ROS——Gazebo仿真——全向轮小车——运动学模型分析
文章目录
- 运动学模型
- 小车坐标系下运动模型分析
- 小车坐标系与世界坐标系转换
- 小车坐标系转换到世界坐标系
- 世界坐标系转换到小车坐标系
- 小车运动与电机转动对应关系
- 完整代码
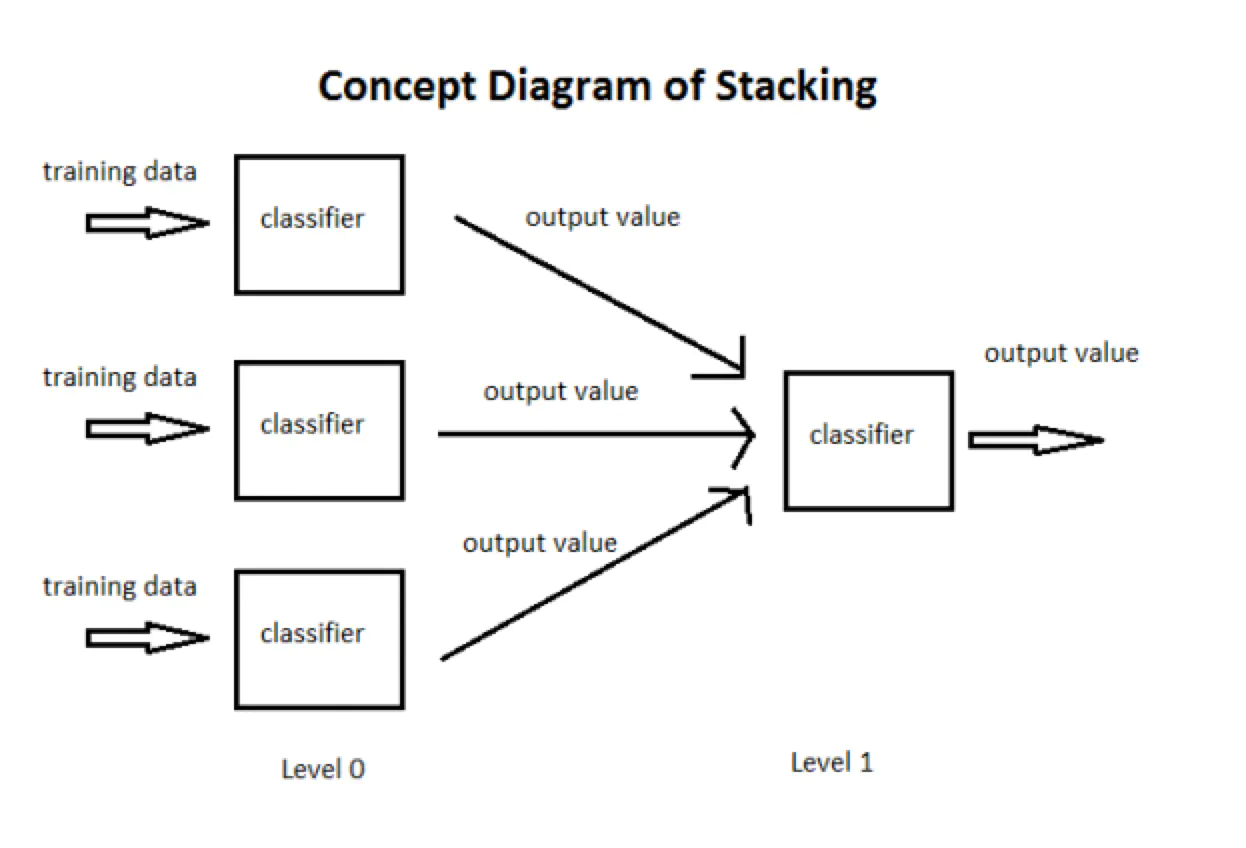
运动学模型
三轮全向轮小车结构示意图如图所示:
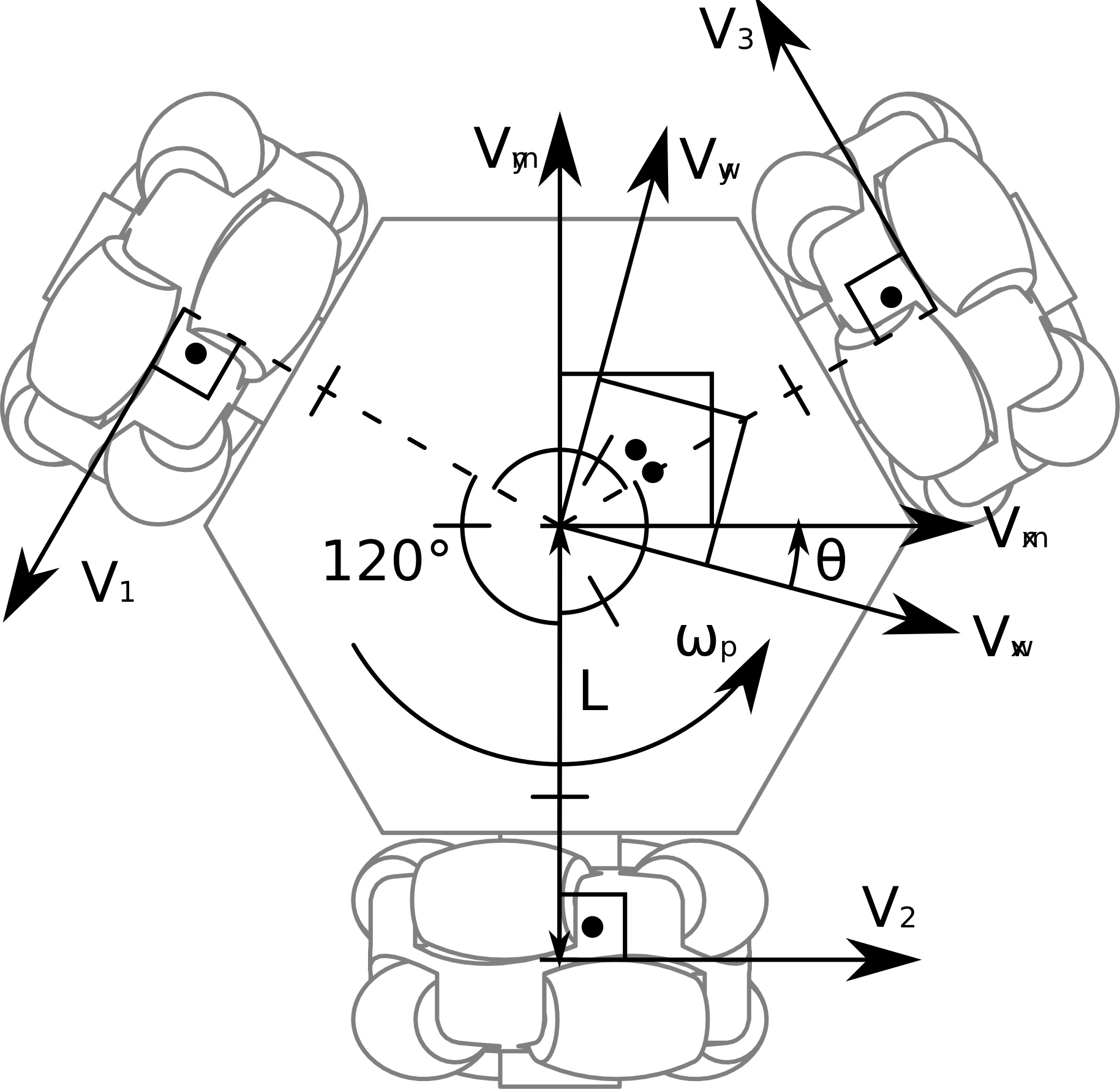
图中V1,V2和V3也分别称为V_left,V_back和V_right,对应三个轮子的转速,转动的正方向如图所示。
小车坐标系下运动模型分析
- V x m = 2 V 2 − V 1 − V 3 3 {V}_x^m=\frac{2V_2-V_1-V3}{3} Vxm=32V2−V1−V3
- V y m = 3 V 3 − 3 V 1 3 {V}_y^m=\frac{\sqrt{3}V_3-\sqrt{3}V_1}{3} Vym=33V3−3V1
- ω p = V 1 + V 2 + V 3 3 L {\omega}_p=\frac{V_1+V_2+V_3}{3L} ωp=3LV1+V2+V3
对应C语言代码如下:
bool forwardMobile(smart_car::KinematicsForward::Request &request, smart_car::KinematicsForward::Response &response) {response.output.x = ((2.0L * request.input.v_back) - request.input.v_left - request.input.v_right) / 3.0L;response.output.y = ((sqrt3 * request.input.v_right) - (sqrt3 * request.input.v_left)) / 3.0L;response.output.theta = (request.input.v_left + request.input.v_back + request.input.v_right) / L3;return true;}
小车坐标系与世界坐标系转换
小车坐标系转换到世界坐标系
小车坐标系转换到世界坐标系的公式如下:
- V x w = cos ( θ ) V x m − sin ( θ ) V y m {V}_x^w=\cos(\theta)V_x^m-\sin(\theta)V_y^m Vxw=cos(θ)Vxm−sin(θ)Vym
- V y w = sin ( θ ) V x m + cos ( θ ) V y m {V}_y^w=\sin(\theta)V_x^m+\cos(\theta)V_y^m Vyw=sin(θ)Vxm+cos(θ)Vym
其中 V x w {V}_x^w Vxw与 V y w {V}_y^w Vyw分别代表世界坐标系下 x x x与 y y y轴的方向, V x m {V}_x^m Vxm与 V y m {V}_y^m Vym分别代表小车坐标系下 x x x与 y y y轴的方向。
对应c语言代码如下:
void mobileToWorldCore(double Vxm, double Vym, double& Vxw, double& Vyw) {Vxw = (std::cos(theta) * Vxm) - (std::sin(theta) * Vym);Vyw = (std::sin(theta) * Vxm) + (std::cos(theta) * Vym);}
世界坐标系转换到小车坐标系
同理,小车坐标系转换到小车坐标系的公式如下:
- V x m = cos ( θ ) V x w + sin ( θ ) V y w {V}_x^m=\cos(\theta)V_x^w+\sin(\theta)V_y^w Vxm=cos(θ)Vxw+sin(θ)Vyw
