Spring详细内容En(1)
1.Spring
- It was developed by Rod Johnson in 2003.
- Spring framework makes the easy development of JavaEE application.
1)Spring Framework
- Spring is a
lightweight framework. - It can be thought of as
a framework of frameworks becauseit provides support to various frameworks such asStruts, Hibernate, Tapestry, EJB, JSF, etc. - The Spring framework comprises several modules such as
IOC, AOP, DAO, Context, ORM, WEB MVC etc.
2)Inversion Of Control (IOC) and Dependency Injection
- These are the design patterns that are used to remove dependency from the programming code.
They make the code easier to test and maintain.
class Employee{
Address address;Employee(){address=new Address();}
}
there is dependency between the Employee and Address (tight coupling).
class Employee{Address address;Employee(Address address){this.address=address;}}
IOCmakes the code loosely coupled.- In such case, there is no need to modify the code if our logic is moved to new environment.
- In Spring framework, IOC container is responsible to inject the dependency.
- We provide metadata to the IOC container either by
XML fileorannotation.
Advantage of Dependency Injection
- makes the code
loosely coupledso easy to maintain - makes the code
easy to test
3) Advantages of Spring Framework
1) Predefined Templates
- Spring framework provides templates for JDBC, Hibernate, JPA etc. technologies.
- So there is no need to write too much code.
- It hides the basic steps of these technologies.
2)Loose Coupling
- The Spring applications are
loosely coupledbecause ofdependency injection.
3)Easy to test
- The Dependency Injection makes easier to test the application.
- The EJB or Struts application require server to run the application but
Spring framework doesn't require server.
4)Lightweight
- Spring framework is
lightweightbecause of itsPOJO implementation. - The Spring Framework doesn’t force the programmer to inherit any class or implement any interface. That is why it is said
non-invasive.
5)Fast Development
- The Dependency Injection feature of Spring Framework and it support to various frameworks makes the easy development of JavaEE application.
6)Powerful abstraction
- It provides powerful abstraction to
JavaEE specificationssuch as JMS, JDBC, JPA and JTA.
7)Declarative support
- It provides declarative support for
caching,validation,transactions and formatting.
2.Spring Modules
- The Spring framework comprises of many modules such as
core,beans,context,expression language,AOP,Aspects,Instrumentation,JDBC,ORM,OXM,JMS,Transaction,Web,Servlet,Strutsetc. - These modules are grouped into
Test,Core Container,AOP,Aspects,Instrumentation,Data Access / Integration,Web (MVC / Remoting)as displayed in the following diagram.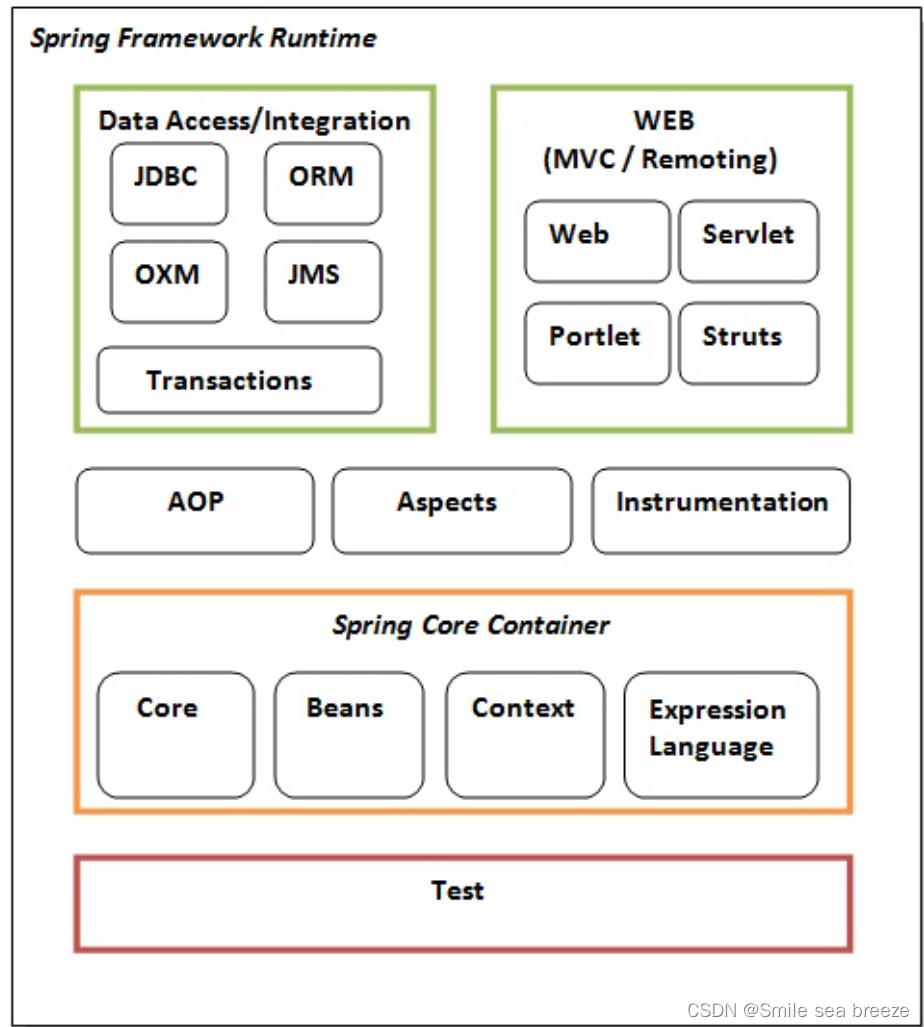
1)Test
This layer provides support of testing with JUnitand TestNG.
2) Spring Core Container
The Spring Core container contains core, beans, context and expression language (EL)modules.
Core and Beans
These modules provideIOC and Dependency Injectionfeatures.
