input())phoneBook = {}for num in range(0, n):#输入的是元组(sum,1111222)tup = tuple(input().split(' '))#将元组存入字典中 {sum:1111222}phoneBook[tup[0]] = tup[1]for num in range(0, n):name = input()if name in phoneBook:print("%s=%s" %(name,phoneBook[name]))else:print('Not found')





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...