- V y m = − sin ( θ ) V x w + cos ( θ ) V y w {V}_y^m=-\sin(\theta)V_x^w+\cos(\theta)V_y^w Vym=−sin(θ)Vxw+cos(θ)Vyw
对应c语言代码如下:
void worldToMobileCore(double Vxw, double Vyw, double& Vxm, double& Vym) {Vxm = (std::cos(theta) * Vxw) + (std::sin(theta) * Vyw);Vym = - (std::sin(theta) * Vxw) + (std::cos(theta) * Vyw);}
小车运动与电机转动对应关系
- V 1 = − V x m 2 − 3 V y m 2 + L ω p {V}_1=-\frac{V_x^m}{2}-\frac{\sqrt{3}V_y^m}{2}+L\omega_p V1=−2Vxm−23Vym+Lωp
- V 2 = V x m + L ω p {V}_2=V_x^m+L\omega_p V2=Vxm+Lωp
- V 3 = − V x m 2 + 3 V y m 2 + L ω p {V}_3=-\frac{V_x^m}{2}+\frac{\sqrt{3}V_y^m}{2}+L\omega_p V3=−2Vxm+23Vym+Lωp
对应C语言代码为:
bool inverseMobile(smart_car::KinematicsInverse::Request &request, smart_car::KinematicsInverse::Response &response) {long double V__m_x2 = - request.input.x / 2.0L;long double sqrt3V__m_y2 = (sqrt3 * request.input.y) / 2.0L;long double Lomega_p = L * request.input.theta;response.output.v_left = V__m_x2 - sqrt3V__m_y2 + Lomega_p;response.output.v_back = request.input.x + Lomega_p;response.output.v_right = V__m_x2 + sqrt3V__m_y2 + Lomega_p;return true;
完整代码
#include <cmath>#include <string>#include <ros/ros.h>#include <geometry_msgs/Pose2D.h>#include <sensor_msgs/JointState.h>#include <smart_car/FrameToFrame.h>#include <smart_car/KinematicsForward.h>#include <smart_car/KinematicsInverse.h>#include <kdl/frames.hpp>#include <kdl_parser/kdl_parser.hpp>long double L;long double L3;long double sqrt3;long double theta = 0;void mobileToWorldCore(double Vxm, double Vym, double& Vxw, double& Vyw) {Vxw = (std::cos(theta) * Vxm) - (std::sin(theta) * Vym);Vyw = (std::sin(theta) * Vxm) + (std::cos(theta) * Vym);}bool mobileToWorld(smart_car::FrameToFrame::Request &request, smart_car::FrameToFrame::Response &response) {mobileToWorldCore(request.input.x, request.input.y, response.output.x, response.output.y);}void