Context
This module supports internationalization (I18N), EJB, JMS, Basic Remoting.
Expression Language
- It is an extension to the EL defined in JSP.
- It provides support to setting and getting property values, method invocation, accessing collections and indexers, named variables, logical and arithmetic operators, retrieval of objects by name etc.
3)AOP, Aspects and Instrumentation
- These modules support
aspect oriented programmingimplementation where you can useAdvices,Pointcutsetc. to decouple the code. - The aspects module provides support to integration with AspectJ.
- The instrumentation module provides support to class instrumentation and classloader implementations.
4)Data Access / Integration
- this group comprises of
JDBC, ORM, OXM, JMS and Transaction modules. - These modules basically provide support to interact with the database.
5)Web
- This group comprises of Web, Web-Servlet, Web-Struts and Web-Portlet.
- These modules provide support to create web application.
3.Spring application
Step
- create the java project
- add spring capabilities
- create the class
- create the xml file to provide the values
- create the test class
1) Create the Java Project
Go to File menu - New - project - Java Project. Write the project name e.g. firstspring - Finish. Now the java project is created.
2) Add spring jar files
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><parent><artifactId>heima_datastuct</artifactId><groupId>org.example</groupId><version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version></parent><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><artifactId>spring_01</artifactId><properties><maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source><maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target></properties><!--导入spring的context坐标,context依赖core、beans、expression--><!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-core --><dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-core</artifactId><version>5.3.25</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId><version>5.3.23</version><scope>compile</scope></dependency></dependencies>
3) Create Java class
package com.amy;/*** @author: Amy* @create: 2023-02-14 14:32**/public class Student {private String name;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public void displayInfo(){System.out.println("Hello: "+name);}}
- This is simple bean class, containing only one property name with its getters and setters method.
- This class contains one extra method named displayInfo() that prints the student name by the hello message.
4) Create the xml file
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"><bean id="student" class="com.amy.Student"><property name="name" value="Amy"></property></bean></beans>
- The bean element is used to define the bean for the given class.
- The property subelement of bean specifies the property of the Student class named name.
- The value specified in the property element will be set in the Student class object by the IOC container.
