Spring Boot 自动装配流程
Spring Boot 自动装配流程-1
- ImportSelector
- Import
- ImportSelector
- 详解Spring的ImportSelector接口
- PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(xxx)方法
- ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
- Spring Boot Starter自动装配原理 全流程
本章的存在意义是记录本人在学习过程中, 记录自己的疑惑, 梳理知识点, 很多知识点会引用他人的文章,属于二次消化的一个系列
ImportSelector
Import
SpringBoot 的 @Import 用于将指定的类实例注入之Spring IOC Container中。
传送门
ImportSelector
ImportSelector接口是spring中导入外部配置的核心接口
传送门
疑问点
- ImportSelector是如何被Spring框架调用的呢?
详解Spring的ImportSelector接口
为了解决此疑惑, 特意去复习了一下spring的加载流程, 流程图如下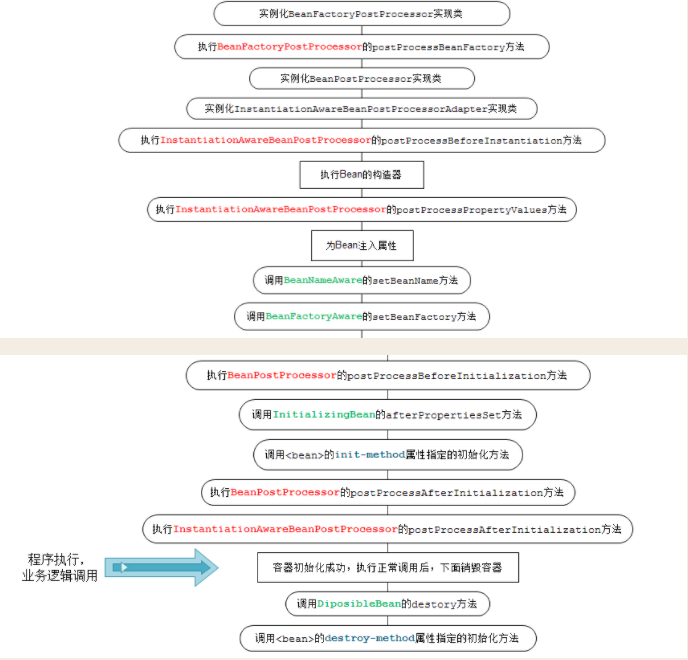
根据流程图可知, bean的初始化在 前几步之中, 那么import Select 接口的执行也必然在这之前
我们以ClassPathXmlApplicationContext为例子,看看Spring在启动过程中是如何调用到ImportSelector接口的。
为了方便阅读, 这里整理了一些注释, 以及顺序整理成了从上到下的这么一个执行顺序
首先执行spring的核心方法 refresh
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {//刷新前的预处理;prepareRefresh();//获取BeanFactory;默认实现是DefaultListableBeanFactory,在创建容器的时候创建的ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();//BeanFactory的预准备工作(BeanFactory进行一些设置,比如context的类加载器,BeanPostProcessor和XXXAware自动装配等)prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);try {//BeanFactory准备工作完成后进行的后置处理工作postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);//执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的方法;invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);//注册BeanPostProcessor(Bean的后置处理器),在创建bean的前后等执行registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);//初始化MessageSource组件(做国际化功能;消息绑定,消息解析);initMessageSource();//初始化事件派发器initApplicationEventMulticaster();//子类重写这个方法,在容器刷新的时候可以自定义逻辑;如创建Tomcat,Jetty等WEB服务器onRefresh();//注册应用的监听器。就是注册实现了ApplicationListener接口的监听器bean,这些监听器是注册到ApplicationEventMulticaster中的registerListeners();//初始化所有剩下的非懒加载的单例beanfinishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);//完成context的刷新。主要是调用LifecycleProcessor的onRefresh()方法,并且发布事件(ContextRefreshedEvent)finishRefresh();}......}
从上面的实现中,我们可以看到该方法做了很多准备、初始化、事件通知等工作。具体的我们就不一一看了,今天我们只关心其中的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法。
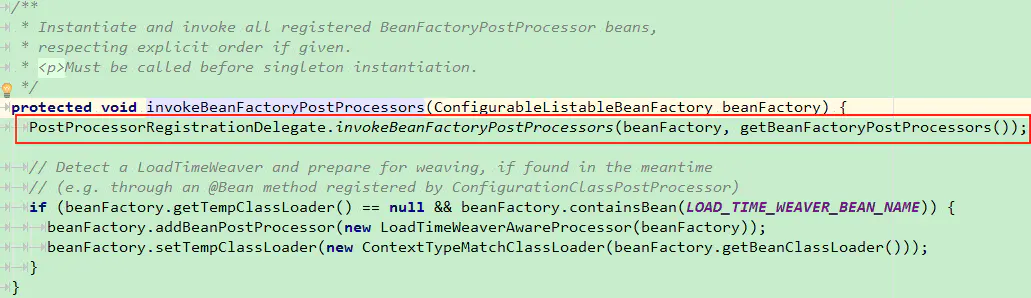