worldToMobileCore(double Vxw, double Vyw, double& Vxm, double& Vym) {Vxm = (std::cos(theta) * Vxw) + (std::sin(theta) * Vyw);Vym = - (std::sin(theta) * Vxw) + (std::cos(theta) * Vyw);}bool worldToMobile(smart_car::FrameToFrame::Request &request, smart_car::FrameToFrame::Response &response) {worldToMobileCore(request.input.x, request.input.y, response.output.x, response.output.y);}bool forwardMobile(smart_car::KinematicsForward::Request &request, smart_car::KinematicsForward::Response &response) {response.output.x = ((2.0L * request.input.v_back) - request.input.v_left - request.input.v_right) / 3.0L;response.output.y = ((sqrt3 * request.input.v_right) - (sqrt3 * request.input.v_left)) / 3.0L;response.output.theta = (request.input.v_left + request.input.v_back + request.input.v_right) / L3;return true;}bool forwardWorld(smart_car::KinematicsForward::Request &request, smart_car::KinematicsForward::Response &response) {forwardMobile(request, response);mobileToWorldCore(response.output.x, response.output.y, response.output.x, response.output.y);return true;}bool inverseMobile(smart_car::KinematicsInverse::Request &request, smart_car::KinematicsInverse::Response &response) {long double V__m_x2 = - request.input.x / 2.0L;long double sqrt3V__m_y2 = (sqrt3 * request.input.y) / 2.0L;long double Lomega_p = L * request.input.theta;response.output.v_left = V__m_x2 - sqrt3V__m_y2 + Lomega_p;response.output.v_back = request.input.x + Lomega_p;response.output.v_right = V__m_x2 + sqrt3V__m_y2 + Lomega_p;return true;}bool inverseWorld(smart_car::KinematicsInverse::Request &request, smart_car::KinematicsInverse::Response &response) {worldToMobileCore(request.input.x, request.input.y, request.input.x, request.input.y);inverseMobile(request, response);return