5) Create the test class
package com.amy;import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;/*** @author: Amy* @create: 2023-02-14 14:39**/public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);Student student = (Student) factory.getBean("student");student.displayInfo();;}}
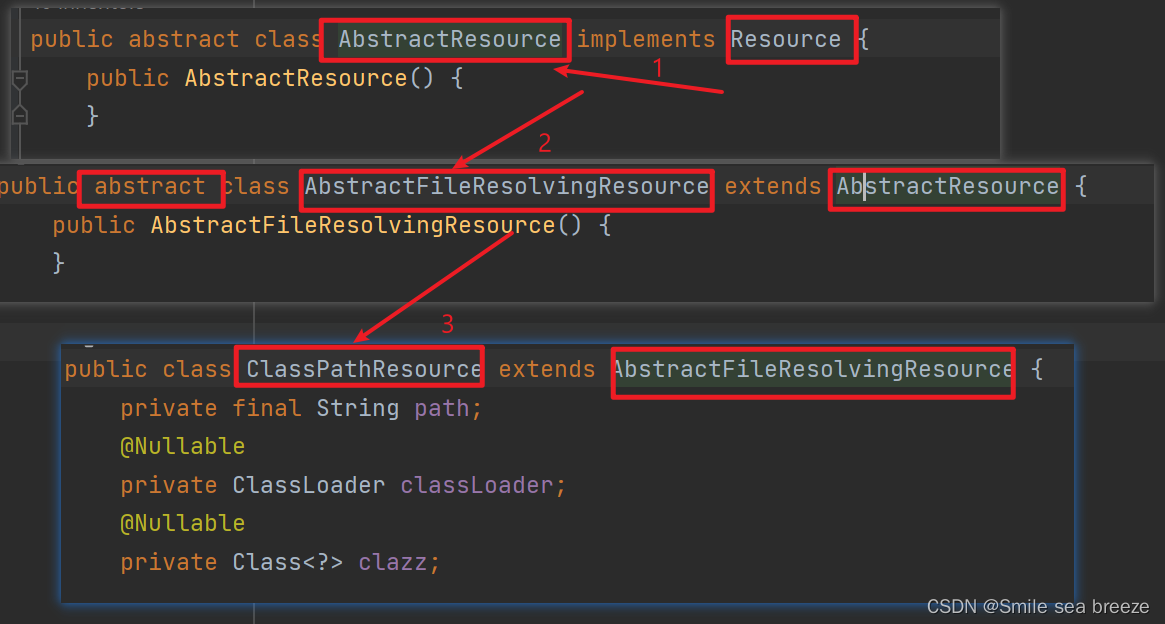
- The
Resource objectrepresents the information ofapplicationContext.xml file.- The Resource is the interface and the
ClassPathResourceis the implementation class of theReource interface.- The
BeanFactoryis responsible to return the bean.- The
XmlBeanFactoryis the implementation class of theBeanFactory.- There are many methods in the BeanFactory interface.
- One method is
getBean(), which returns the object of the associated class.
Hello: Amy
4. IoC Container
- The
IoC containeris responsible toinstantiate, configure and assemble the objects. - The IoC container gets informations from the
XML fileand works accordingly. The
main tasks performed by IoC containerare:- to instantiate the application class
- to configure the object
- to assemble the dependencies between the objects
There are
two types of IoC containers. They are:BeanFactoryApplicationContext
1)Difference between BeanFactory and the ApplicationContext
- The
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryand theorg.springframework.context.ApplicationContext interfacesacts as theIoC container. - The ApplicationContext interface is built on top of the BeanFactory interface.
- It adds some extra functionality than BeanFactory such as simple integration with
Spring's AOP, message resource handling (for I18N), event propagation, application layer specific context (e.g. WebApplicationContext)for web application. - So it is better to use ApplicationContext than BeanFactory.