从上面的代码中我们可以看到,invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法把具体的调用方法委托给了PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate类。另外,从该方法的名字当中我们也可以看出,该方法主要的目的是:实例化,并调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor类的。BeanFactoryPostProcessor是一个接口,有很多的实现类,这里我们就暂且不管BeanFactoryPostProcessor的具体用处了 (Spring中BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor都是Spring初始化bean时对外暴露的扩展点)。我们先进入PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate一窥究竟。
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(xxx)方法
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.// 如果有BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors 的话,就先调用它们// 处理过的BeansSet<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<String>();// 是否是BeanDefinitionRegistry类型的BeanFactory. BeanDefinitionRegistry的作用是可以用来注册,删除,获取BeanDefinitionsif (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;// 普通类型的BeanFactoryPostProcessor集合List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new LinkedList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();// BeanDefinitionRegistry类型的BeanFactoryPostProcessor集合(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor继承于BeanFactoryPostProcessor)List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryPostProcessors =new LinkedList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();// 对集合beanFactoryPostProcessors进行分类,如果是BeanDefinitionRegistry类型的BeanFactoryPostProcessor;则调用方法 - postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()。、、// postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry)该方法的作用是在标准的BeanDefinitions初始化完成后可以修改容器上下文内部的beanDefinition。for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryPostProcessor =(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;registryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);registryPostProcessors.add(registryPostProcessor);}else {regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);}}// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.// 这里不要初始化FactoryBeans,我们需要保留这些普通的beans 不在这里初始化,目的是为了让bean factory post-processor去处理他们。// 根据BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors 实现的不同接口,拆分开来去调用他们。String[] postProcessorNames =beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.