true;}void onPoseWorldMessage(const geometry_msgs::Pose2D::ConstPtr& input){theta = input->theta;}int main(int argc, char **argv){ros::init(argc, argv, "kinematics");ros::NodeHandle node;{std::string description;if(!node.getParam("robot_description",description)) {ROS_ERROR("Could not find '/robot_description'.");return -1;}KDL::Tree tree;if (!kdl_parser::treeFromString(description, tree)) {ROS_ERROR("Failed to construct KDL tree.");return -1;}KDL::Chain chain;if (!tree.getChain("base_link", "rim_back_link", chain)) {ROS_ERROR("Failed to get chain from KDL tree.");return -1;}KDL::Frame frame = chain.getSegment(0).pose(0);L = std::sqrt(std::pow(frame.p.x() - 0.0L, 2.0L) + std::pow(frame.p.y() - 0.0L, 2.0L));node.setParam("parameter/wheel/distance", (double) L);L3 = 3.0L * L;sqrt3 = std::sqrt(3.0L);double parameter;if (!node.getParam("parameter/initial/theta", parameter)) {parameter = 0;}theta = parameter;}ros::ServiceServer forwardMobileService = node.advertiseService("kinematics_forward_mobile", forwardMobile);ros::ServiceServer forwardWorldService = node.advertiseService("kinematics_forward_world" , forwardWorld );ros::ServiceServer inverseMobileService = node.advertiseService("kinematics_inverse_mobile", inverseMobile);ros::ServiceServer inverseWorldService = node.advertiseService("kinematics_inverse_world" , inverseWorld );ros::ServiceServer mobileToWorldService = node.advertiseService("kinematics_mobile_to_world" , mobileToWorld);ros::ServiceServer worldToMobileService = node.advertiseService("kinematics_world_to_mobile" , worldToMobile);ros::Subscriber subscriber = node.subscribe("pose/world", 1, onPoseWorldMessage);ros::spin();return 0;}





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...