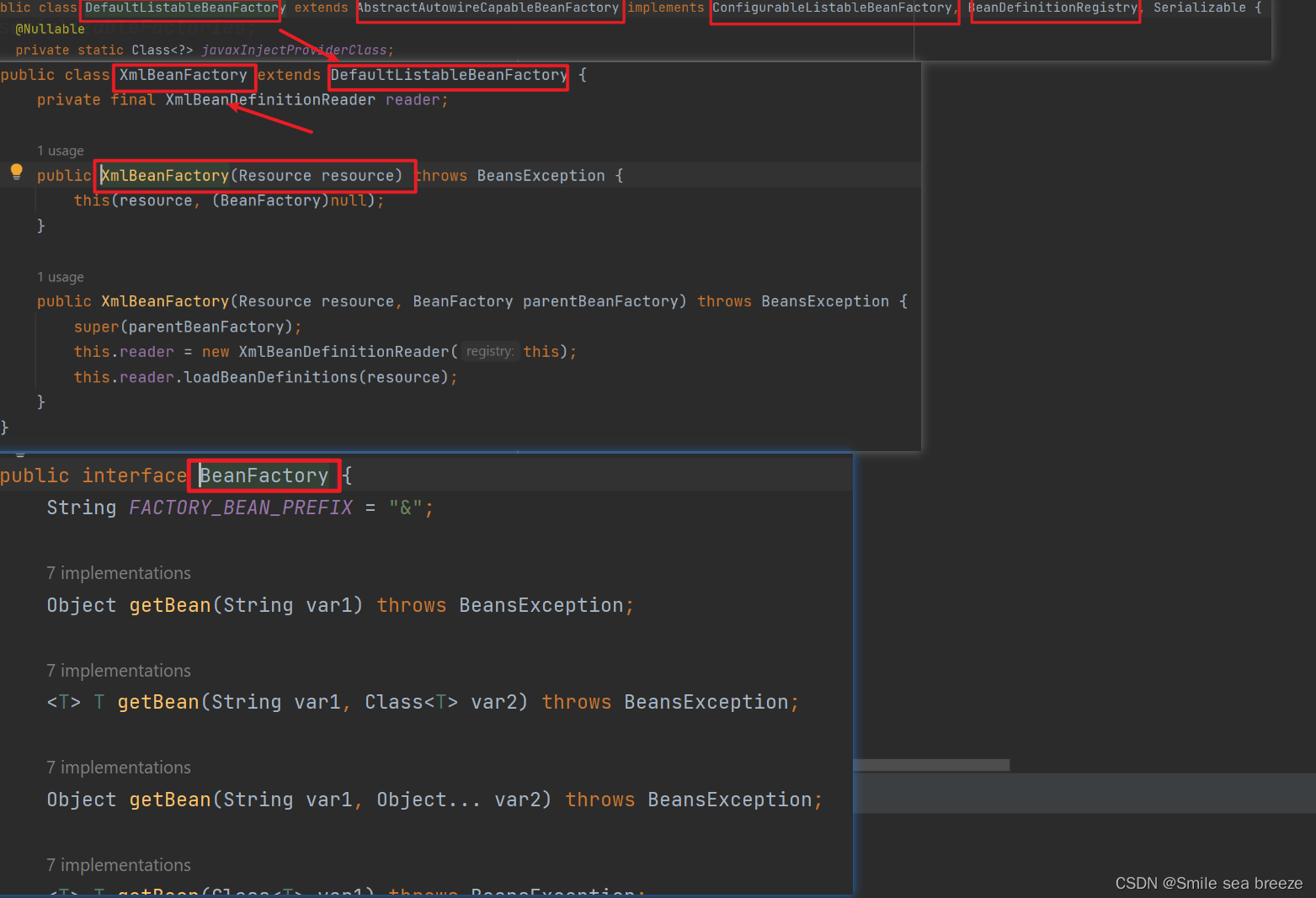
2)Using BeanFactory
- The
XmlBeanFactoryis the implementation class for theBeanFactory interface. To use the BeanFactory, we need to create the instance of XmlBeanFactory class
Resource resource=new ClassPathResource(“applicationContext.xml”);
BeanFactory factory=new XmlBeanFactory(resource);the constructor of
XmlBeanFactoryclass receives the Resource object so we need to pass the resource object to create the object of BeanFactory.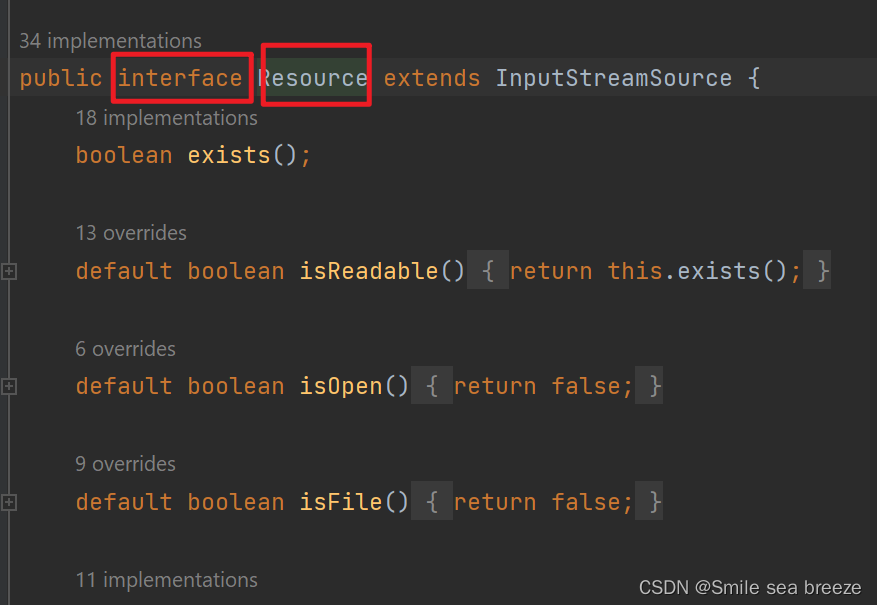
3)Using ApplicationContext
- The
ClassPathXmlApplicationContextclass is the implementation class ofApplicationContext interface. We need to instantiate the
ClassPathXmlApplicationContextclass to use theApplicationContextApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“applicationContext.xml”);
The constructor of
ClassPathXmlApplicationContextclass receives string, so we can pass the name of the xml file to create the instance of ApplicationContext.
5. Dependency Injection in Spring
Dependency Injection (DI)isa design patternthat removes the dependency from the programming code so that it can be easy to manage and test the application.Dependency Injectionmakes our programming codeloosely coupled.
1)Dependency Lookup
- The Dependency Lookup is an approach where we get the resource after demand.
A obj = new AImpl(); - In such way, we get the resource(instance of A class) directly by new keyword. Another way is factory method:
A obj = A.getA(); - This way, we get the resource (instance of A class) by calling the static factory method getA().
Alternatively, we can get the resource by
JNDI (Java Naming Directory Interface)as:Context ctx = new InitialContext();
Context environmentCtx = (Context) ctx.lookup(“java:comp/env”);
A obj = (A)environmentCtx.lookup(“A”);
Problems of Dependency Lookup
There are mainly two problems of dependency lookup.
tight couplingThe dependency lookup approach makes the code tightly coupled. If resource is changed, we need to perform a lot of modification in the code.Not easy for testingThis approach creates a lot of problems while testing the application especially in black box testing.
2)Dependency Injection
- The
Dependency Injectionis a design pattern thatremoves the dependency of the programs. - In such case we provide the information from the external source such as