// 首先,调用实现了优先级接口 - PriorityOrdered的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessorsList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));processedBeans.add(ppName);}}// 排序sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);// 添加排序好的优先级PostProcessors到registryPostProcessors集合registryPostProcessors.addAll(priorityOrderedPostProcessors);// 调用排序好的优先级BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors,postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法会被调用,用来修改,获取,删除容器上下文中的bean定义。invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, registry);// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.// 调用实现了Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors ,大致逻辑同上PriorityOrdered的处理postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));processedBeans.add(ppName);}}sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);registryPostProcessors.addAll(orderedPostProcessors);invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, registry);// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.// 调用所有其它类型的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessorsboolean reiterate = true;while (reiterate) {reiterate = false;postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class);registryPostProcessors.add(pp);processedBeans.add(ppName);pp.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);reiterate = true;}}}// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.// 调用所有的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory 方法。invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryPostProcessors, beanFactory);// 调用容器中BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的bean(不包含BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的beans)。invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);}else {// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.// 若beanFactory不是BeanDefinitionRegistry类型的,则直接调用容器中所有的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory 方法。invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);}// 下面是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的具体调用过程,和上面的过程很相似,这里就不多说了。// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!String[] postProcessorNames =beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,// Ordered, and the rest.List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {// skip - already processed in first phase above}else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));}else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);}else {nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);}}// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));}sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));}invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();}
上面的调用关系中,我们可以看出。在这个方法中有两种类型的PostPorcessor被调用处理了;而这两种PostProcessor的关系如下图:

BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor继承于BeanFactoryPostProcessor。我们大致看看接口定义的方法: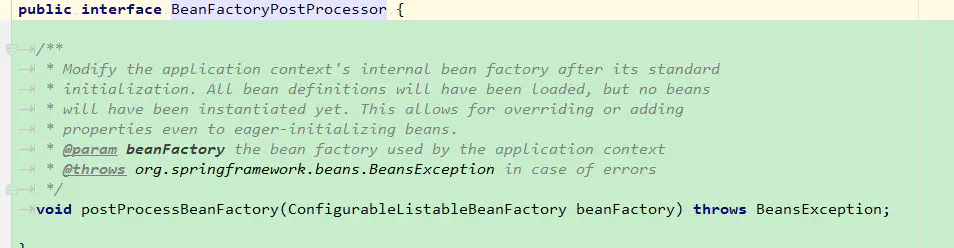
postProcessBeanFactory用于在标准的初始化完成后修改容器上下文中的beanFactory。所有bean定义将被加载,但是它们将暂时不被实例化,这允许覆盖,甚至添加一些属性到延迟初始化的bean上。
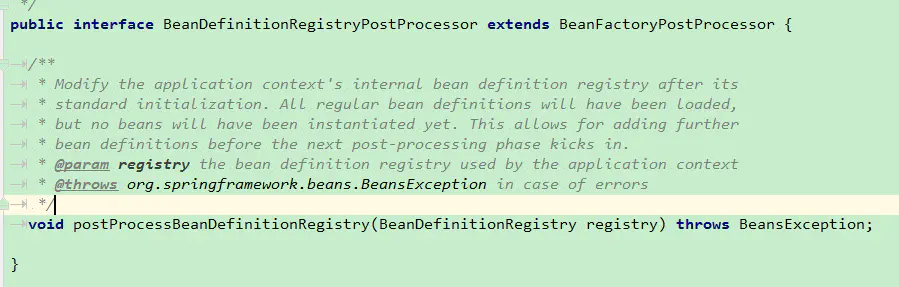
postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法在标准化初始化完成后可以修改容器内部的bean definition registry。所有的常规的bean定义都将被加载,但是没有bean被实例化。这允许我们在下一个处理阶段增加一些新的bean定义。
综合上面的逻辑,postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry是在postProcessBeanFactory方法之前被调用的。
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口,同时还实现了一些其他的接口,如下图: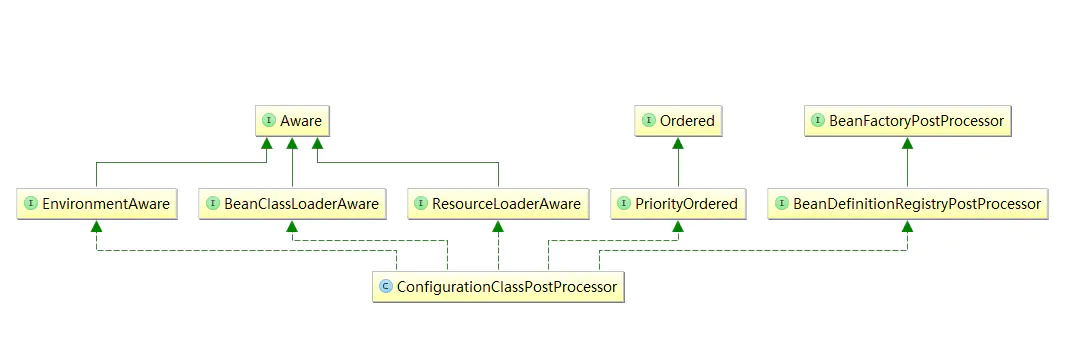
我们先来看看postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法的具体内容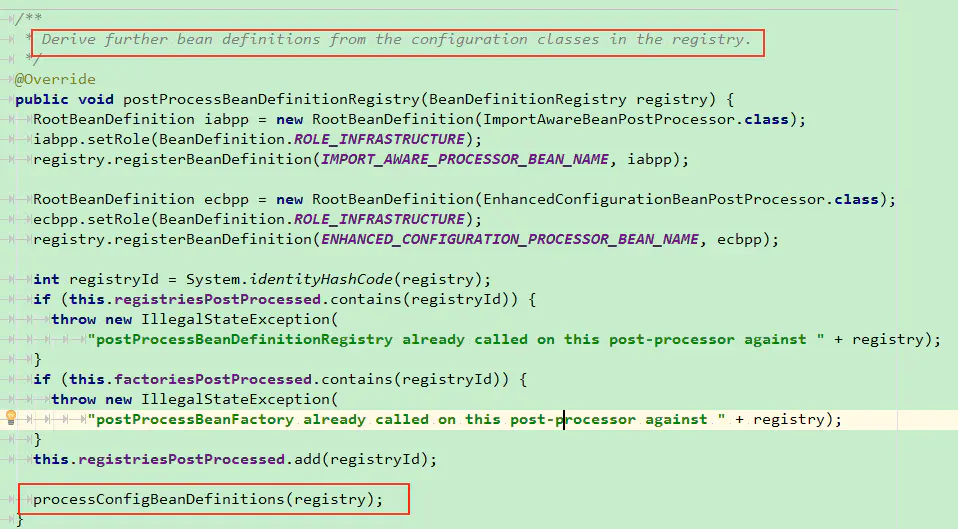
这个方法的主要作用是进一步从配置中获取bean的定义,也就是被@Configuration注解修饰的配置类。该方法中又调用了processConfigBeanDefinitions()方法,该方法主要用于处理@Configuration注解。
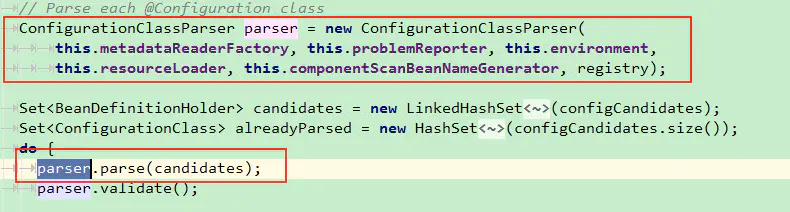
这里忽略一些调用, 最终进入到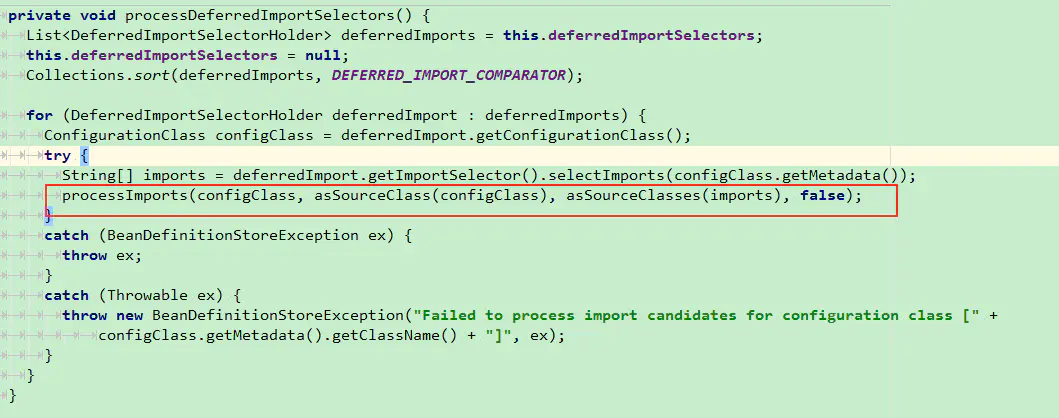
processDeferredImportSelectors方法中调用了processImports方法执行导入,跟进去看看,在processImports 方法中有很重要的一段代码,如下: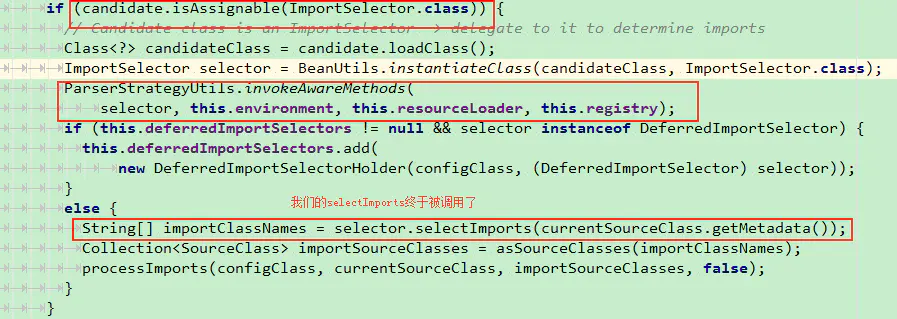
复盘
- ImportSelector的导入实现是通过BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的子接口
- BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor来实现的。
- ImportSelector接口的处理是伴随着@Configuration注解的处理一起处理的。
- ImportSelector接口可以实现自定义条件选择性导入classes。
- ImportSelector接口的字接口DeferredImportSelector在所有@Configuration处理完成后才被处理的。
- 处理ImportSelector接口时,bean定义已经被加载,但是bean还没有被实例化。
- Spring Bootn的自动配置功能就是通过DeferredImportSelector接口的实现类
- EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector做到的。
Spring Boot Starter自动装配原理 全流程
传送门





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...