XML file. It makes our code loosely coupled and easier for testing.
class Employee{
Address address;Employee(Address address){this.address=address;}public void setAddress(Address address){this.address=address;}
}
- In such case, instance of Address class is provided by external souce such as XML file either by constructor or setter method.
Two ways to perform Dependency Injection in Spring framework
- We can inject the dependency by constructor.
- The
<constructor-arg>subelement of is used forconstructor injection.
(1)By Constructor
public class Student {private String name;public Student(String name) {this.name =name;}public void displayInfo(){System.out.println("Hello: "+name);}}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"><bean id="student" class="com.amy.Student"><constructor-arg value="Amy" type="String"></constructor-arg></bean></beans>
- We are providing the information into the bean by this file.
- The
constructor-argelement invokes the constructor.- In such case,
parameterized constructorofStringtypewill be invoked.- The value attribute of constructor-arg element will assign the specified value.
- The type attribute specifies that String parameter constructor will be invoked.
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);Student student = (Student) factory.getBean("student");student.displayInfo();;}}Hello: Amy
Injecting string-based values
If you don’t specify the type attribute in the constructor-arg element, by default string type constructor will be invoked.
(2)By Setter method
- We can inject the dependency by
setter methodalso. The subelement of is used for setter injection.
public class Employee {
private int id;private String name;private String city;public int getId() {return id;}public void setId(int id) {this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getCity() {return city;}public void setCity(String city) {this.city = city;}public void display(){System.out.println(id+" "+name+" "+city);}
}
<?xml version=”1.0” encoding=”UTF-8”?>
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);Employee employee = (Employee) factory.getBean("employee");employee.display();}
}
1 Amy ShangHai































还没有评论,来说两句吧...